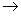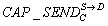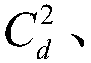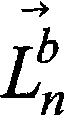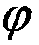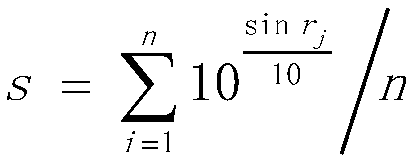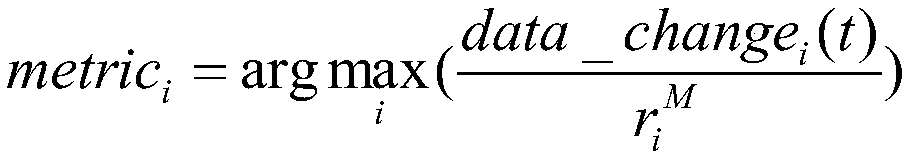Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Improve packet loss rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
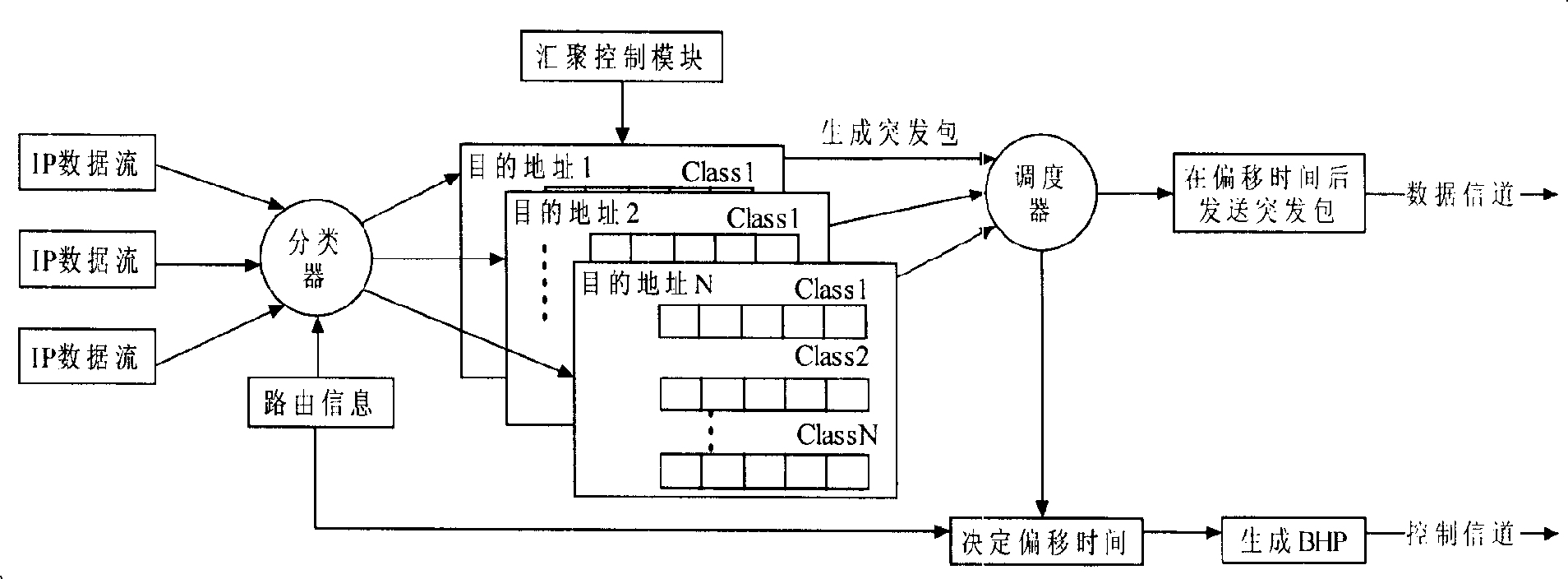
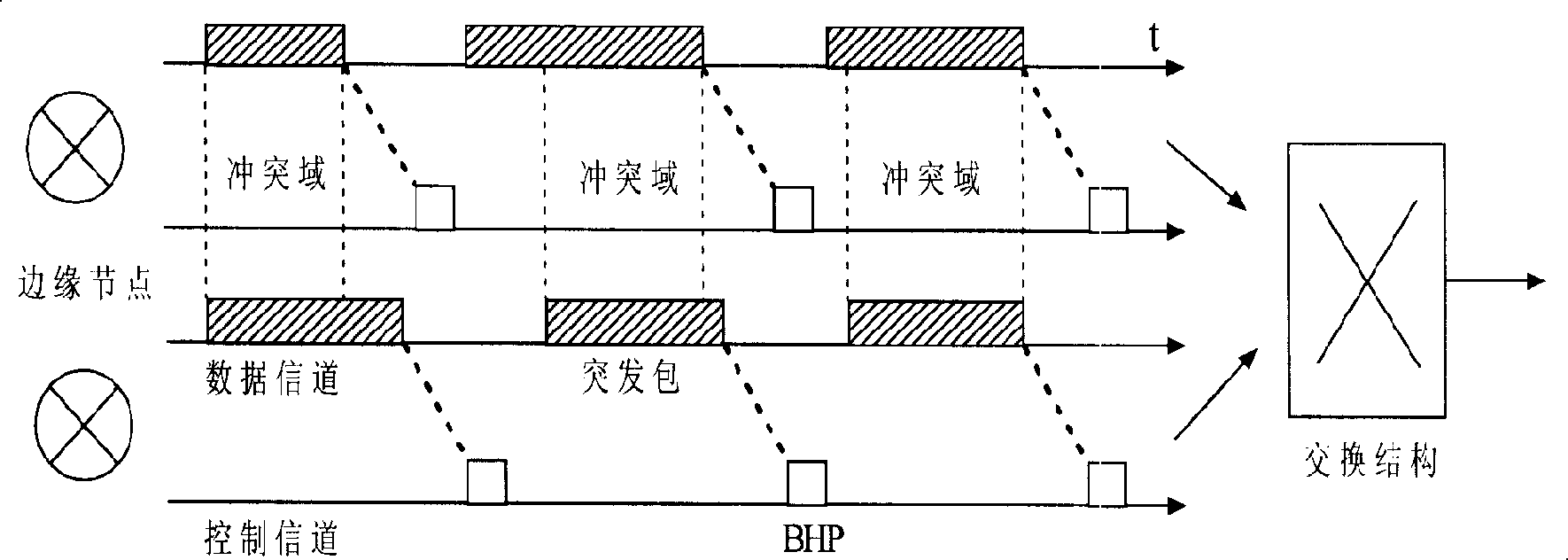
Outburst convergence control method, device, and communication device
InactiveCN101212389AAdjust in timeAvoid Continuous Excessive VariationsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksCommunication deviceReal-time computing
The invention discloses a controlling method for a burst assembly, a corresponding device and a communication equipment thereof. A core of the method and the device in the invention includes the following steps: by comparing an assembly time with a time threshold set in advance, a change trend of carriers in a buffer queue is judged; if the change of the carrier burst is increased or reduced, a length threshold is directly increased or reduced; if the carriers are in an increasing trend, the threshold is randomly increased according to a certain probability; if the carriers are in a reducing trend, the threshold is randomly reduced according to a certain probability; if the carrier is normal, the length threshold is not adjusted, therefore, the length threshold can realize dynamic adjustment with the changes of the carrier. By adopting the method and the device provided by the invention, a delay from a business end to anther business end is assured, thus optimizing the performance of the network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
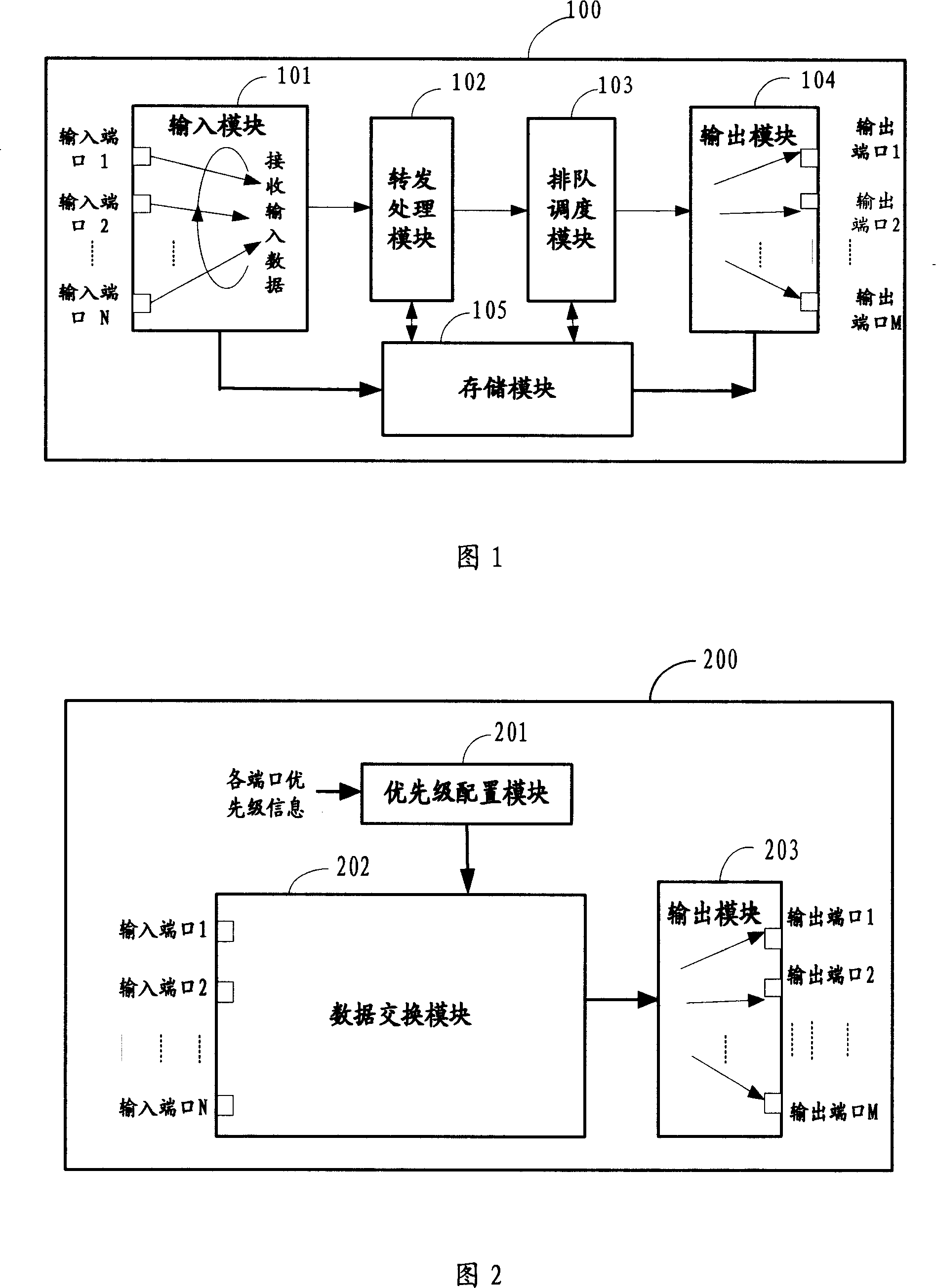
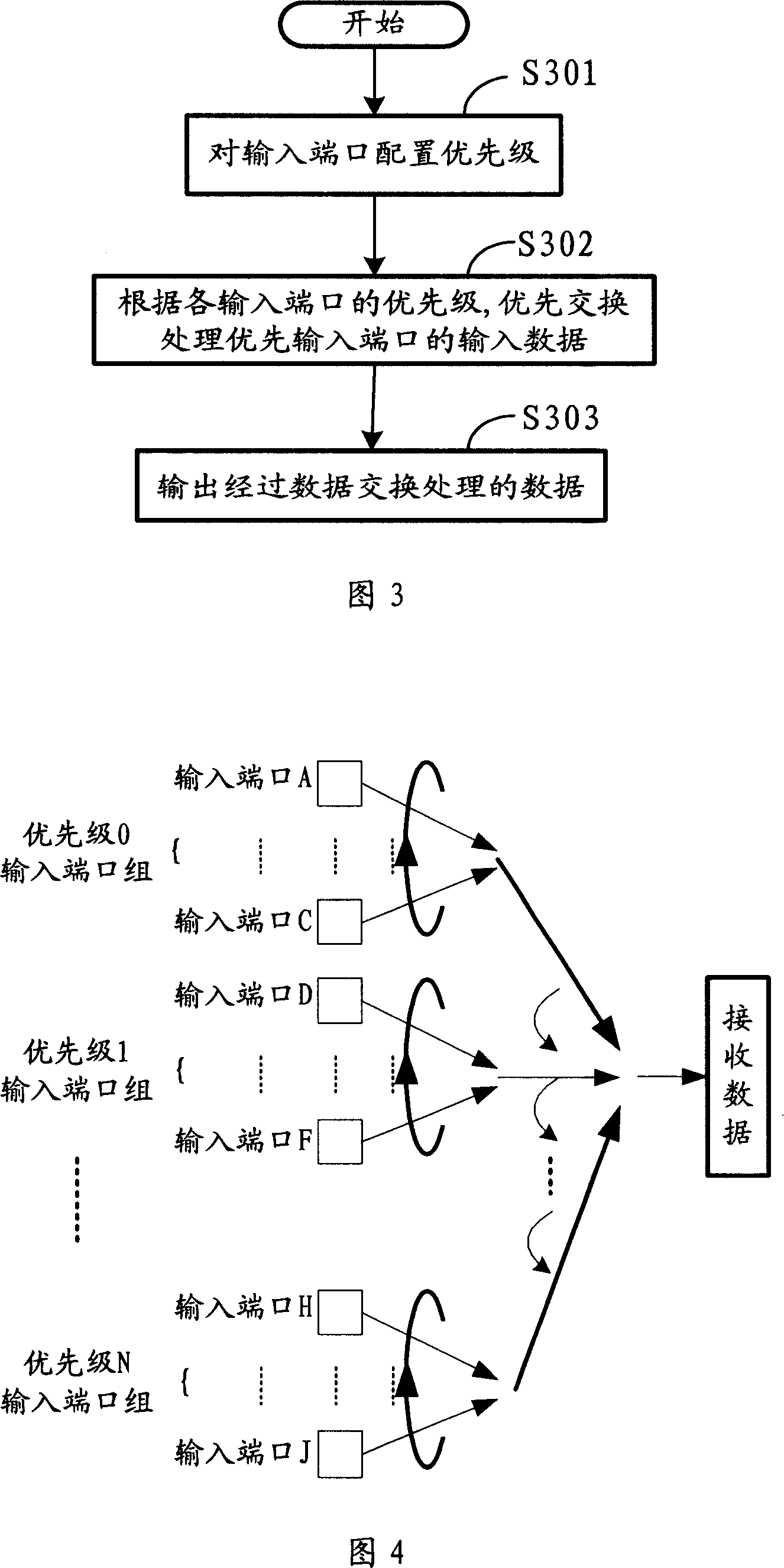
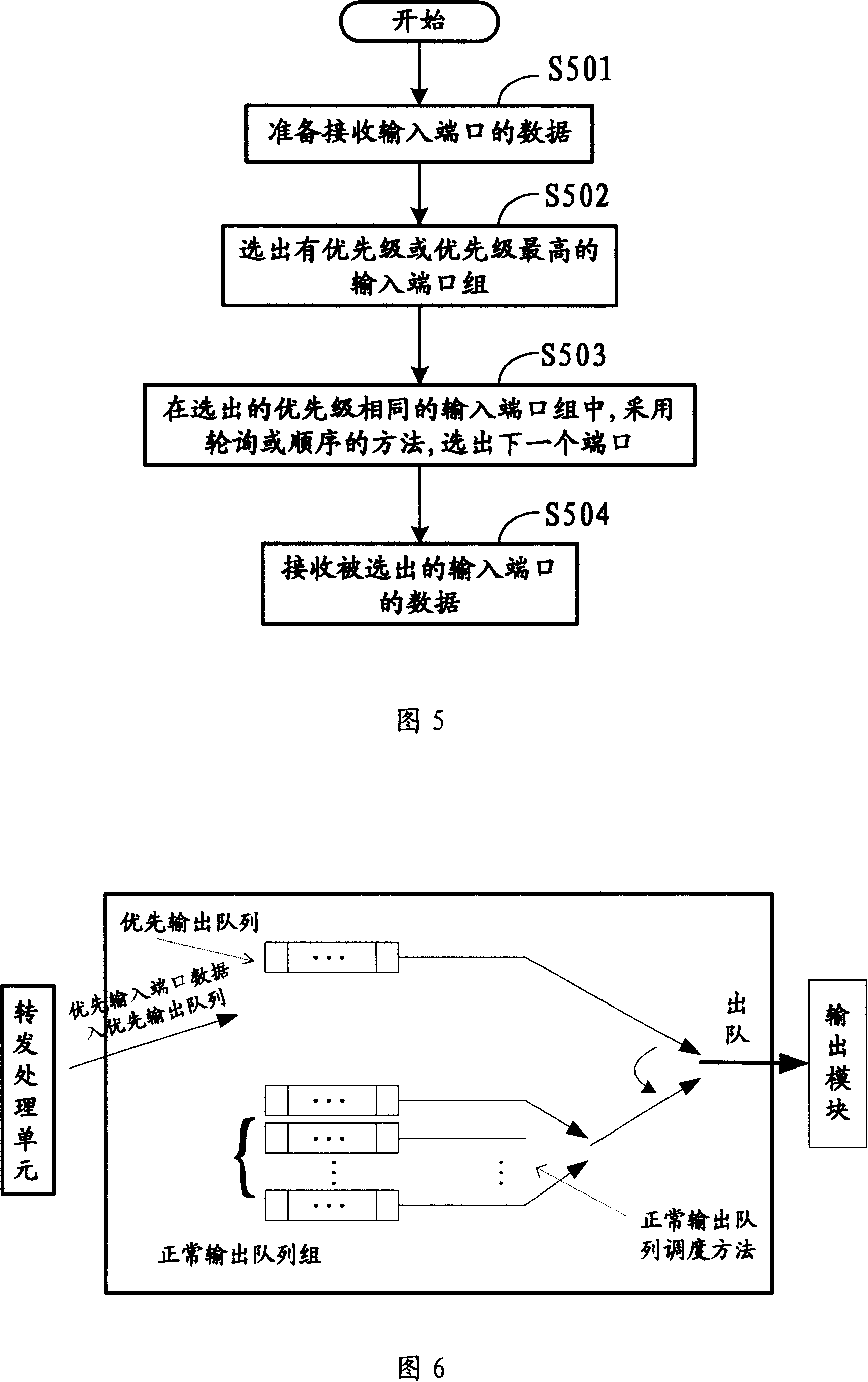
A network data processing method and device
InactiveCN101127686AImprove latencyImprove bandwidth utilizationData switching detailsData switching by path configurationNetwork dataData exchange
The utility model discloses a network data processing method and device; wherein, the method comprises: a plurality of input ends are configured with priorities; input data from the input ends with priorities or high priorities is exchanged and processed first according to the priorities of the input ends; data exchanged and processed is exported; the network device comprises: a priority configuration module, which configures priorities or high priorities to the input ends with smaller bandwidth or more important input ends; a data exchange module, which exchanges and processes input data from the input ends with priorities first; an output module, which exports exchange data. The utility model is applicable to the network device with important input ends to improve the transmission speed and quality of data from the important input ends.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
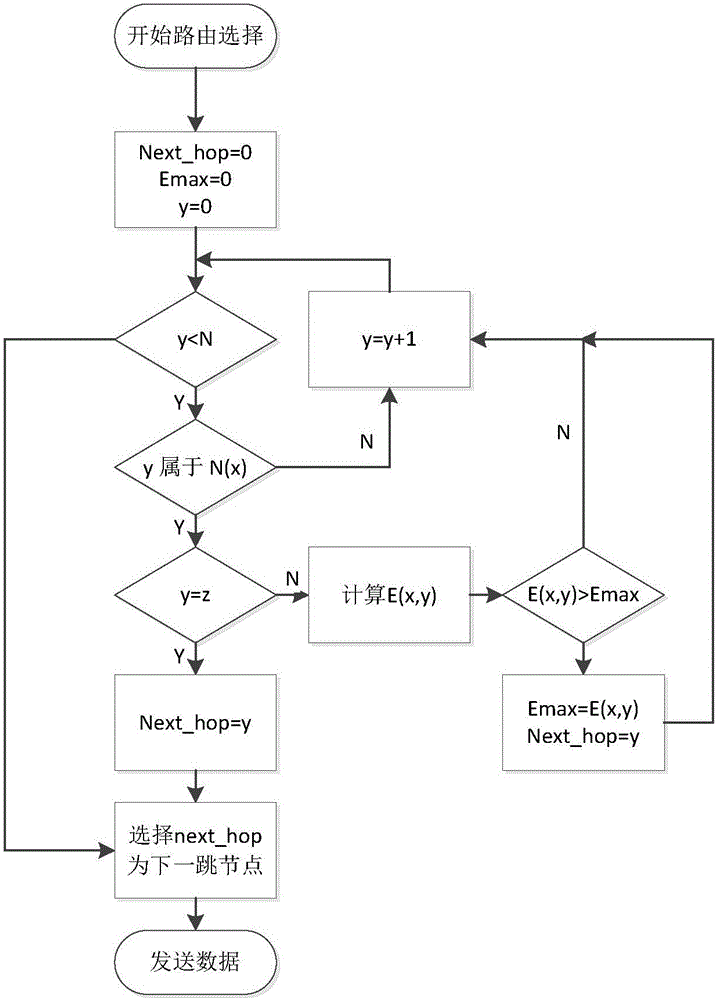
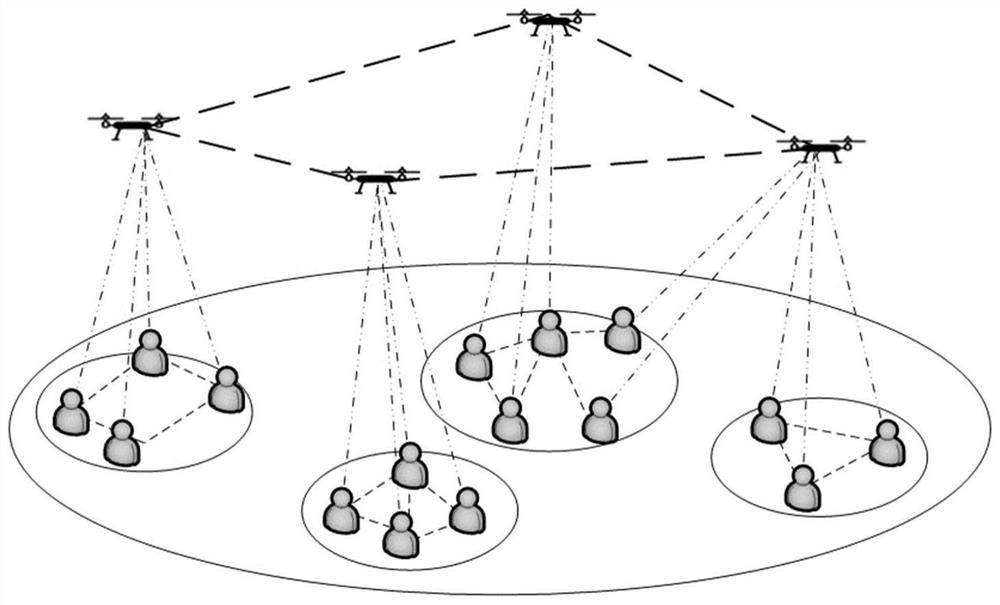
