Micro-RNA regulation in ischemia and ischemia-reperfusion injury
A technology for myocardial ischemia and subjects, applied in the field of miRNA, can solve problems affecting mRNA stability, mRNA translation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] Example 1. Identification of miRNAs that are regulated during short-term ischemia
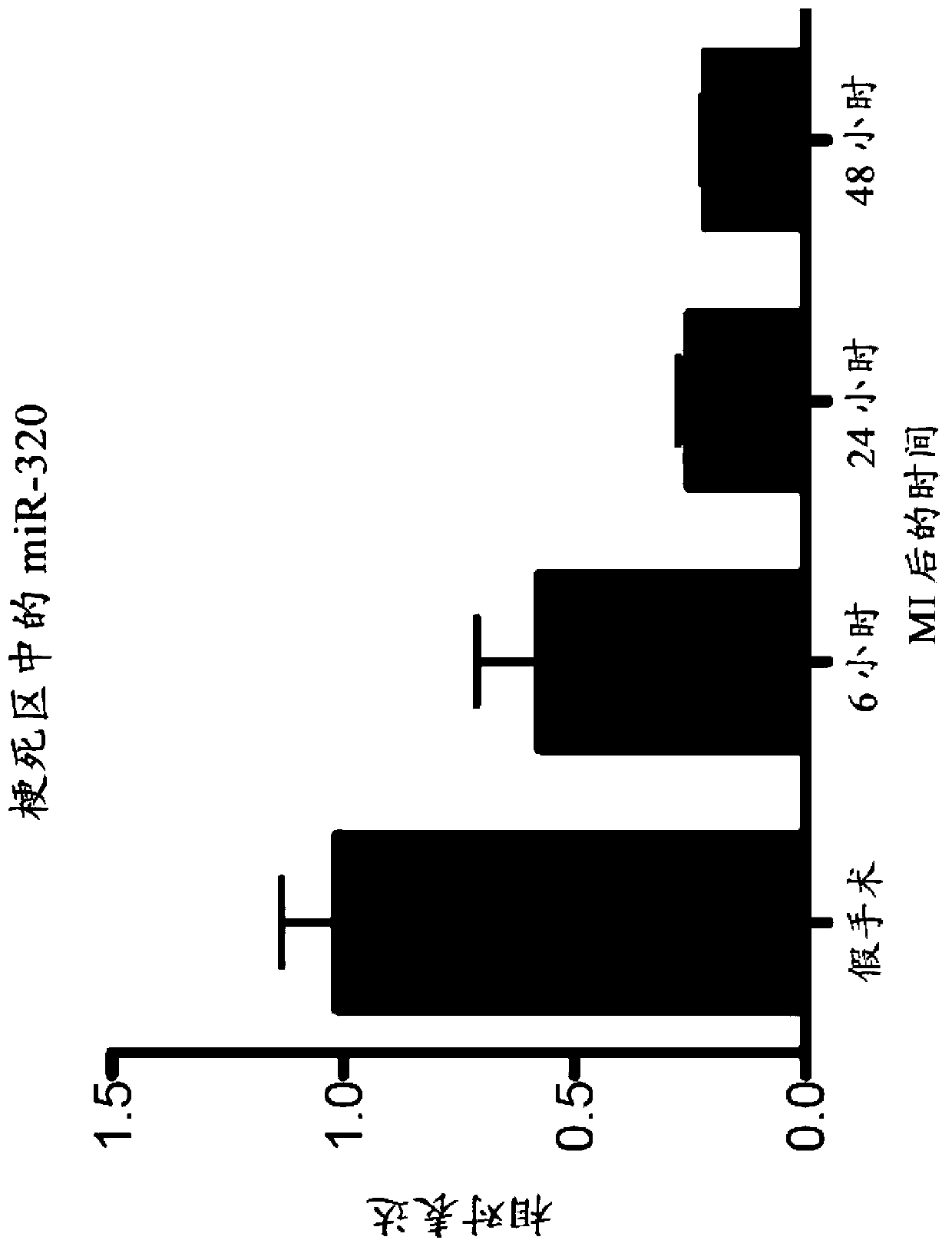
[0085] Cardiac ischemia induces remodeling that can affect ventricular function and prognosis with regard to survival. To determine whether miRNAs are involved in different remodeling processes after ischemic events, miRNA microarray analysis was performed on tissues isolated from the infarcted area at 6, 24 and 48 hours after ischemic injury. Specifically, myocardial ischemia was induced in mice by occluding the left anterior descending artery, and the miRNA expression profiles of tissues in the ischemic area at 6, 24, and 48 hours after induction were compared with those of myocardial tissue from sham-operated animals. Expression profiles are compared. The miRNAs that were significantly regulated in the short term after ischemic injury are listed in Table 1. Data are presented as absolute values of miR expression in sham-operated animals or at 6, 24 and 48 hours after myocardial is...
