Lowe-electric-quantity shutdown method
A low-battery, low-power-consumption technology, which is applied in measuring devices, data processing power supplies, measuring flow/mass flow, etc., can solve problems such as short service life, battery damage, battery aging, etc., and achieve the effect of prolonging service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
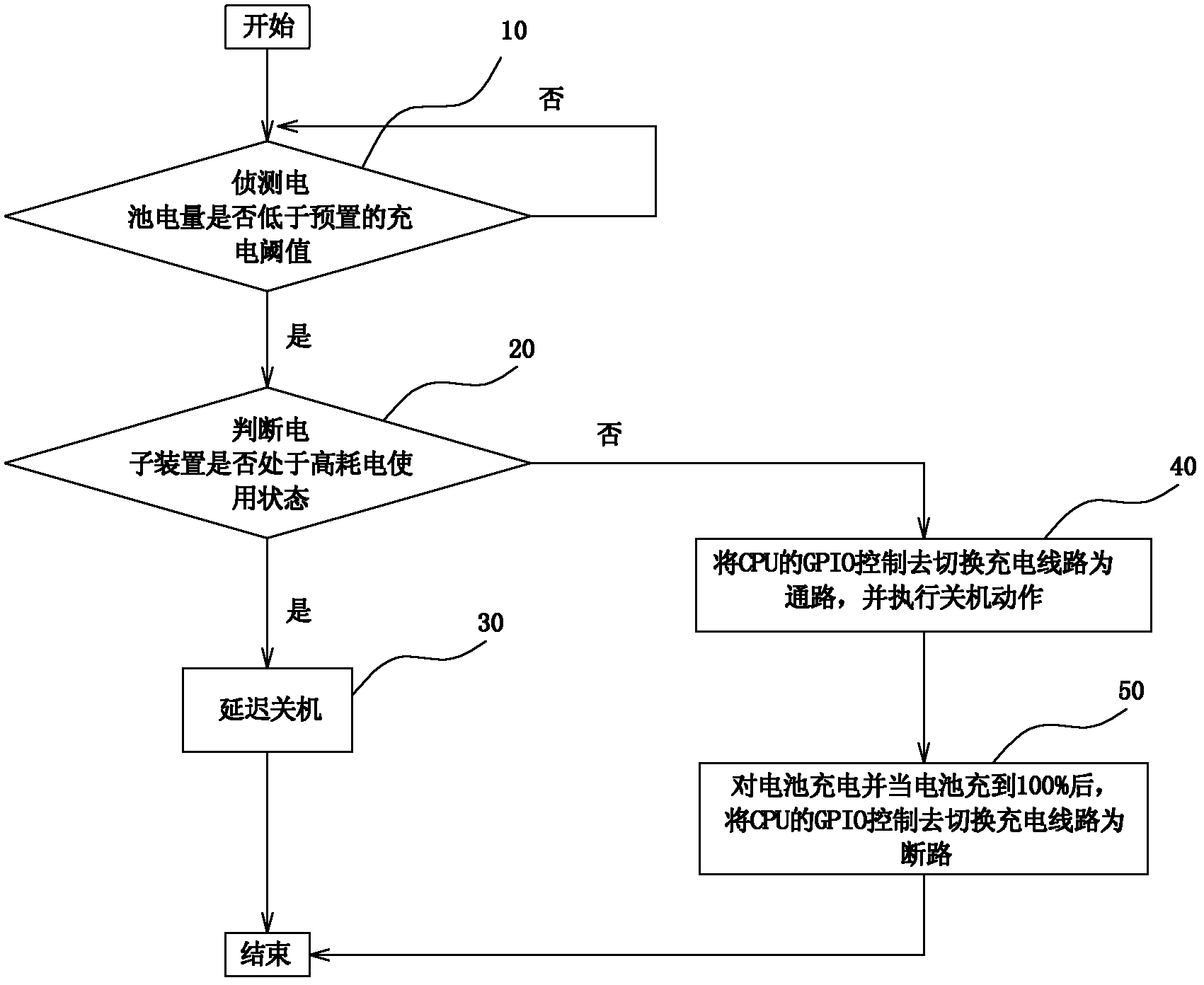
[0022] see figure 1 As shown, the low-power shutdown method of the present invention can perform a shutdown operation according to the use state of the electronic device, wherein the use state of the electronic device includes a high power consumption use state and a low power consumption use state, and the high power consumption use