Pulmonary valve stents to prevent displacement
A pulmonary artery and valve technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as stent displacement, avoid blood vessel tearing, improve stability, and avoid displacement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
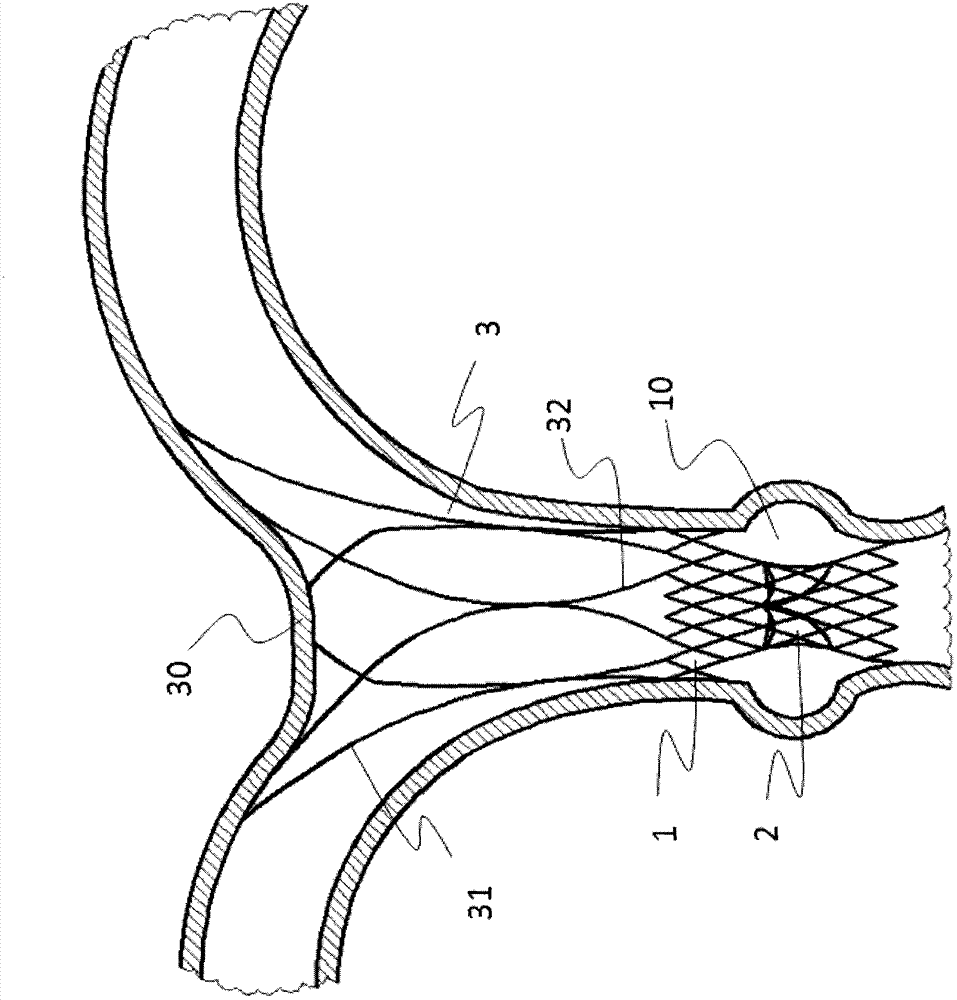
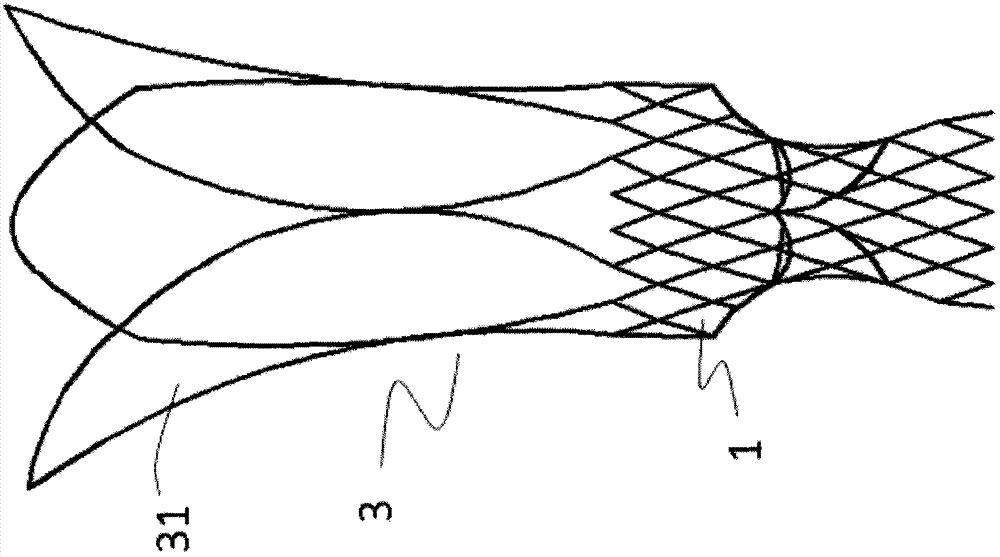
[0047] Such as figure 1As shown, a displacement-preventing pulmonary valve stent includes a valve sewing section 1 and an artificial valve 2, the artificial valve 2 is connected to the valve sewing section 1, and the valve sewing section 1 When released, it is located on the right ventricular outflow tract or the main pulmonary artery 10. The valve stent also includes a limiting mechanism 3, and the bottom part 32 of the limiting mechanism 3 is connected to the distal end of the valve sewing section 1. Connected, the top part 31 of the limiting mechanism 3 is released and interferes with the intersection 30 of the main pulmonary artery and its branches, providing an axial limiting function.
