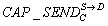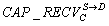Interference sensing cross-layer routing method based on node sending and receiving capacity
A receiving capability and node technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems that packets cannot be received and forwarded in time, the network performance is degraded, and the network performance is affected, and the effect of improving the average end-to-end delay and small bottleneck link interference is achieved
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] exist figure 1 Among the 9 nodes in the network shown, there are 5 data streams, namely S D, S1 D, S2 D, S3 D, S4 d. For the convenience of analysis, it is assumed that the transmission data stream S1 D, S2 D, S3 D, S4 The route of D has been established, and now it is necessary to establish the transmission data flow S D’s route, and node B has sent a routing request packet RREQ (Route Request) to node C, now it is defined that node C sends data flow S D group ability and receive data streams belonging to S D group ability as follows.
[0040] CAP + SEND C S → D = P send _ state C S → D · P service ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com