state can be startup navigation, DVB-T also has video playback etc., and the low power consumption state can be to stop navigation, close DVB-T and stop playing movies etc.; Described low power shutdown method comprises the following steps:
[0023] Step 10: Detect whether the battery power is lower than the preset charging threshold; the preset charging threshold can be set as required, for example, the preset charging threshold can be set to 10% of the maximum battery power; when the battery power is lower than When the charging threshold is preset, execute step 20; otherwise, continue to execute step 10;
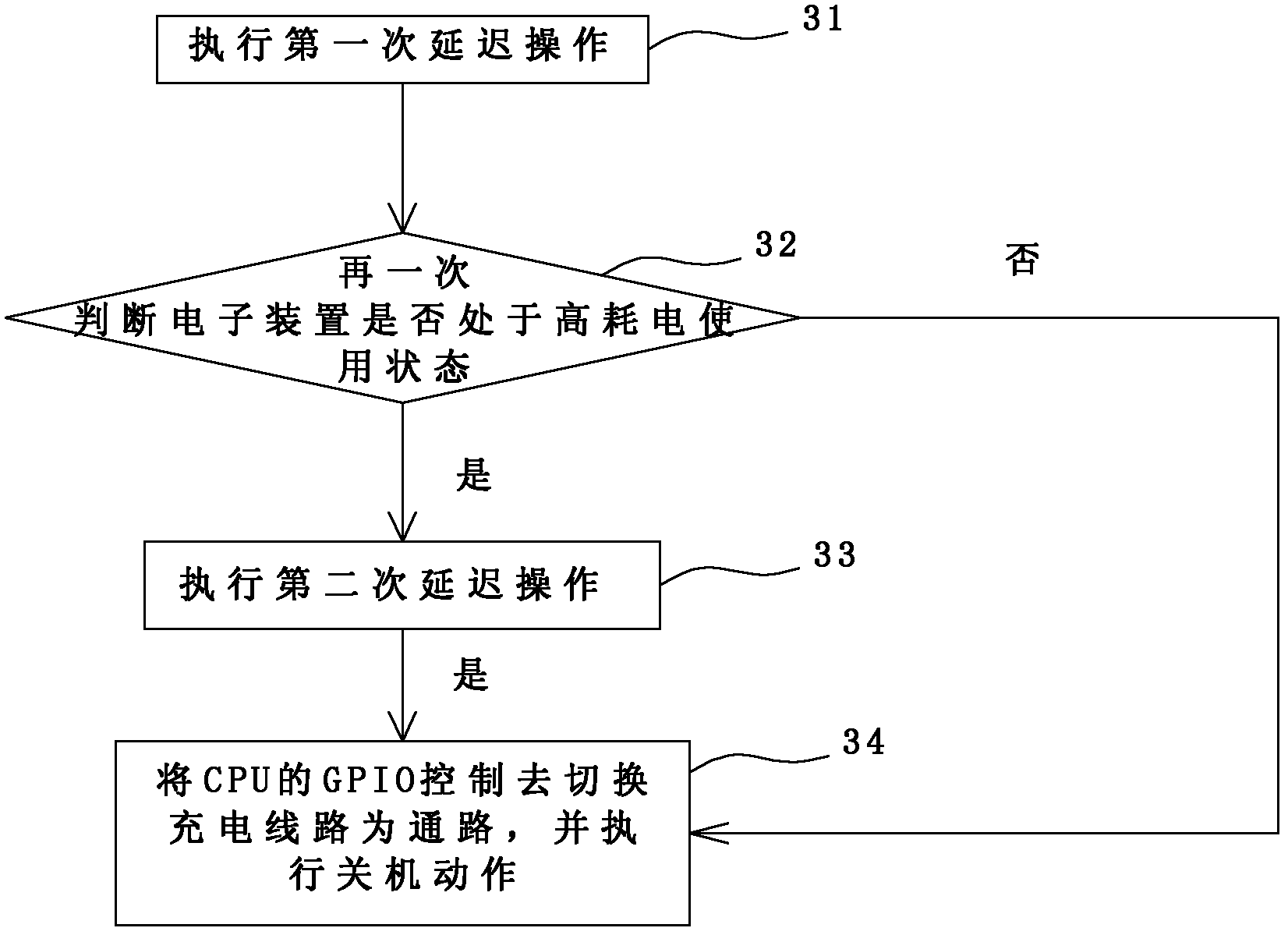
[0024] Step 20: Determine whether the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com