Dynamic routing method of three-dimensional heterogeneous network in emergency scene based on unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN111263419AImprove operational efficiencyEasy and intuitive deploymentNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionSimulationTrunking
The invention discloses a dynamic routing method of a three-dimensional heterogeneous network in an emergency scene based on an unmanned aerial vehicle. The method can adapt to a fusion network with dynamic topology change; an unmanned aerial vehicle is used as a relay node to form the relay node; nodes in the same area are not communicated; node communication in different areas is relayed and routed through unmanned aerial vehicle nodes; ground nodes are only used as tail end nodes in routing. In each communication process, the method comprises the steps that A scene modeling is conducted onthe unmanned aerial vehicle nodes and the ground nodes respectively; B a link weight is improved on the basis of a traditional OLSR protocol, and a routing path is selected by taking cost = alpha * ETT + beta * Ei + (1-alpha-beta) * T as a reference; and C the core idea of the OLSR routing protocol is to select an MPR set to reduce the routing overhead, and the improved LBMRE-OLSR abandons a classical MPR set selection algorithm to select the MPR set based on the node expected transmission time, the node energy and the node congestion degree.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Power communication hierarchical routing path determining method
ActiveCN105471730AImprove communication performanceImprove packet loss rateRadio transmissionData switching networksOrbitNetwork topology
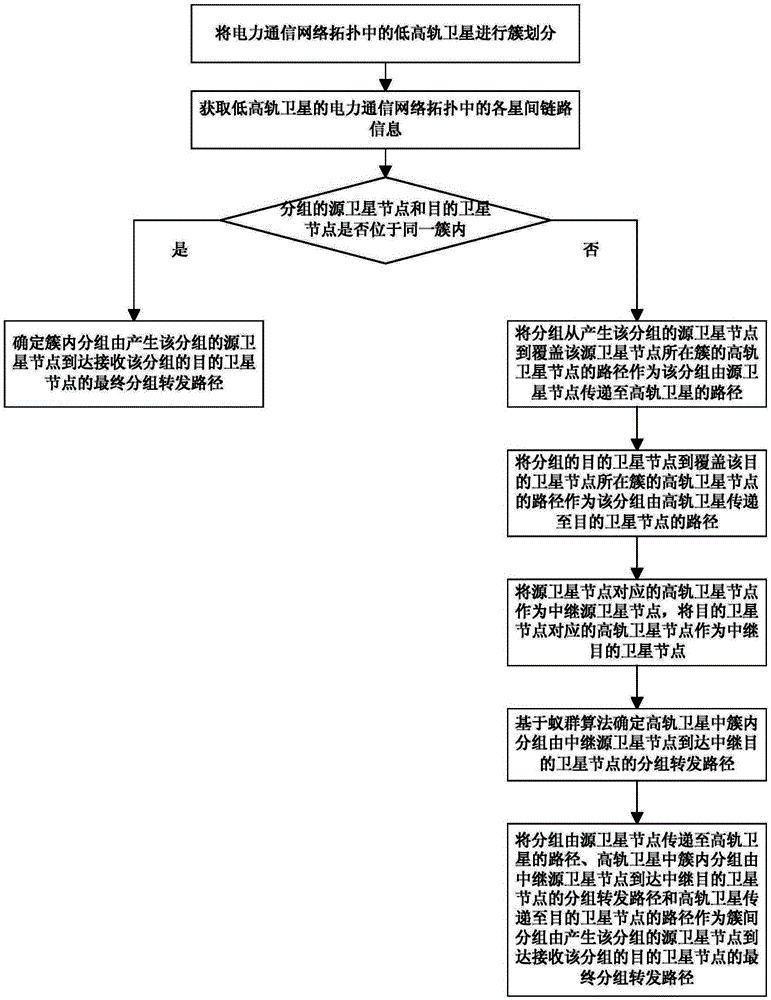
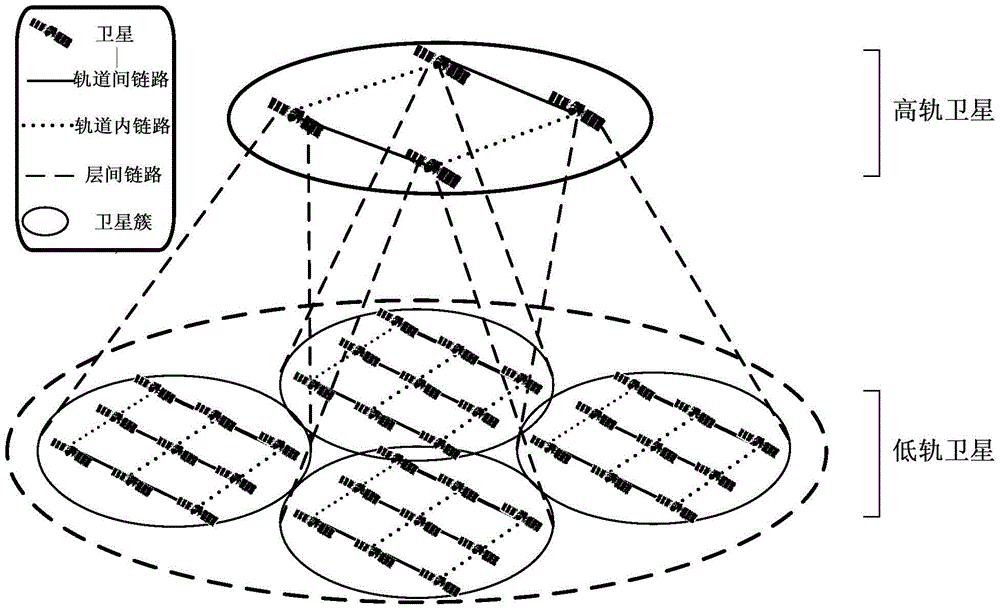
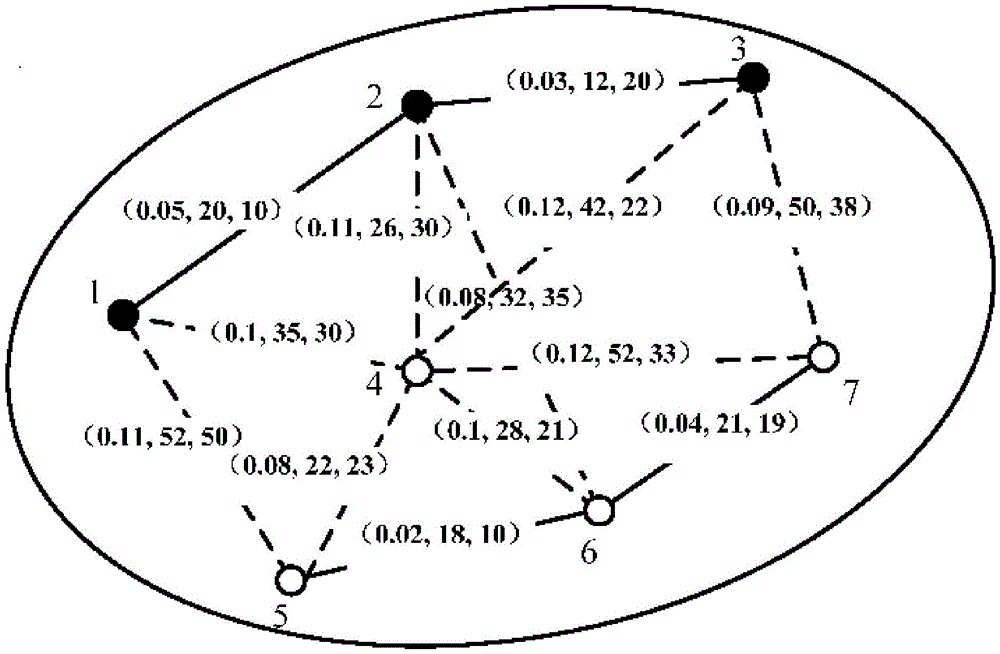
The invention relates to a power communication hierarchical routing path determining method comprising the following steps: clustering low- and high-orbit satellites in a power communication network topology; when the source satellite node and the destination satellite node of a packet are in the same cluster, determining a final packet forwarding path from the source satellite node generating the packet to the destination satellite node receiving the packet for the intra-cluster packet based on an ant colony algorithm; and when the source satellite node and the destination satellite node of a packet are not in the same cluster, taking a path for transmitting the packet from the source satellite node to a high-orbit satellite, a packet forwarding path for an inter-cluster packet in the high-orbit satellite to reach a relay destination satellite node from a relay source satellite node and a path for transmitting the high-orbit satellite to the destination satellite node as the final packet forwarding path from the source satellite node generating the packet to the destination satellite node receiving the packet for the inter-cluster packet. The method can be used to jointly optimize the communication performance of the system, and is advantageous in communication.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
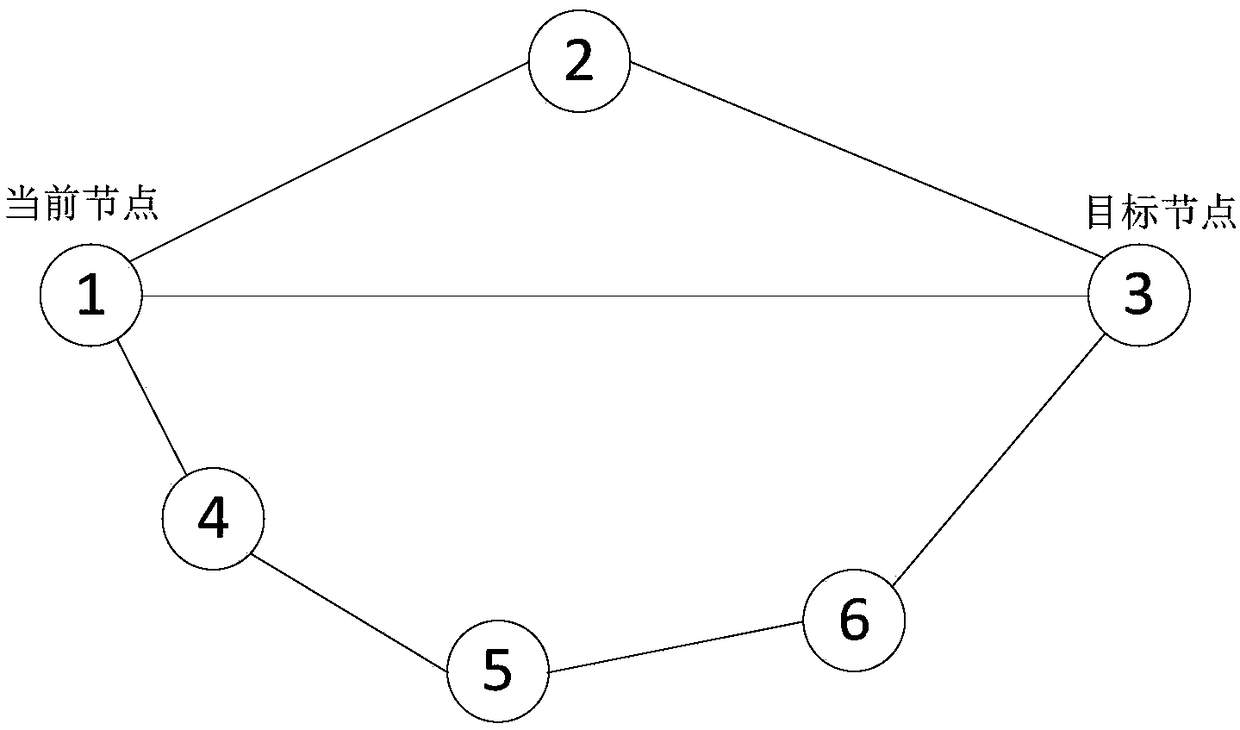
Delay constraint routing method and device based on airport information network
InactiveCN108881009AImprove packet loss rateReduce packet lossData switching networksPacket lossBackup path
