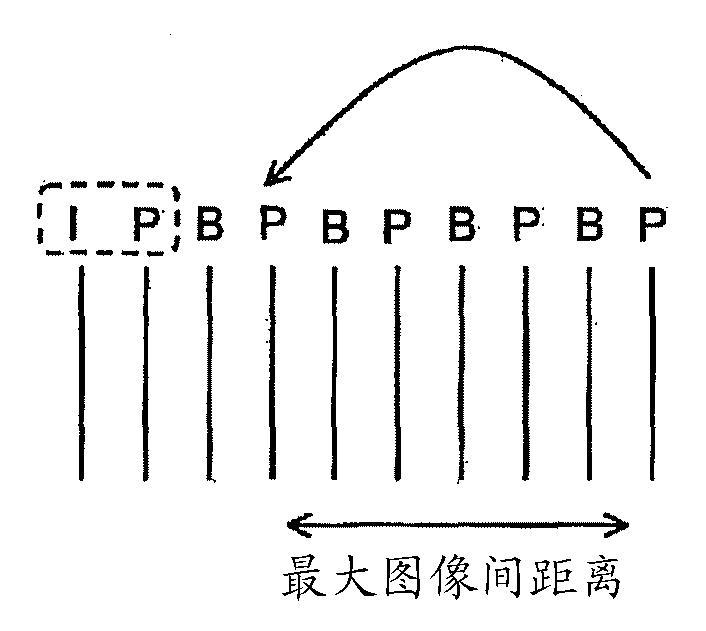
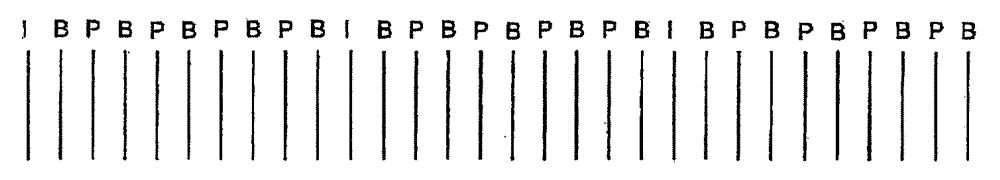
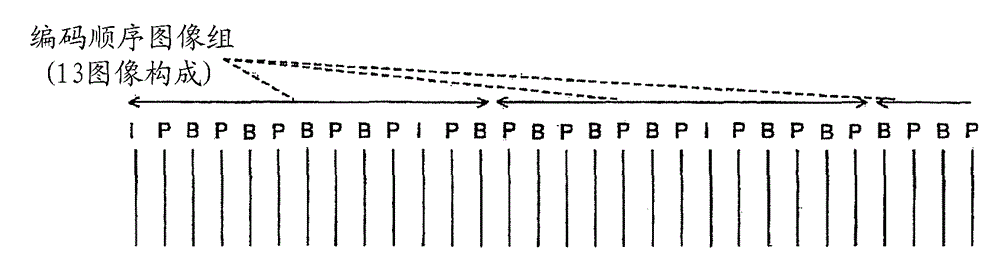
Moving picture coding control method, moving picture coding device
A moving image, coding control technology, applied in the field of moving image coding, can solve the problem of increased computation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0098] image 3 is a flowchart showing the processing of the moving picture coding control method according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0099] First, the image next to the encoded image in the input video signal is set as an encoding target (step S101 ). The input image set as an encoding target is encoded using H.264 and other predetermined encoding methods (step S102 ). Whether or not CPB underflow has occurred is determined based on the encoding of the input image (step S103 ), and if CPB underflow has occurred, the process proceeds to step S107 . In addition, whether or not CPB underflow has occurred can be determined by a method used in, for example, the H.264 standard.
[0100] If the CPB underflow does not occur, it is determined whether the encoding of the final image is completed (step S104 ), and if the encoding of the final image is also completed, the encoding process is terminated.
[0101] If not, it is determined whether or not the enc...
no. 2 example
[0140] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figure 9 is a flowchart showing the processing of the moving picture coding control method according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0141] First, the image next to the encoded image in the input video signal is set as an encoding target (step S201 ). The input image set as an encoding target is encoded using H.264 and other predetermined encoding methods (step S202 ). Whether or not CPB underflow has occurred is determined from the encoding of the input image (step S203 ), and if CPB underflow has occurred, the process proceeds to step S208 . In addition, whether or not CPB underflow has occurred can be determined by a method used in, for example, the H.264 standard.
[0142] If CPB underflow does not occur, it is determined whether the encoding of the final image is completed (step S204 ), and if the encoding of the final image is also completed, the encoding process is termi...
no. 3 example
[0182] Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figure 12 is a flowchart showing the processing of the moving picture encoding control method according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0183] First, the image next to the encoded image in the input video signal is set as an encoding target (step S301 ). The input image set as an encoding target is encoded using H.264 and other predetermined encoding methods (step S302 ). Whether or not CPB underflow has occurred is determined from the encoding of the input image (step S303 ), and if CPB underflow has occurred, the process proceeds to step S308 . In addition, whether or not CPB underflow has occurred can be determined by a method used in, for example, the H.264 standard.
[0184] If CPB underflow does not occur, it is determined whether the encoding of the final image is completed (step S304 ), and if the encoding of the final image is also completed, the encoding process is term...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com