Photo-inactivated viruses and systems and methods of using same
A technology to inactivate and virus, applied in the field of light inactivated microorganism system, can solve the problems of complicated serological diagnosis and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1: Modified Photoinactivation Technology Using Psoralen and Broad Spectrum Light Pulses to Inactivate Viruses
[0052] Previous experiments with photoinactivation of viruses included a procedure for "black light" (UVA) irradiation of HVP2 psoralen mixtures in petri dishes. In this procedure, the virus-psoralen mixture is exposed to a "black light" UVA lamp in two sets of 30-minute exposures. The results of this experiment were unsatisfactory because it was time consuming, caused heating and evaporation, and above all resulted in lower antigenicity.
[0053] In order to overcome the shortcomings of the above procedure, this example describes an improved psoralen photoinactivation technique, wherein psoralen photoinactivation was carried out by using Xenon Corporation (Woburn, MA) (Xenon Corporation (Woburn, MA) ) SteriPulse-XL irradiation equipment (RS-3000C type). Information on the SteriPulse-XL system is described in Xenon's publication entitled "Germicidal ...
experiment example 1
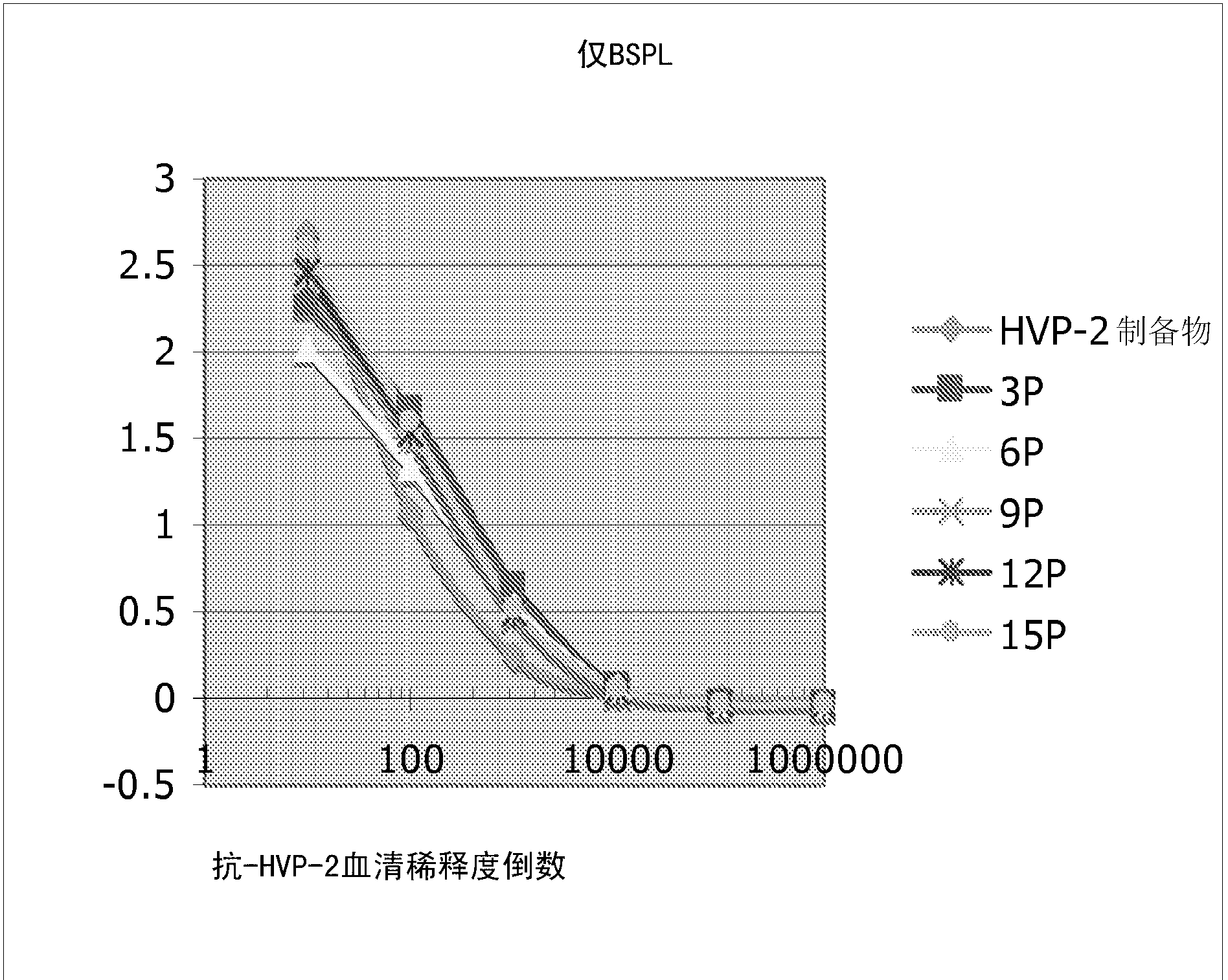
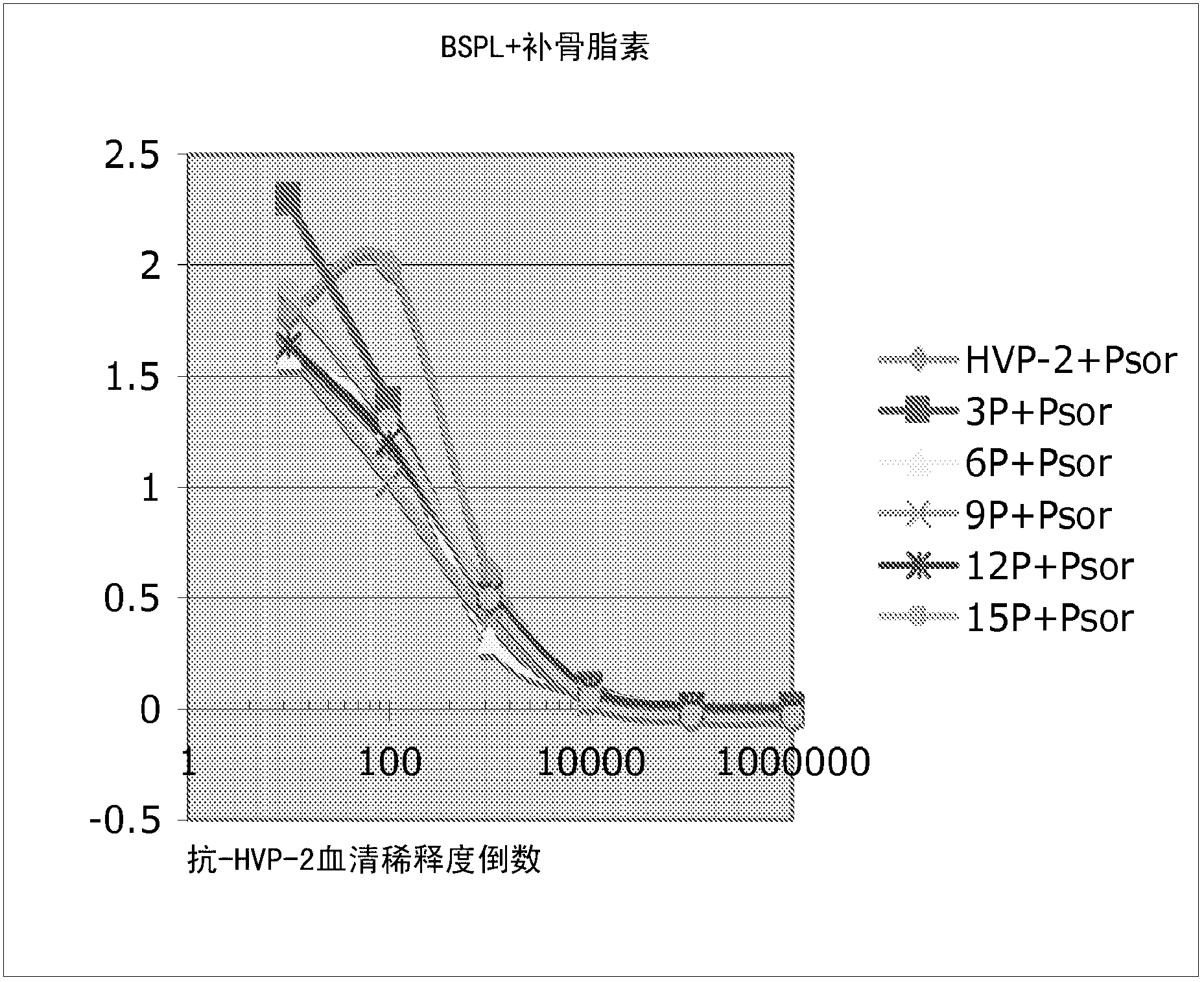
[0065] Experimental example 1. The purpose of this experiment was to compare the inactivation process by BSPL with the photoinactivation by the combined use of psoralen and BSPL. Inactivation by BSPL alone was performed as follows: five 1 ml dilutions of HVP2 (10 8 PFU / ml) were transferred to 5 polyethylene tubes (Polytubing, 1 x 1500'2 Mil, product number S-3520, ULINE, Atlanta GA) heat-sealed at one end. Next, heat seal the end at a position 5 cm away from the first seal. First, another 5 ml of diluted virus was mixed with psoralen (4-Aminomethyl-trioxalen hydrochloride, Sigma, Catalog # A43305 mg) to a final concentration of 20 μg / ml psoralen, and then 1 ml was transferred to the above five polyethylene tubes respectively. Each tube was irradiated with different doses of BSPL (with and without psoralen). A pair of polyethylene tubes in each group was placed on a plastic tray lying flat on a bed of crushed ice, one containing the virus and the other containing the virus ...