The invention provides a delay constraint routing method and a delay constraint routing device based on an airport information network. The method comprises the steps of determining a first set according to connection information or distance information between each node in a network, wherein the first set comprises routing information of at least one backup path, and the routing information comprises a backup node corresponding to the backup path; aiming at each backup path in the first set, acquiring a delay factor corresponding to the backup path according to the comprehensive delay corresponding to the backup path, and a packet loss probability of a link between the current node and the backup node; and using the standby node corresponding to the standby path with the minimum delay factor in the first set as the next hop node of the current node, and sending data to be sent of the current node to the standby node. When the standby node is selected, the comprehensive delay corresponding to the backup path, and the packet loss probability of the link between the current node and the backup node are considered, so that the condition that the finally selected path is the path withrelatively small delay and stable link can be ensured, and thus the delivery rate and end-to-end delay of the network are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Interference sensing cross-layer routing method based on node sending and receiving capacity
InactiveCN103108372AImprove average end-to-end latencyImprove throughputWireless communicationPathPingPacket loss
The invention relates to an interference sensing cross-layer routing method based on node sending and receiving capacity. The method defines parameters for judging the sending and receiving capacity of a node based on an 802.11 medium access control (MAC) layer, and the two parameters can reflect that strength and weakness of interference of the periphery of the node and communication load degree born by the node, based on the fact, a MAC layer and a network layer are combined and a new routing criterion is defined, the new criterion is related to the number of surrounding active neighbor nodes, the number of data flow passing the nodes, capacity of node access channel and topology changing conditions around the nodes, and real conditions of the network can be further reflected. The interference sensing cross-layer routing method based on the node sending and receiving capacity aims to reduce interference, selects a path which is largest in bottleneck node comprehensive capacity or a path which is smallest in bottleneck link interference as far as possible, and the path which is largest in the bottleneck node comprehensive capacity or the path which is smallest in the bottleneck link interference is used as routing, and therefore average end-to-end delay and packet loss probability are reduced, and the throughput is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
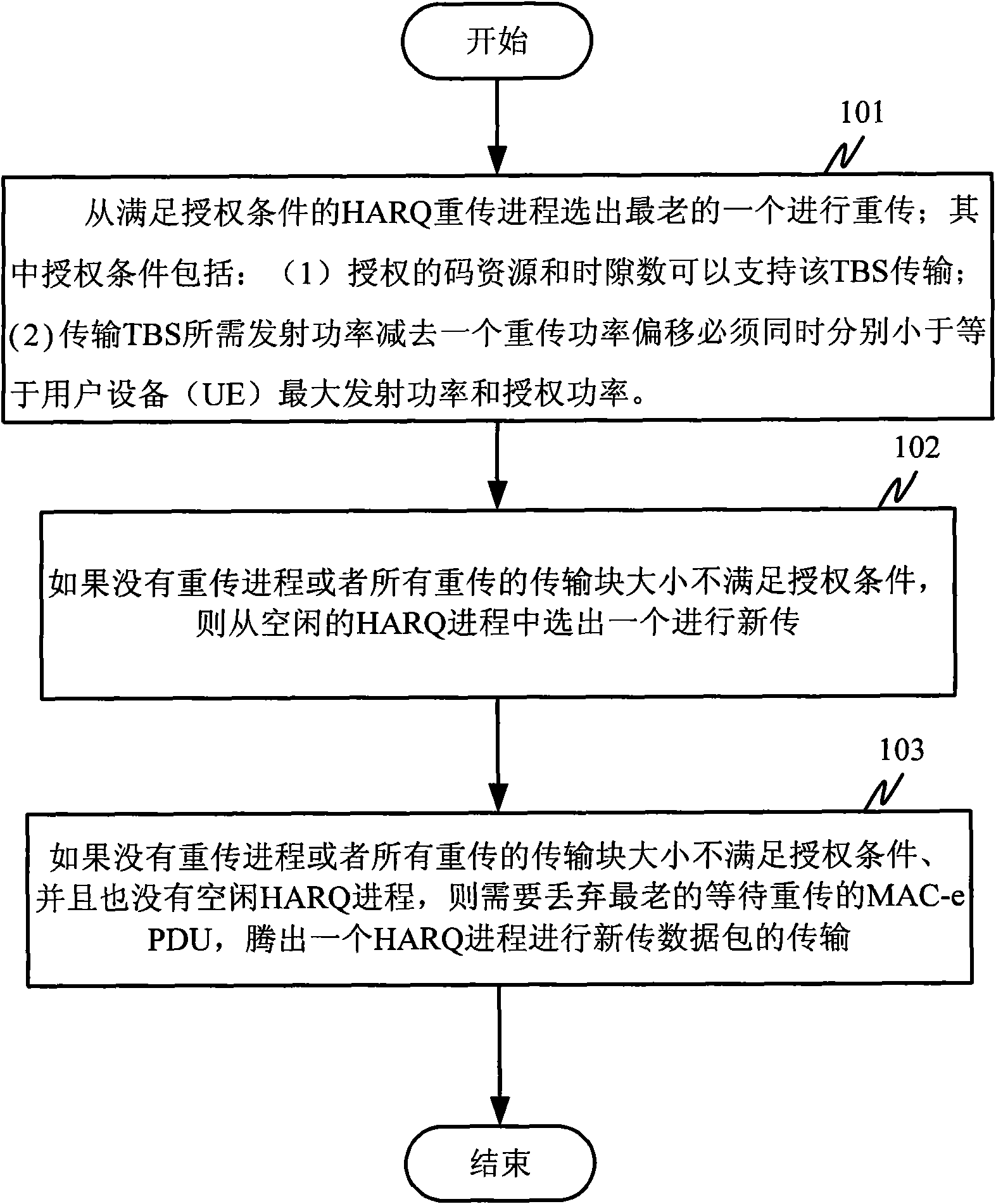
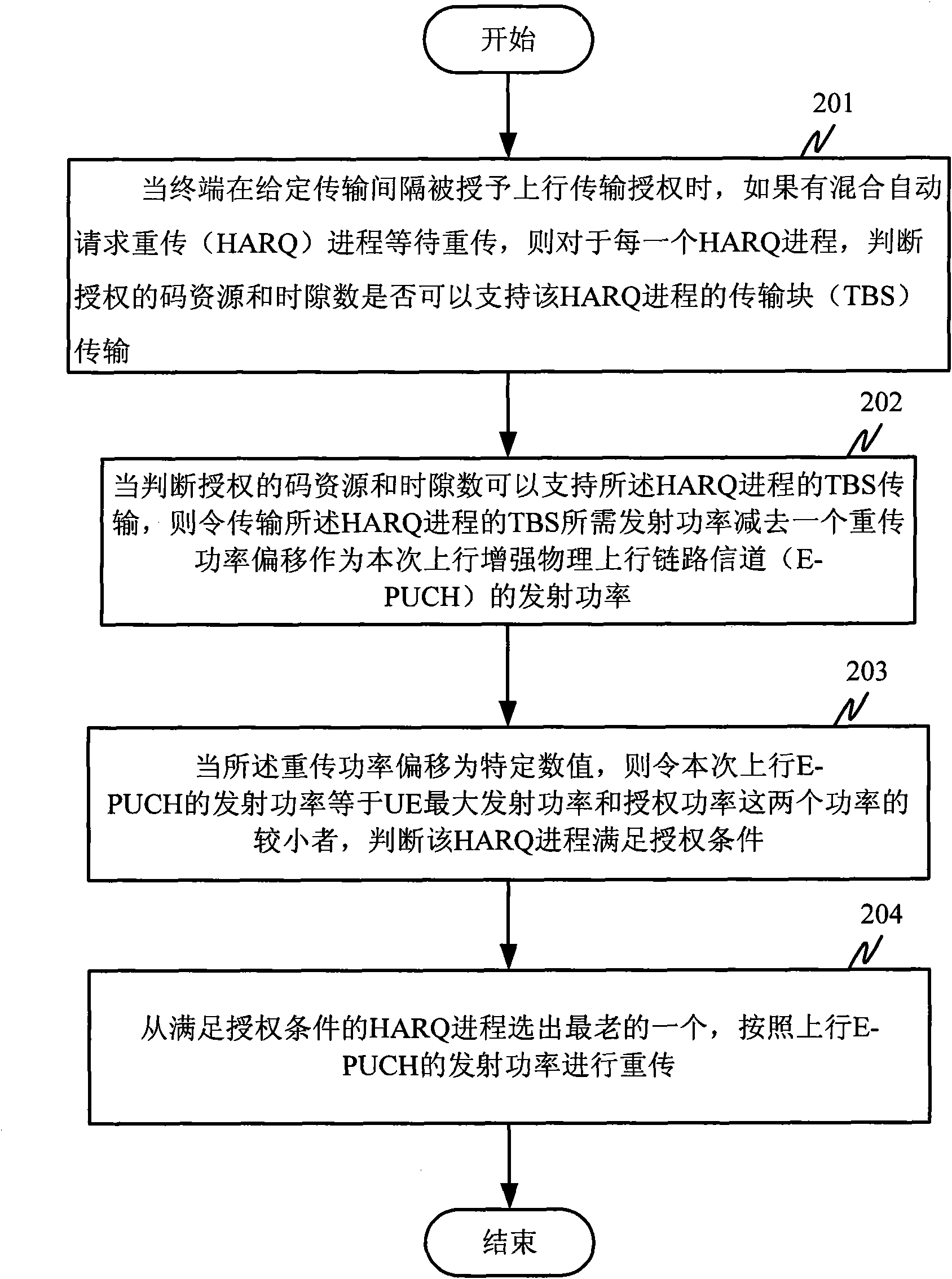
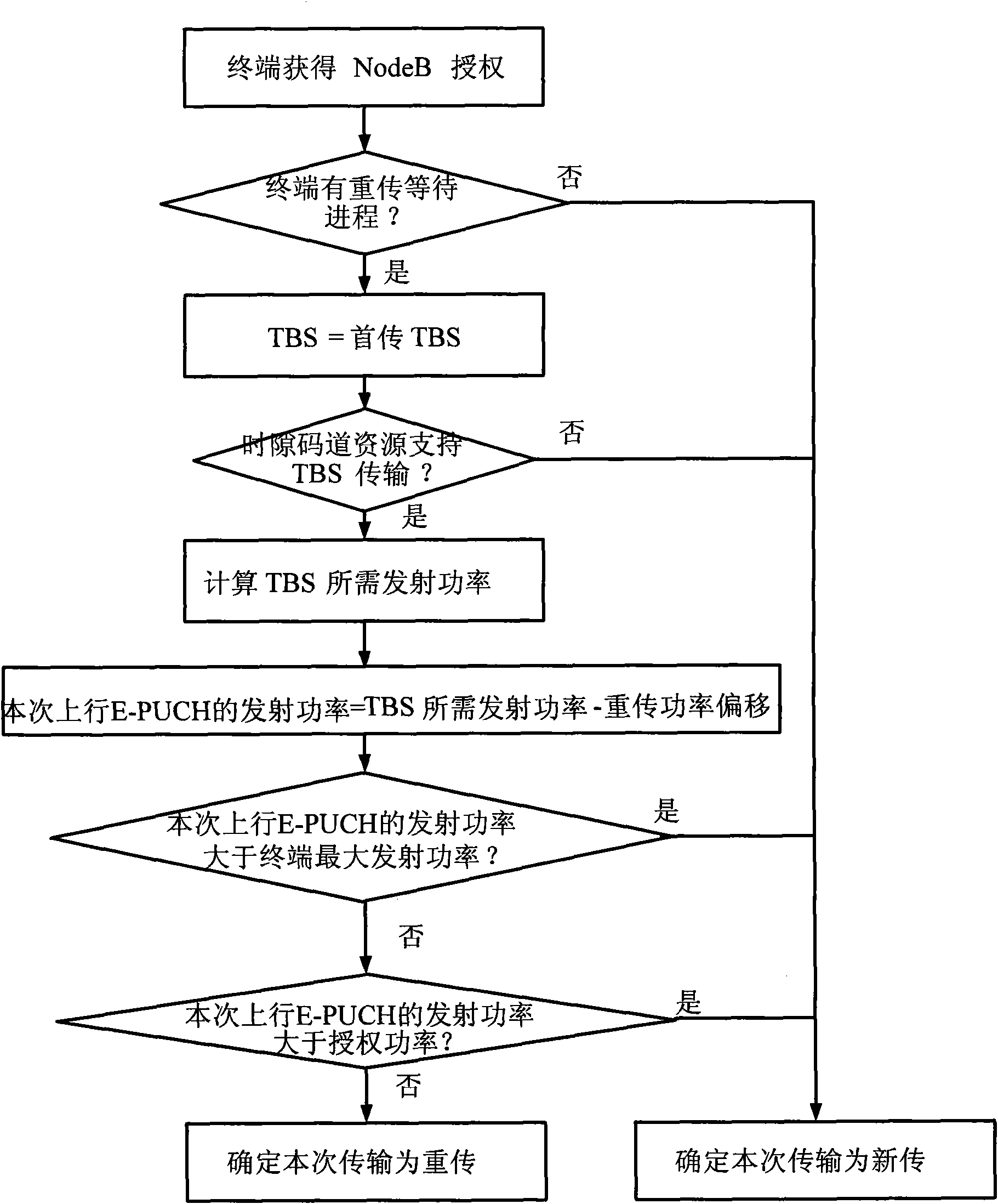
Retransmission method and device of high-speed uplink packet access terminal
