Screening and identification method of electricigen enzyme
A technology of microorganisms and microbial strains, applied in the field of microbial enzymes, can solve problems such as interference with dyeing reactions and poor dyeing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Culture of Proteus hauseri
[0036] 1) Solid culture
[0037] Composition of LB medium: tryptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L and agar 15g / L, pH7.0, inoculate the isolated and screened Proteus mirabilis on solid medium Incubate at 30°C for 16h.
[0038] 2) Liquid culture
[0039] First, a single colony was picked from the LB agar plate with an inoculation loop and inoculated into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of LB culture solution at 30°C and 150 rpm for 12 hours.
[0040] 3) Dry weight analysis
[0041] Pour the bacterial suspension cultured for 12 hours into a glass filter group equipped with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, weigh the dry filter membrane at 50°C before installation, connect the suction pipe to the suction filter, and cover the filter group with a petri dish to prevent dust Invasion, pump air continuously until the bacteria liquid is partially dehydrated, then add deionized water to the bacteria liquid to diss...
Embodiment 2
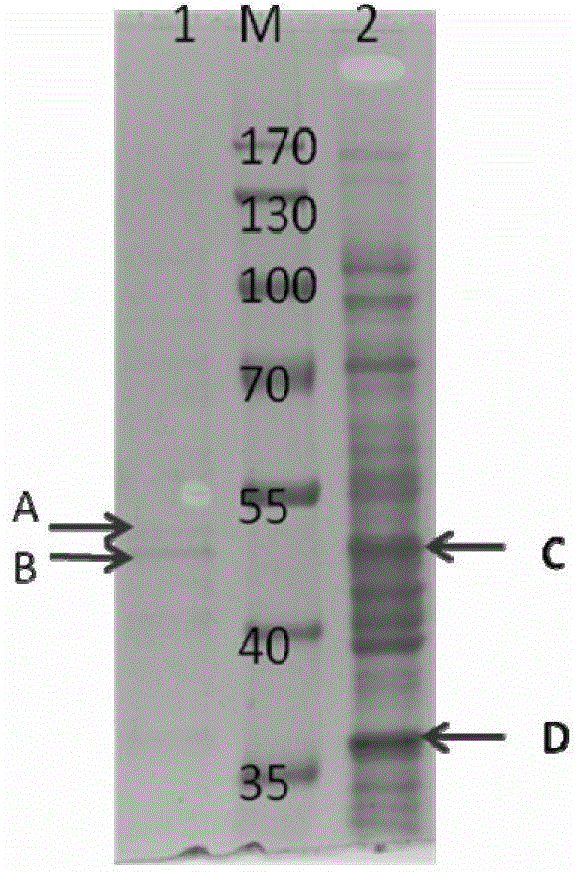
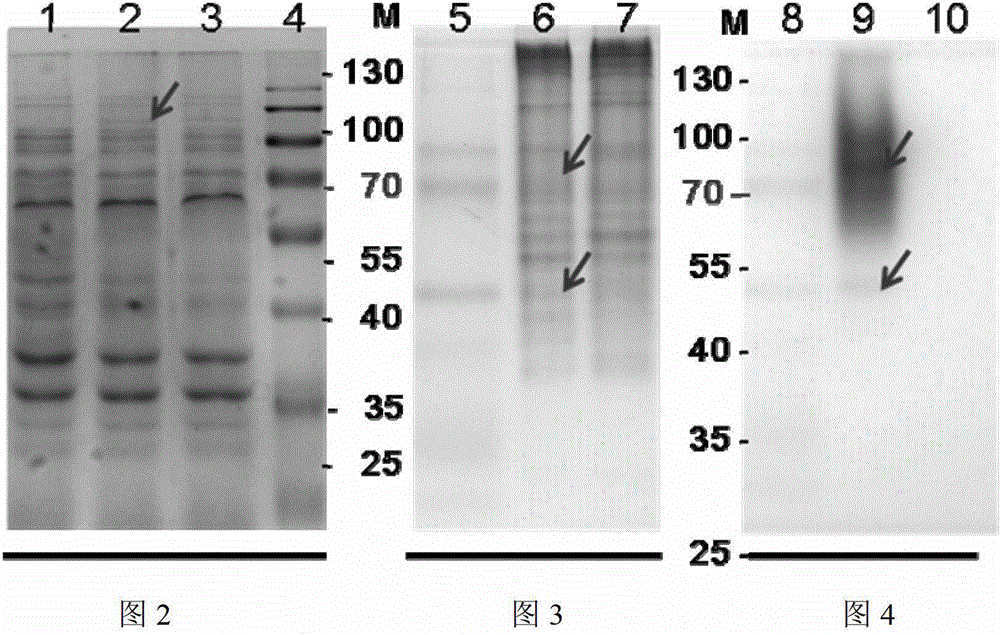
[0042] Embodiment 2: SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis
[0043] Prepare 10% separating gel in a small beaker, carefully pour the gel solution into the mold to avoid bubbles, and polymerize at room temperature for 30 minutes. Then prepare a 5% stacking gel solution, mix well and add it on top of the prepared separating gel, immediately insert a comb into the stacking gel, place it at room temperature for 1 hour to polymerize, and pull out the comb to form a sample hole. Put the whole set of colloids into the electrophoresis tank, add electrophoresis buffer (0.025mol / L tris, 0.192mol / L glycine, 0.1% sodium dodecylsulfonate, pH 8.3), and mix 30μL samples with 10 μL of quadruple protein loading buffer was mixed evenly, heated at 100°C for 5 min, and carefully added to the sample well for electrophoresis analysis. Adjust the voltage to 120V, perform electrophoresis separation for about 1.5 hours, take out the film and stain it with 0.025% Coomassie blue for 1 hour, a...
Embodiment 3
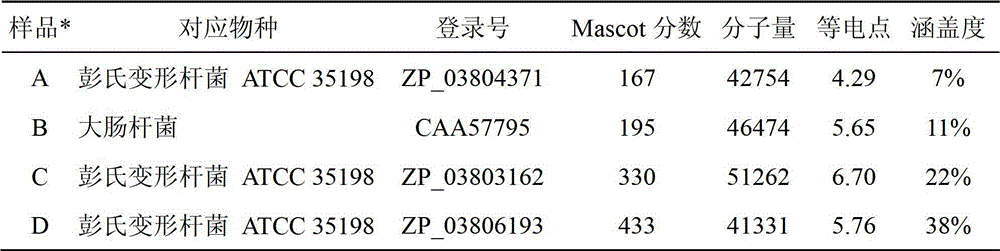
[0044] Example 3: Identification of Protein Identity by Tandem Mass Spectrometry
[0045] 1) Trypsinization:
[0046] Decolorization: add 100μL 50mmol / L NH to the centrifuge tube 4 HCO 3 / Acetonitrile (1:1) test dye gel decolorization solution, keep warm at 37°C for 20 minutes, then remove the solution, and wash repeatedly until the strip becomes colorless and transparent.
[0047] Dry gel: pipette the NH in the centrifuge tube 4 HCO 3 After aspirating with acetonitrile, add 100 μL of 100% acetonitrile, remove the acetonitrile after 10 minutes, and then put it in a 37°C oven for 5-10 minutes to ensure that the glue is completely dry.
[0048] Enzymolysis: Add 5-10 μL of trypsin solution with a concentration of 12.5 mg / L, and place in a 4°C refrigerator for about 30 minutes to ensure that the colloidal particles can absorb the enzyme solution well. After taking it out, enzymolyze in an oven at 37°C overnight.
[0049] Peptide extraction: add 60 μL of 50% acetonitrile and 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com