experiment example 2
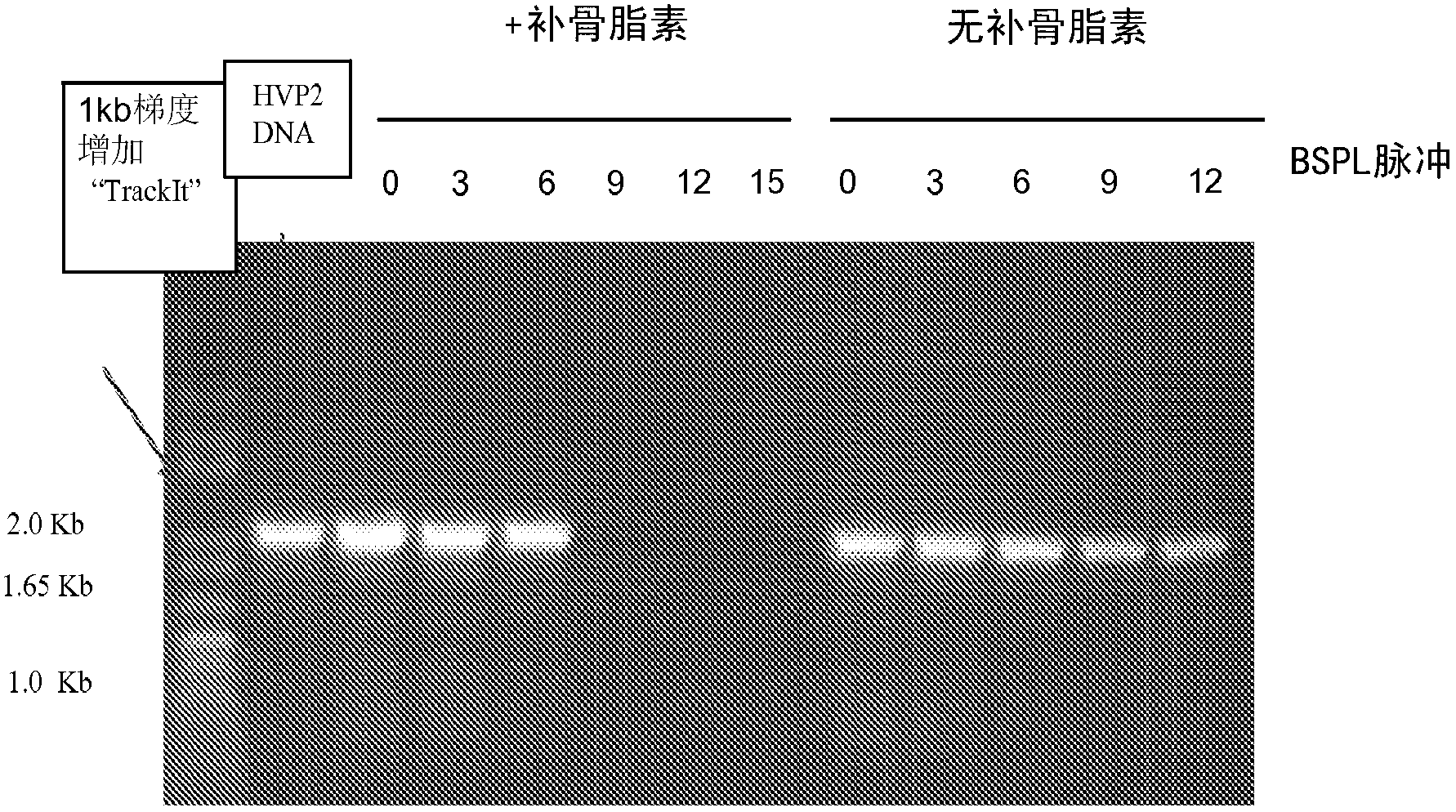
[0070] Experimental example 2. The procedure described in Experimental Example 1 was repeated in this Experimental Example with some minor changes. Samples exposed to 3 pulses of BSPL were not spot detected. Spot detection was performed on samples exposed to BSPL pulses of 6 or higher. Table 2 provides the results of spot detection of HVP2 infection by BSPL compared to photoinactivation process in combination with psoralen and PSPL. The number of spots per BSPL dose is shown in bold numbers. All samples exposed to 3 BSPL pulses or higher were detected by PCR ( Figure 4 ). As in Table 2, samples mixed with psoralen and exposed to BSPL pulses of 6 or higher produced no spotting. The samples exposed to BSPL developed spots only after exposure to pulses of 6, 9 and 12, but not after pulse 15.
[0071] Table 2
[0072] Pulse number
6
9
12
15
J / cm 2
2.70
4.05
5.40
6.75
BSPL+Psoralen
0
0
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com