Embodiment 2
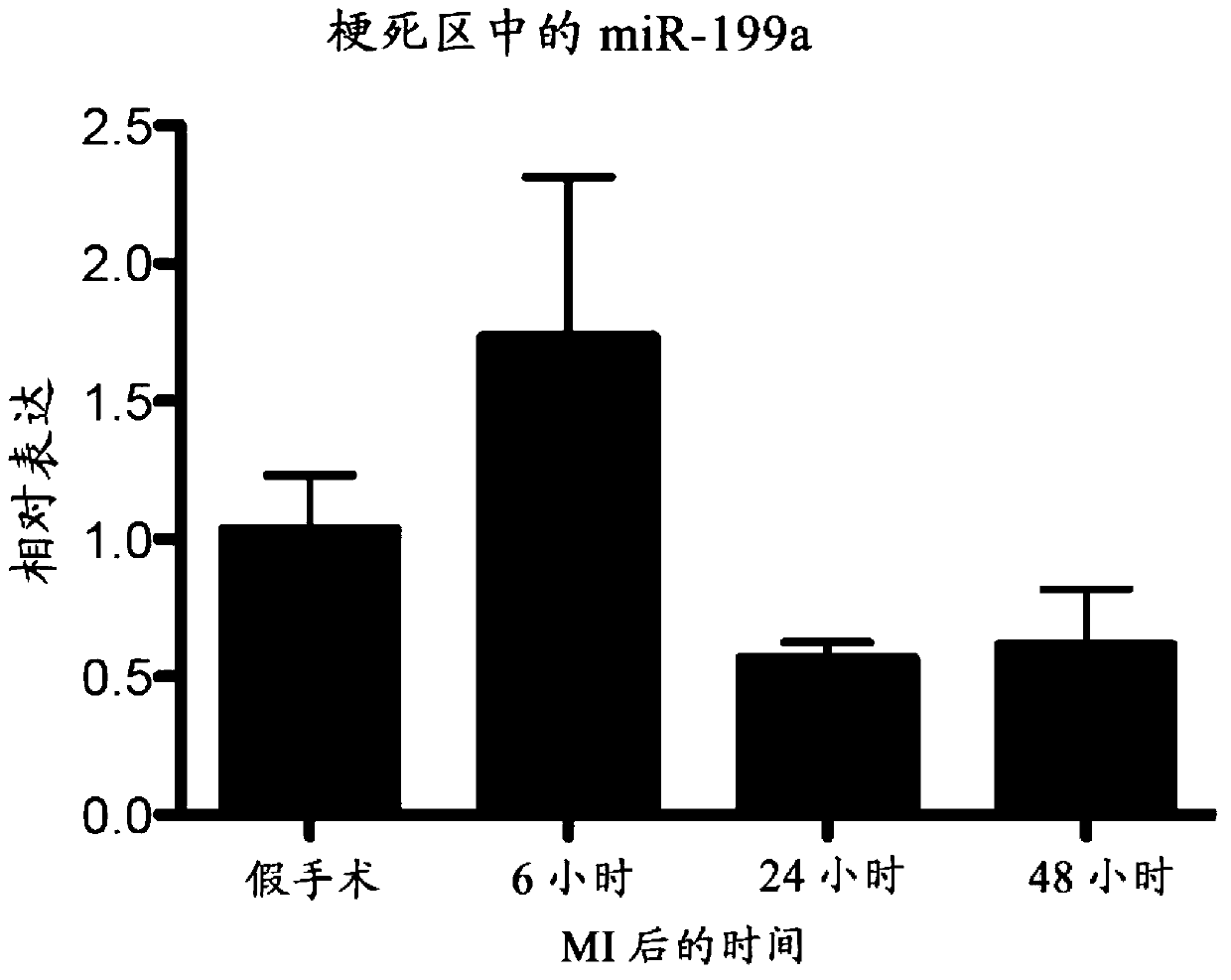
[0094] Example 2. miR-199 regulates HIF1α and miR-210 in ischemic tissue
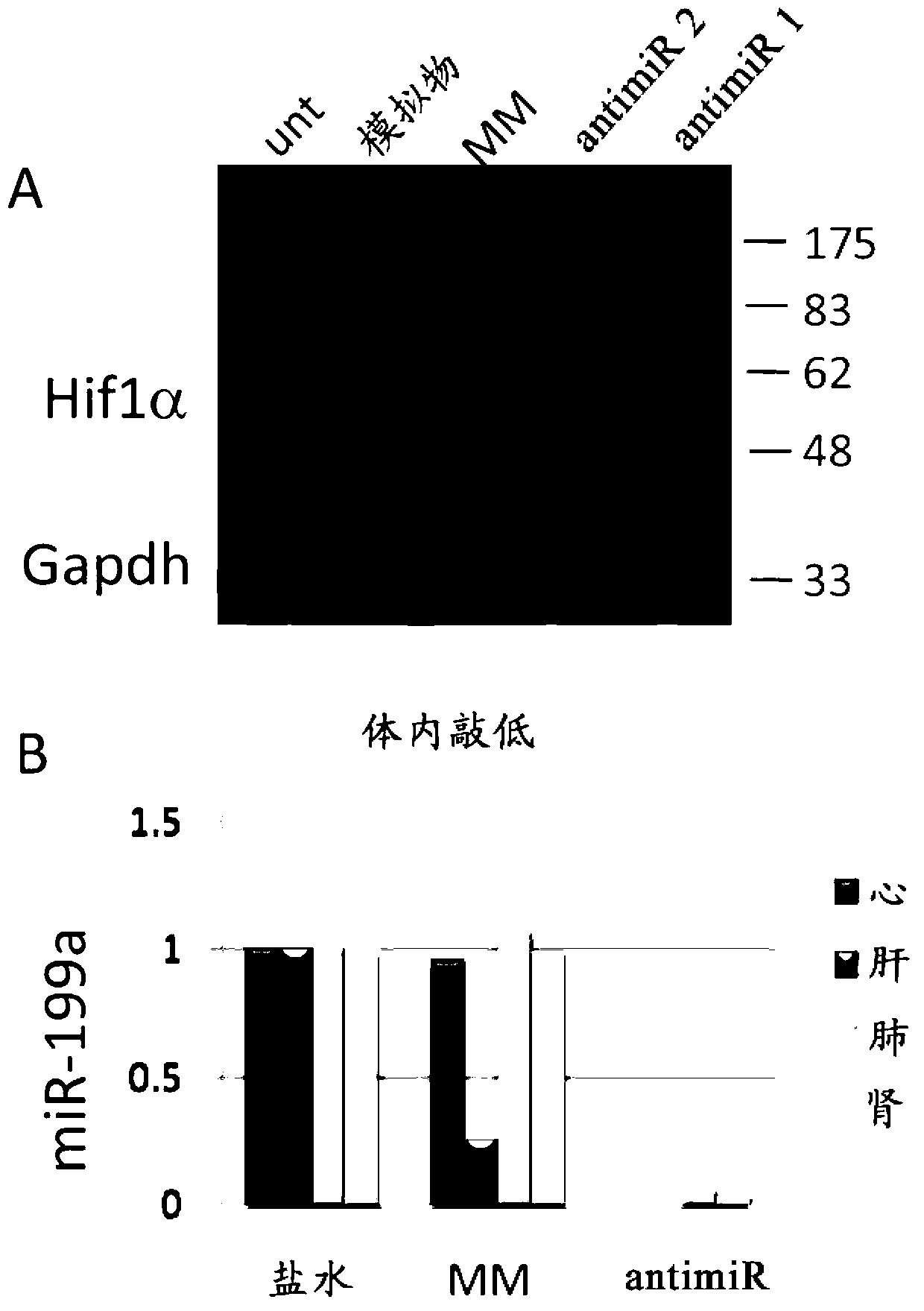
[0095] The expression of miR-199a in ischemic tissues decreased during the first 24 hours after ischemia but began to show recovery 48 hours after the ischemic event. Real-time PCR analysis of miR-199 confirmed that miR-199a expression was significantly reduced in ischemic tissues 24 hours after ischemic injury ( figure 1). Interestingly, we previously identified miR-199 as a miRNA regulated in the marginal zone of myocardial infarction. In response to MI, miR-199 is upregulated 3 and 14 days after MI (van Rooij et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., Vol. 103: 18255-18260; van Rooij et al. Acad. Sci., Vol. 105: 13027-13032). To further elucidate the role of miR-199 after ischemia, we identified the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) as a target of miR-199. To confirm whether HIF1α is a functional target of miR-199, cardiomyocytes were treated with an oligonucleotide with a seque...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3. Identification of miRNAs that are regulated after ischemia-reperfusion injury
[0100] To further examine the role of miRNAs in cardiac remodeling after ischemic injury, miRNA microarrays were performed on cardiac tissue after ischemia-reperfusion. During myocardial ischemia, the blood supply to mitochondria in the infarct area is insufficient to support oxidative phosphorylation. Ischemia is usually followed by reperfusion, allowing readmission of oxygen and metabolic substrates, which replace ischemic metabolites. The reperfusion process induces biochemical, structural and functional changes in the myocardium and can determine cell survival and cell death. Modulation of this process can reduce the deleterious effects of ischemia and / or reperfusion, and thereby enhance the clinical outcome of myocardial infarction.
[0101] Specifically, male C57B16 mice were subjected to myocardial ischemia for 45 minutes. The tissue was then allowed to reperfuse for 24 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com