InactiveCN102104464AHigh trafficImprove packet loss rateError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio transmission for post communicationTelecommunicationsUplink transmission
The invention discloses a retransmission method and device of a high-speed uplink packet access terminal; when a terminal is granted with an uplink transmission authorization at a given transmission interval, and if HARQ (hybrid automatic retransmission request) progresses wait for retransmission, for each HARQ progress, when an authorized code resource and a time slot number are judged to be capable of supporting TBS (transmission block size) transmission of the HARQ progress, a retransmission power deviation is subtracted from a transmission power needed by the transmission of the TBS to obtain a transmission power of the uplink E-PUCH (enhanced physical uplink channel); when the transmission power of the uplink E-PUCH is judged to be respectively less than or identical to the maximum transmission power and the authorized power of UE (user equipment) simultaneously, the HARQ process is judged to satisfy the authorized conditions; and the oldest HARQ progress is selected from the HARQ progresses which satisfy the authorized conditions to be retransmitted according to the transmission power of the uplink E-PUCH. The method and device disclosed by the invention are in favor of the timely retransmission of failed transmission blocks.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Aloha enhanced access method for low-orbit constellation system
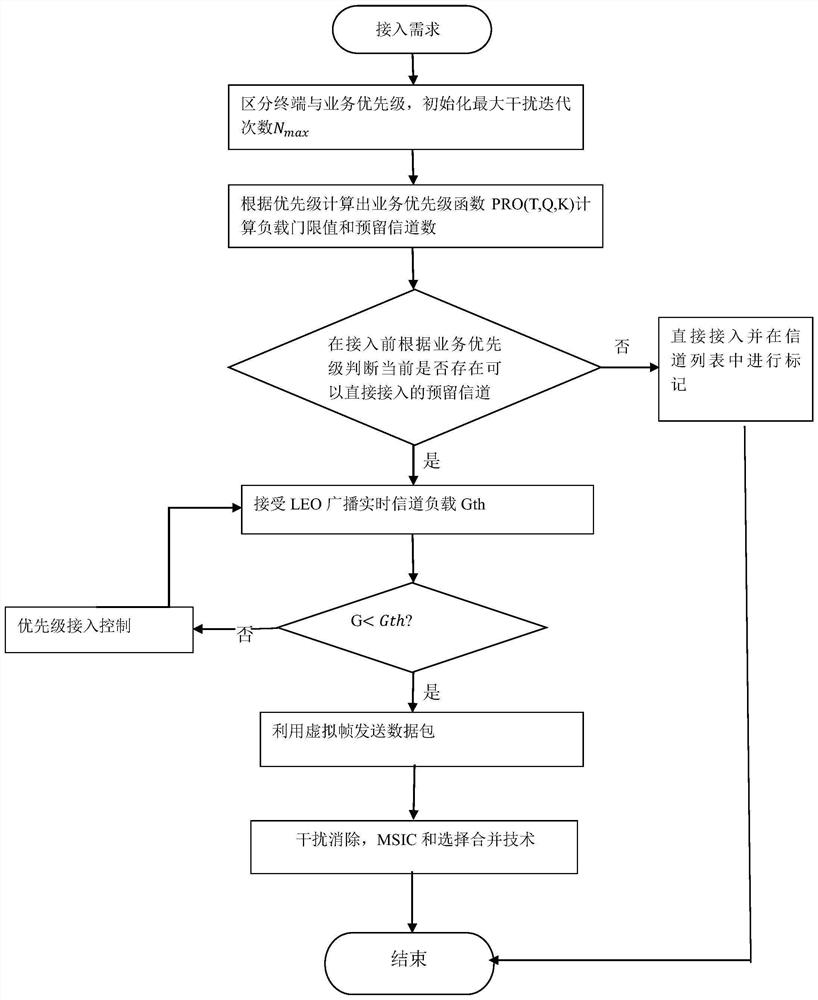
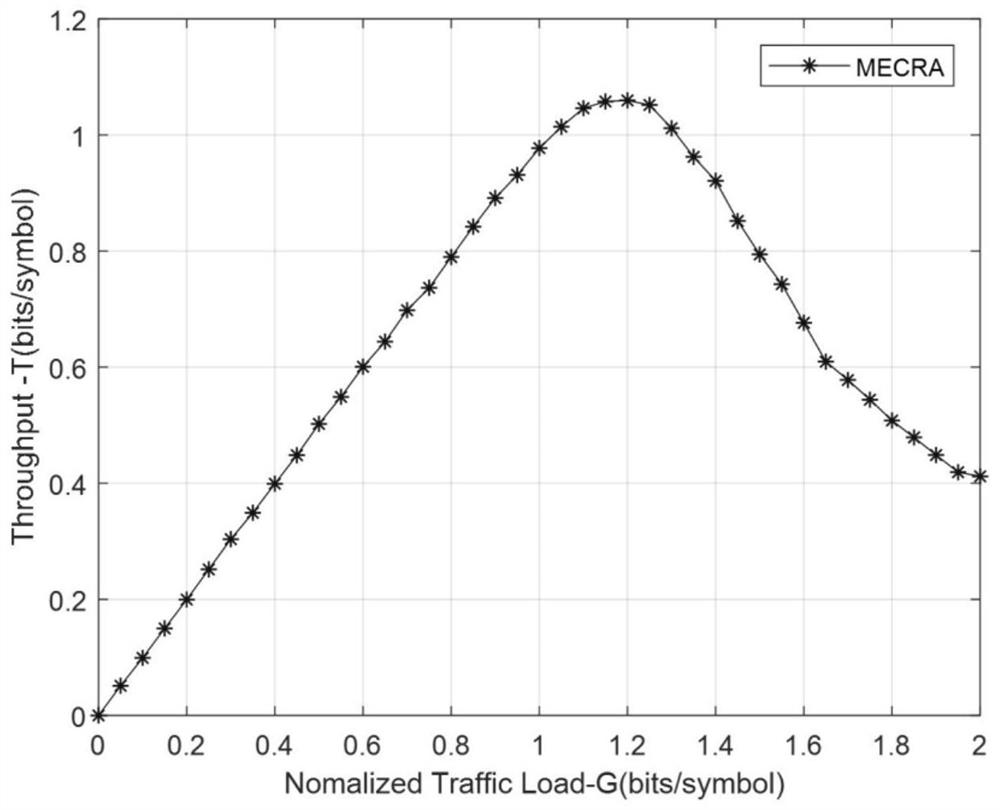
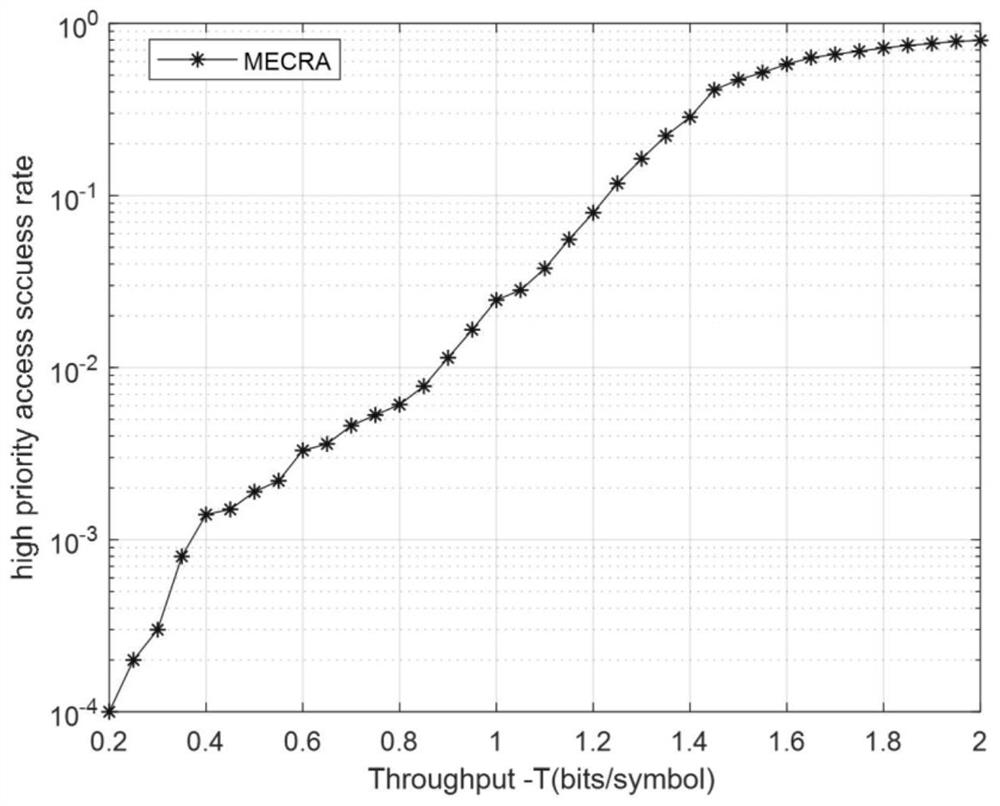
InactiveCN112312581AImprove throughputImprove packet loss rateWireless communicationTelecommunicationsInterference elimination
The invention relates to an Aloha enhanced access method for a low-orbit constellation system, belongs to the field of satellite communication, and is used for solving the problem of quick access whena high-dynamic terminal communicates with a new generation of low-orbit constellation system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a system satellite access system model; reserving different numbers of channels for users with different priorities of the related high-dynamic terminals in advance; when the user terminal has an access demand, calculating the specific moment of sending the data packet by utilizing access control; when the data packet is sent, enabling the user terminal to divide a channel into time slots by utilizing a local clock and randomly puts thedata packet into the time slots to be sent; finally, utilizing the characteristic that the user terminal is covered by multiple satellites of the system in the communication process, wherein after receiving the data packet, each receiving end satellite forwards the data packet to the low-orbit constellation system for interference elimination until all the data packets are successfully decoded orthe maximum number of iterations is reached. According to the method disclosed in the invention, the throughput rate and packet loss rate indexes of the system can be optimized, the resource utilization rate is improved, and the first access success rate of the high-dynamic terminal can be optimized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Load balancing method based on graph convolutional neural network and deep reinforcement learning
