A label distribution method, device and system
An allocation method and technology of allocation method, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem of large consumption of label resources, and achieve the effect of saving label resources and flexible application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
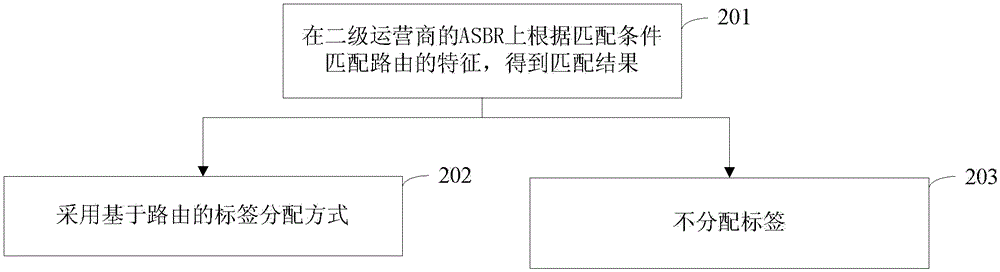
[0035] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a label assignment method, which includes the following steps:
[0036] 101: Match the characteristics of the route according to the matching condition to obtain a matching result. The matching condition includes: whether the characteristic of the route is a specified characteristic and / or whether the characteristics of multiple routes are the same.
[0037] Specifically, the characteristics of the aforementioned route include: route prefix, route mask length, BGP route attribute and route VPN label.
[0038] Correspondingly, the foregoing matching conditions include: whether the length of the route mask is a specified length, whether the route prefix is a specified route prefix, whether the VPN labels of multiple routes are the same, and whether the next hops of multiple routes are the same or a combination of several.
[0039] 102: Select a corresponding label assignment method for the route according to the matchin...
Embodiment 2
[0043] This embodiment uses a CSC scenario as an example to illustrate the label allocation method in the embodiment of the present invention.
[0044] The CSC scenario refers to such a networking model: in addition to directly providing VPN services to customers, some large operators will also package some network resources to some small operators for operation. That is to say, BGP / MPLSVPN services provide The user of the provider may also be a service provider, in this case, the former is called the first-level operator, and the latter is called the second-level operator.
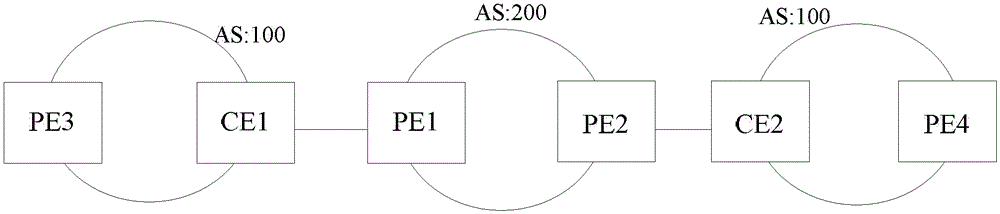
[0045] like Figure 2a As shown, the operator corresponding to AS (Autonomous System, autonomous system): 200 is a first-level operator, and the operator corresponding to AS: 100 is a second-level operator. The CE of the first-level operator, such as CE1, only advertises the internal routes of the second-level operator to the PE of the first-level operator, such as PE1, but does not publish the routes of...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Such as Figure 3a As shown, this embodiment takes the cross-domain VPNOptionC scenario as an example to illustrate the label allocation method of the present invention. In this scenario, the ASBR does not maintain or advertise VPN-IPv4 routes. PEs in different ASs, such as AS:100 and AS:200 in the figure, are between RR-1 (Route Reflector, route reflector) and RR-2. Establish a Multihop EBGP connection between them, and directly exchange VPN-IPv4 routes. ASBRs advertise IPv4 label routes to PE devices in their respective ASs through MP-IBGP (Multi-Protocol internal BGP, multi-protocol internal border gateway protocol), and will reach the AS. The IPv4 label route of the inner PE device is notified to its ASBR peer in the peer AS. The purpose of publishing IPv4 labeled routes is to bond the tunnels in their respective domains together to form an end-to-end tunnel between PE devices in different AS domains, such as PE2 and PE4.
[0060] Since the ASBR does not maintain ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com