[0048] The top portion 31 of the limiting mechanism is a self-expanding stent made of shape-memory material or elastic material, more preferably nickel-titanium shape-memory alloy. As a preferred embodiment, such as Figure 2a and 2b As shown, the top portion 31 of the limiting mechani...
specific Embodiment 2
[0051] A displacement-preventing pulmonary valve stent, comprising a valve sewing section 1 and an artificial valve 2, the artificial valve 2 is connected to the valve sewing section 1, and the valve sewing section 1 is positioned at On the right ventricular outflow tract or the main pulmonary artery 10, the valve stent also includes a limiting mechanism 3, the bottom part 32 of the limiting mechanism 3 is connected to the distal end of the valve sewing section 1, and the After the top part 31 of the limiting mechanism 3 is released, it interferes with the junction 30 of the main trunk and branches of the pulmonary artery, providing an axial limiting function.
[0052] The top part 31 of the limiting mechanism is a self-expanding stent made of shape-memory material or elastic material, preferably nickel-titanium shape-memory alloy. As a preferred embodiment, such as Figure 8 As shown, the self-expanding stent is a bowl-shaped mesh stent 6, so that it softly touches the inner...
specific Embodiment 3
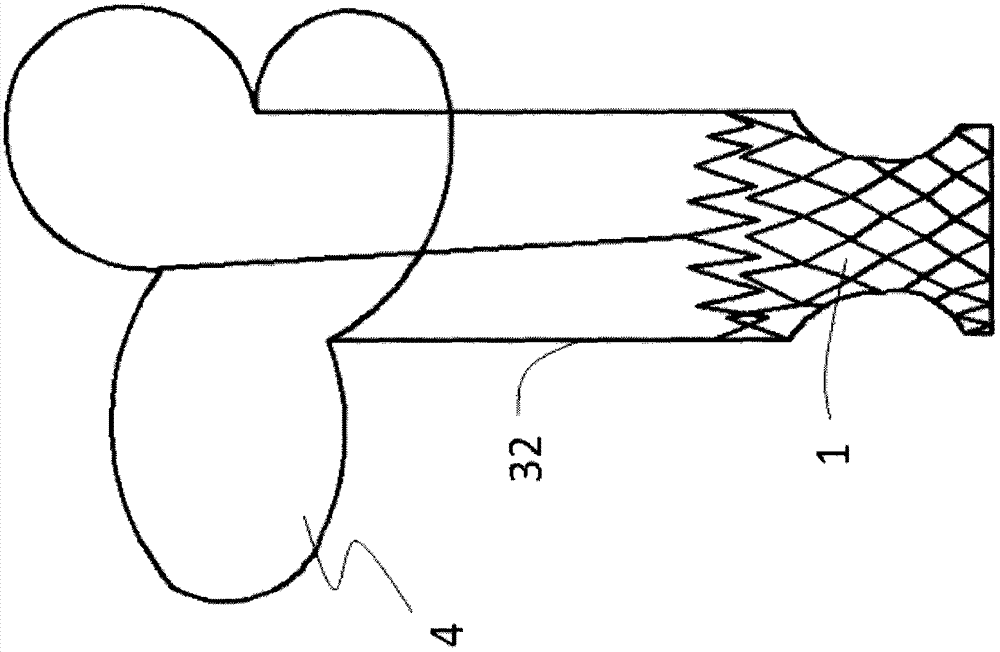
[0060] The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment 2 is that the top part 31 of the limiting mechanism is an air-filled or liquid-filled balloon 7, and the balloon is flat to avoid blocking the branch vessels of the pulmonary artery after collision. Such as Figure 9 As shown, the balloon 7 is provided with an inflatable or liquid-filled valve 72, which inflates the balloon 7 to act as a buffer and limiter, preventing the top of the limiter 3 from damaging the vessel wall. In addition, the connecting member 5 is a continuation of the skeleton of the leaflet 41 of the petal-shaped stent 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com