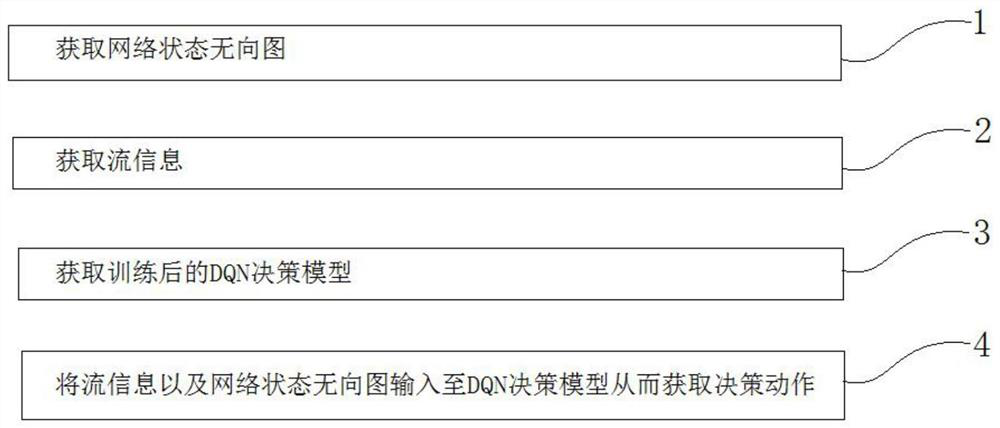
ActiveCN113572697AImprove performanceLoad balancingNeural architecturesData switching networksDecision modelUndirected graph
The invention discloses a load balancing method based on a graph convolutional neural network and deep reinforcement learning. The load balancing algorithm based on the graph convolutional neural network and deep reinforcement learning comprises the following steps: acquiring a network state undirected graph, wherein the network state undirected graph comprises a characteristic matrix of switches and data link load weight information between the switches; obtaining stream information; obtaining a trained DQN decision model; and inputting the flow information and the network state undirected graph into the DQN decision model to obtain a decision action. According to the method, deep reinforcement learning and the graph convolutional neural network are combined and applied to a load balancing algorithm, so that the model can make a decision according to state information, the topological structure of the network is considered as a decision factor, the model can make a decision according to a more comprehensive network state, and the decision performance of the model is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Deployment scheme of wireless multi-hop network buffer queue
InactiveCN105933243ASolve the large amount of dataEmbody relevanceData switching networksData transmissionEngineering
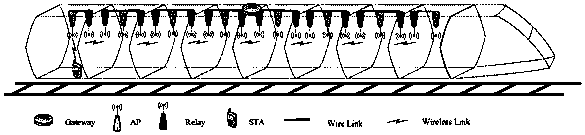
The present invention discloses a deployment scheme of a wireless multi-hop network buffer queue. The deployment scheme is applied to a train car WiFi system, a train central deployment gateway node and train and ground communication equipment are used for the communication with a ground base station BS, each car is provided with one AP for bearing the access needs of multiple users in the car, the cars are wirelessly connected by using a wireless relay, and the AP in the car and a car relay are connected in a wired way. By the setting problem of the buffer queue length of each hop of data transmission in a wireless multiple-hop network, under the premise that a system satisfies a maximum end to end delay, the system packet loss rate is reduced as much as possible, and thus the balance between the system resource configuration and system acceptable end to end QoE is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
OBS/OPS network performance optimizing method based on virtual node
InactiveCN1741498AImprove latencyImprove packet loss rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionQuality of serviceTime delays
A method for optimizing OBS / OPS network performance based on virtual node includes combining a numbers of physical nodes on service shortest route to be one virtual node according to network service flow rate of last statistic time section , setting special wavelength to connect head and tail physical node in virtual node to let data packet jump over at least two physical nodes with only one time of processing when data packet is via this virtual node for lowering end to end time delay and packet lost rate in network .
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Supporting node mobility method based on node speed
InactiveCN101800592AFirmly connectedImprove connectivityEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementEnergy consumptionLine segment
The invention discloses a supporting node mobility method based on node speed, a new neighbor node is obtained through judging whether a mobile synchronization frame MSYNC which is sent by a mobile node is replied or not by the method, the distance between the new neighbor node and the mobile node is obtained by the new neighbor node by receiving the strength of a MSYNC signal, meanwhile, whetherreplying MACK or not to the mobile node is determined through a judgment condition; after the judgment condition is met, the time interval for sending the MSYNC next time by the mobile node is calculated by the new neighbor node through the static neighbor information of the new neighbor node and the state information of the mobile node. The judgment condition is that: an included angle of a directed line segment and the moving direction of a mobile node m is bigger than 90 degrees, and the distance between the mobile node m and a new neighbor node n is less than a transmission range R. The energy consumption which is caused by frequent periodicity neighbor searching is avoided by the method in the invention, the scheduling information of a new cluster is quickly obtained when the mobile node moves among clusters, and mass lost packages which are caused by the differences of period scheduling are reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
5G core network equipment and method supporting PDN link optimization
ActiveCN113068204AImplement quality optimization featuresHigh bandwidthWireless communicationCore networkComputer security
Disclosed are 5G core network equipment and method supporting PDN link optimization, which relate to the technical field of mobile communications, are implemented on the basis of an AMF entity, a UDM entity, a PCF entity, an SMF entity, a UPF entity and a remote PDN gateway. The specific process comprises: a UE sending a session establishment request carrying DNN information to the AMF entity; the AMF entity selecting an SMF entity according to the request; the SMF entity initiating a session policy request and requesting session policy information of a target session from a PCF entity; the PCF entity issuing session policy information to the SMF entity; the SMF entity judging whether the requested DNN information supports an N6 interface MPTCP proxy or not, if yes, the SMF entity continuing to judge whether the session policy information carries a correct MPTCP proxy working mode and priority or not, and initiates a session establishment or modification process carrying an MAR rule cell to the UPF entity; the UPF entity analyzing the MAR rule cell and configuring an MPTCP proxy entity function; and after the session is established, the UPF entity successfully establishing MPTCP proxy connection with the remote PDN gateway. According to the invention, a plurality of PDN link quality optimization functions can be realized.
Owner:INSPUR SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD
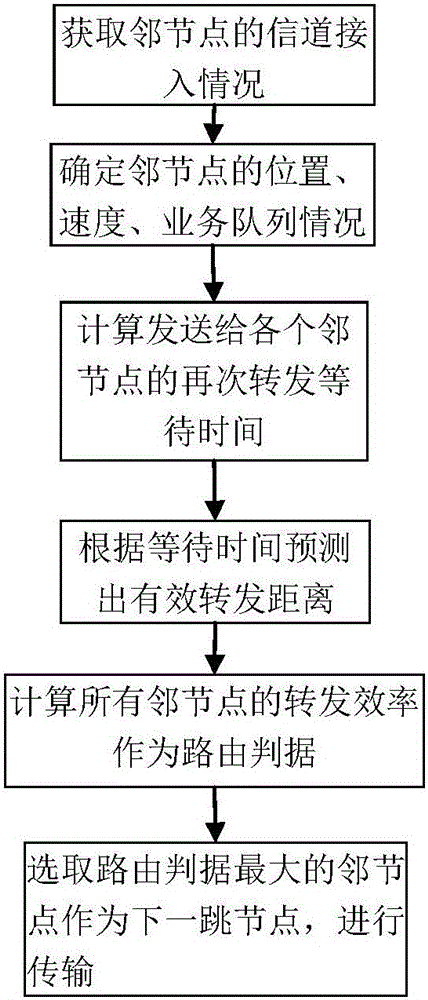
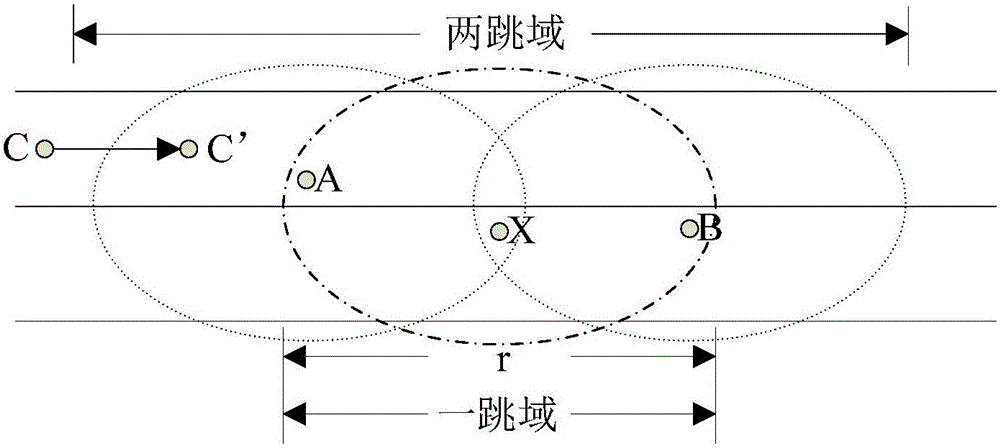
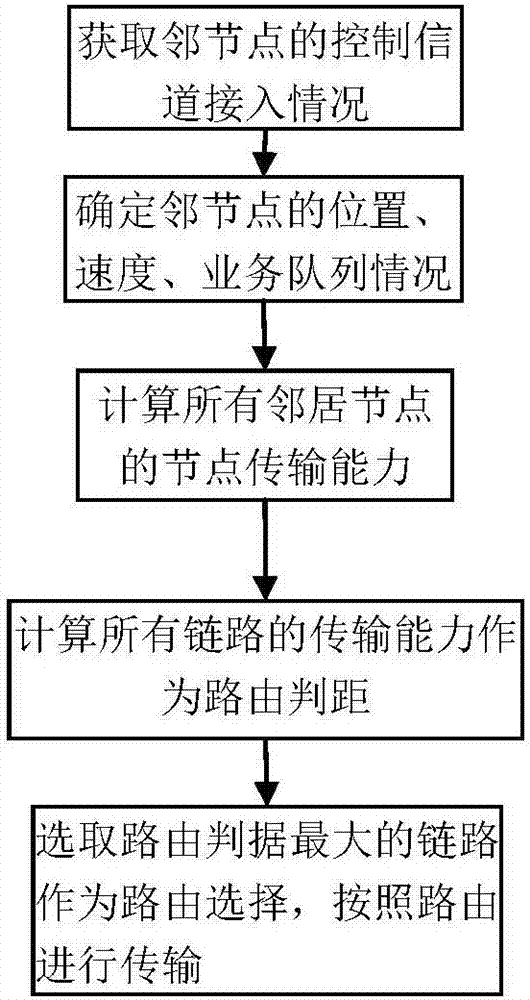
Cross-layer vehicular network routing method based on forwarding efficiency prediction
ActiveCN105873165AImprove forwarding efficiencyImprove average end-to-end latencyData switching networksHigh level techniquesEngineeringControl channel
The invention discloses a cross-layer vehicular network routing method based on forwarding efficiency prediction. According to the method, through combination of an existing MAC layer access protocol, by taking transmission failure probability resulting from channel fading into consideration, an effective transmission distance of nodes in single-time transmission is defined. Moreover, through combination of time slot distribution conditions of multi-channel MAC layers access on a control channel and the data processing capabilities of the nodes, the waiting time delay of single-time transmission is defined. A forwarding frequency of single-time forwarding is defined by using the two parameters. Through prediction of forwarding efficiencies of all selectable nodes in a next hop and routing selection by taking unit time transmission distance optimization as a strategy, forwarding can be carried out by using the nodes more effectively. The method aims at improving the effectiveness of each time of forwarding; production of the low efficiency forwarding is reduced; the average end to end time delay is reduced; and a packet loss rate is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
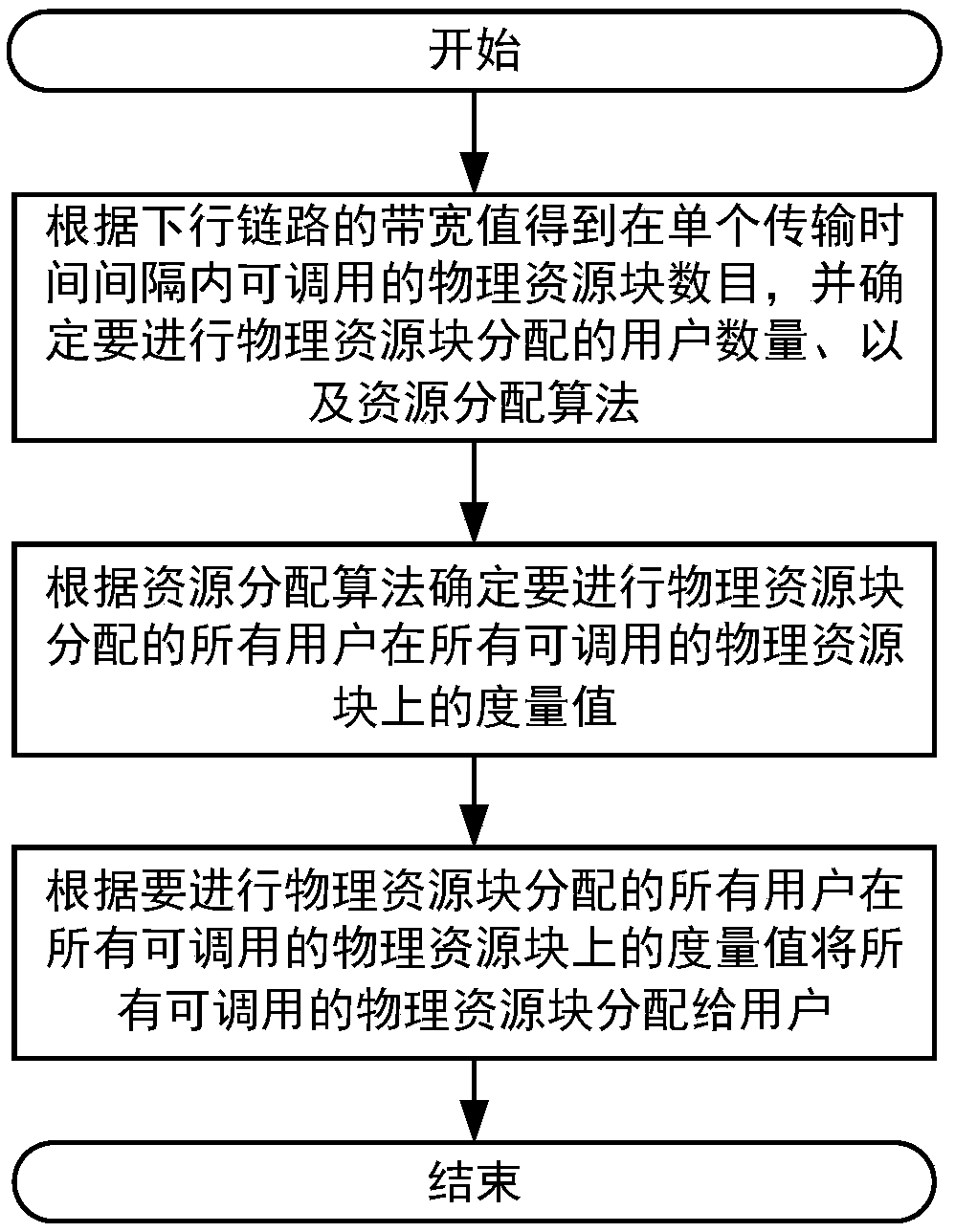
LTE downlink scheduling method based on throughput capacity optimization
ActiveCN108738158ALarge amount of data transferSolve technical issues that reduce the amount of actual data transfersCriteria allocationSignal allocationResource blockAllocation algorithm
The invention discloses an LTE downlink scheduling method based on throughput capacity optimization. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of acquiring the quantity of callablephysical resource blocks within a single transmission time interval according to a bandwidth value of a downlink, determining the quantity of users to be subjected to physical resource block distribution and a resource distribution algorithm, determining measures of all users to be subjected to physical resource block distribution on all the callable physical resource blocks according to the determined resource distribution algorithm, and distributing all the callable physical resource blocks to the users according to the measures of all the users to be subjected to physical resource block distribution on all the callable physical resource blocks. According to the method provided by the invention, the technical problem that the existing LTE downlink scheduling method does not deeply consider mutual influence factors of the distributed physical resource blocks during an actual data transmission process, and thus the actual data transmission quantity of the user is reduced during the physical resource block distribution process can be solved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY
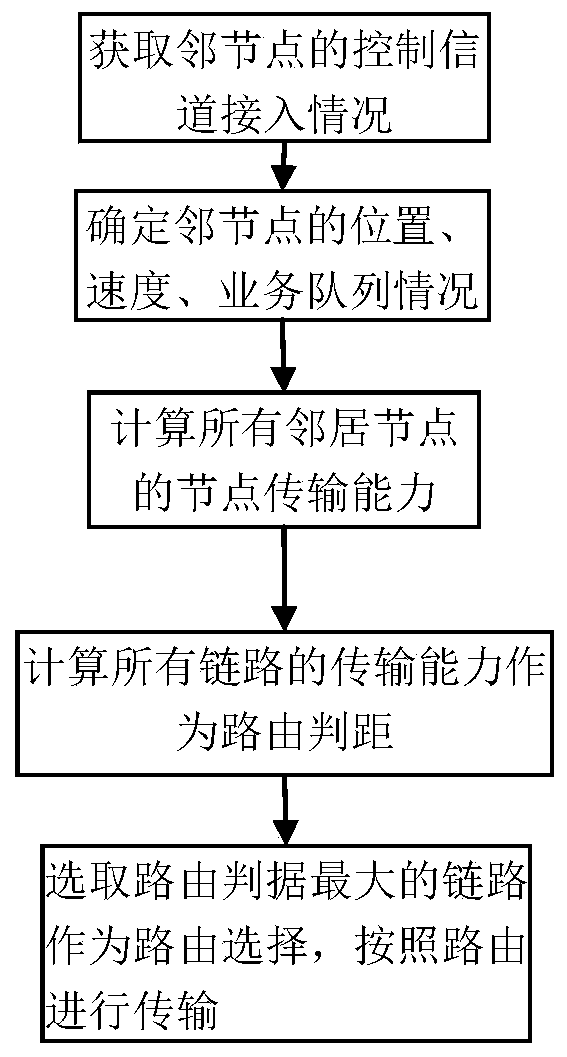
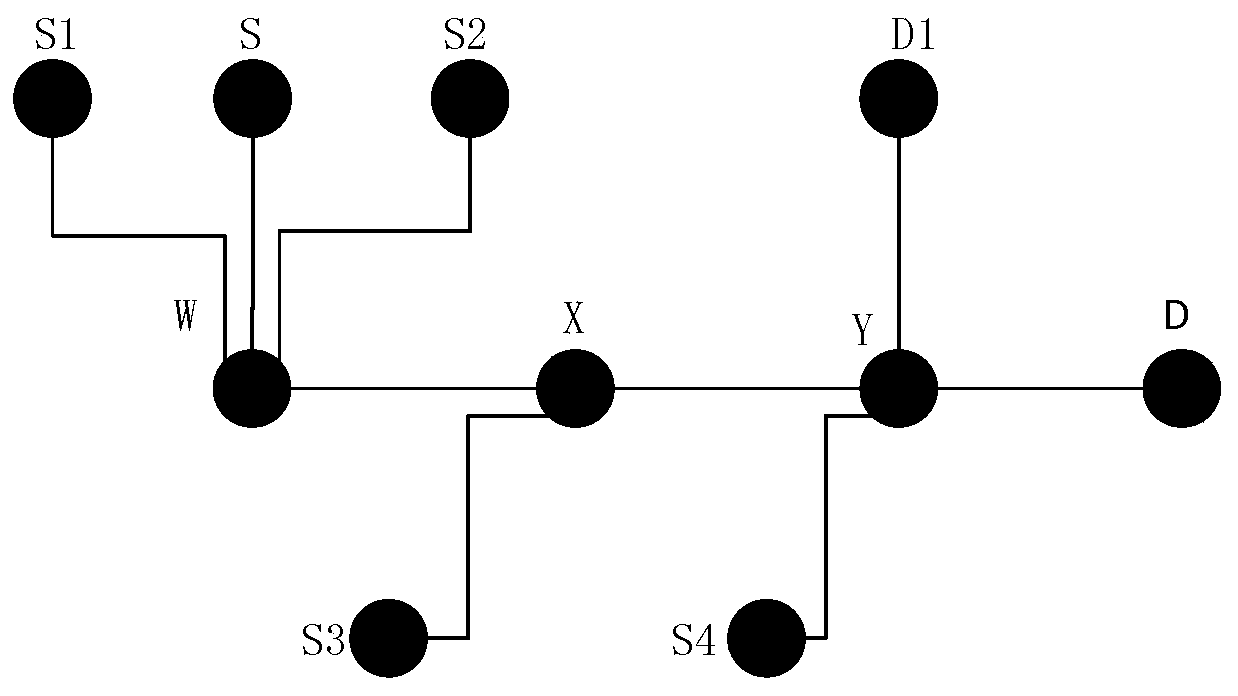
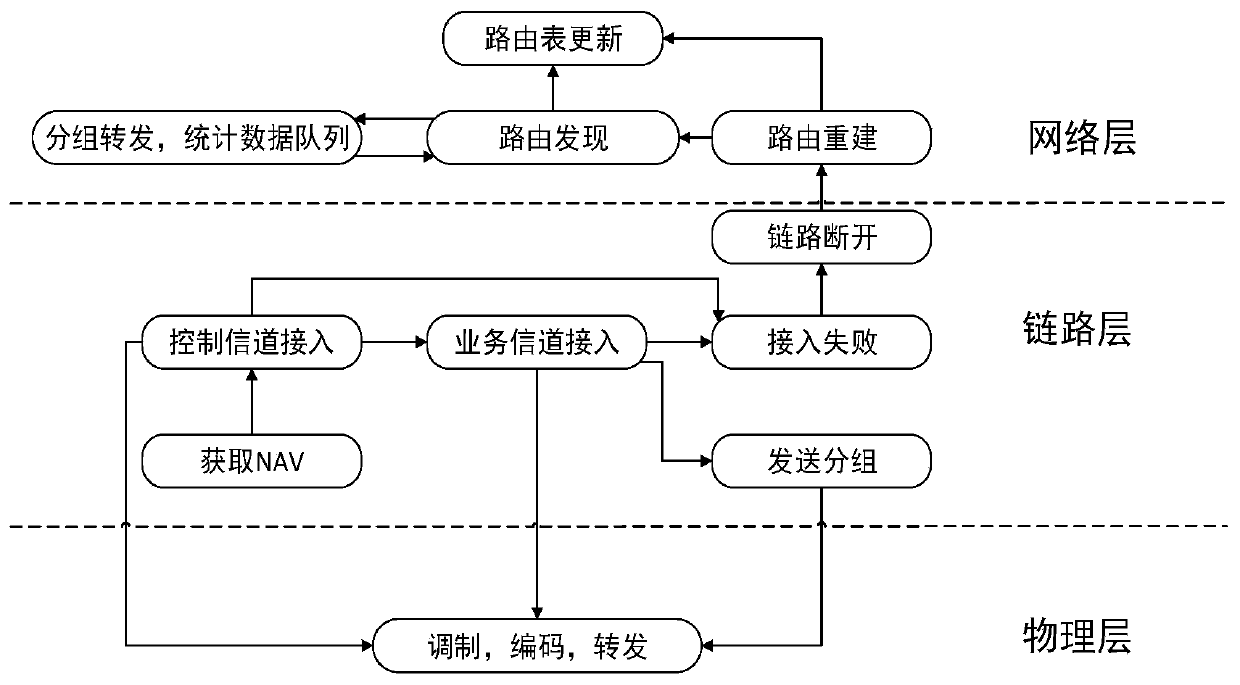
Cross-layer vehicle network routing method based on link transmission capacity
ActiveCN107105388AImprove stabilityImprove average end-to-end latencyNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesPacket lossProtocol design
The present invention provides a cross-layer vehicle network routing method based on a link transmission capacity. In a vehicle network city scene, the method combines an existing MAC layer access protocol to reflect transmission effectiveness between nodes through defining and representing parameters of the communication capacity between the nodes through considering the transmission failure probability generated by channel fading and neighbor node channel usage condition; and on this basis, a new routing metric suitable for city scenes is given to realize the protocol design of a network layer and an MAC layer so as to more effectively utilize the nodes for forwarding. The cross-layer vehicle network routing method based on the link transmission capacity takes the improvement of the link stability as an objective and reduces the number of times of repeatedly establishing a route as far as possible so as to reduce the average end-to-end time delay and reduce the packet loss probability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
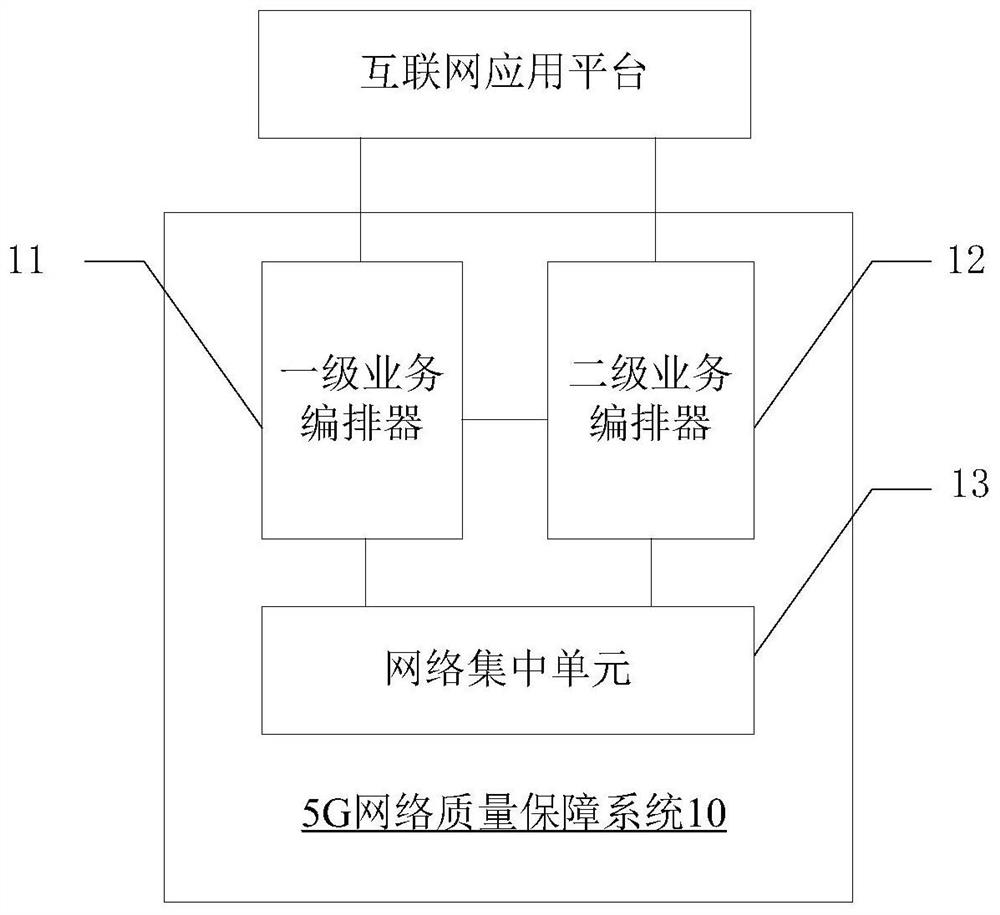
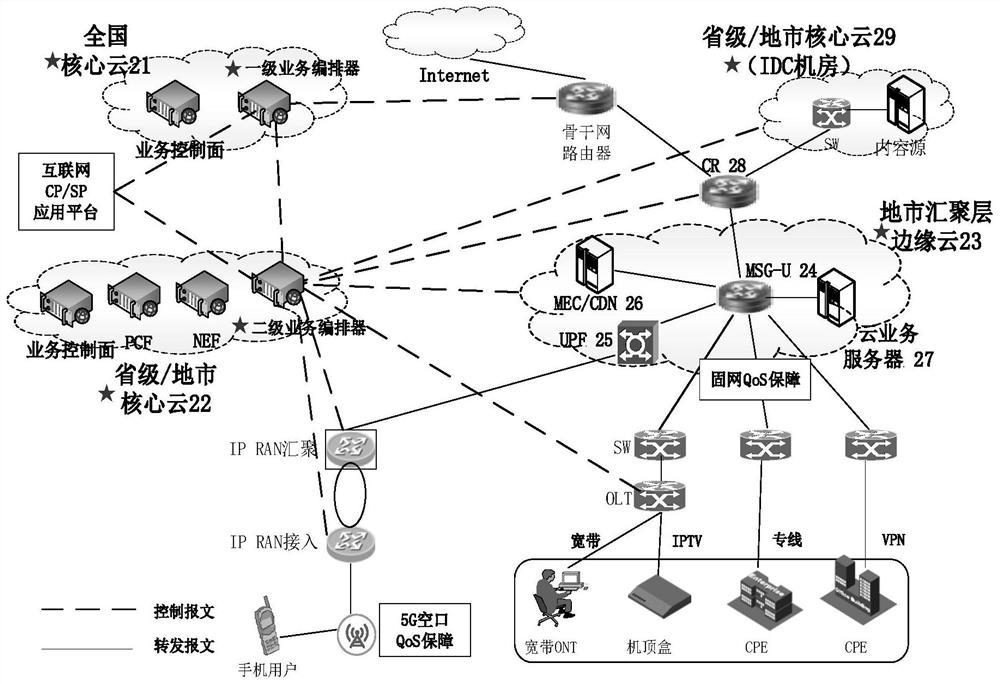
5G network quality guarantee system and method
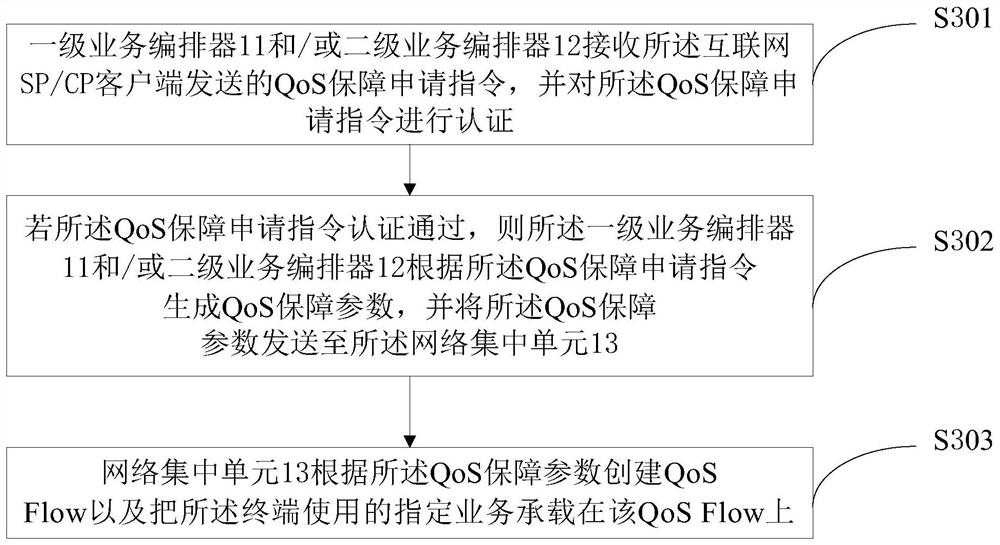
PendingCN114079932AImprove latencyImprove packet loss rateNetwork traffic/resource managementQos quality of serviceThe Internet
The invention provides a 5G network quality guarantee system and method. The system comprises a first-level service choreographer disposed on a nationwide core cloud, a second-level service choreographer disposed on a provincial / prefecture-level core cloud, and a network concentration unit disposed on the provincial / prefecture-level core cloud and a convergence layer edge cloud. The method comprises the steps that a QoS guarantee application instruction sent by an Internet SP / CP client is received by setting the first-level service choreographer and / or the second-level service choreographer, and the QoS guarantee application instruction is authenticated; if the QoS guarantee application instruction passes authentication, the first-level service choreographer and / or the second-level service choreographer generate / generates QoS guarantee parameters according to the QoS guarantee application instruction, and sends the QoS guarantee parameters to the network concentration unit; and the network concentration unit provides a QoS guarantee strategy for a terminal according to the QoS guarantee parameters. According to the invention, a lightweight quality guarantee system which is low in cost, simple and easy to implement and a network quality guarantee scheme which is rapidly deployed are provided, and the quality of service of a network is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
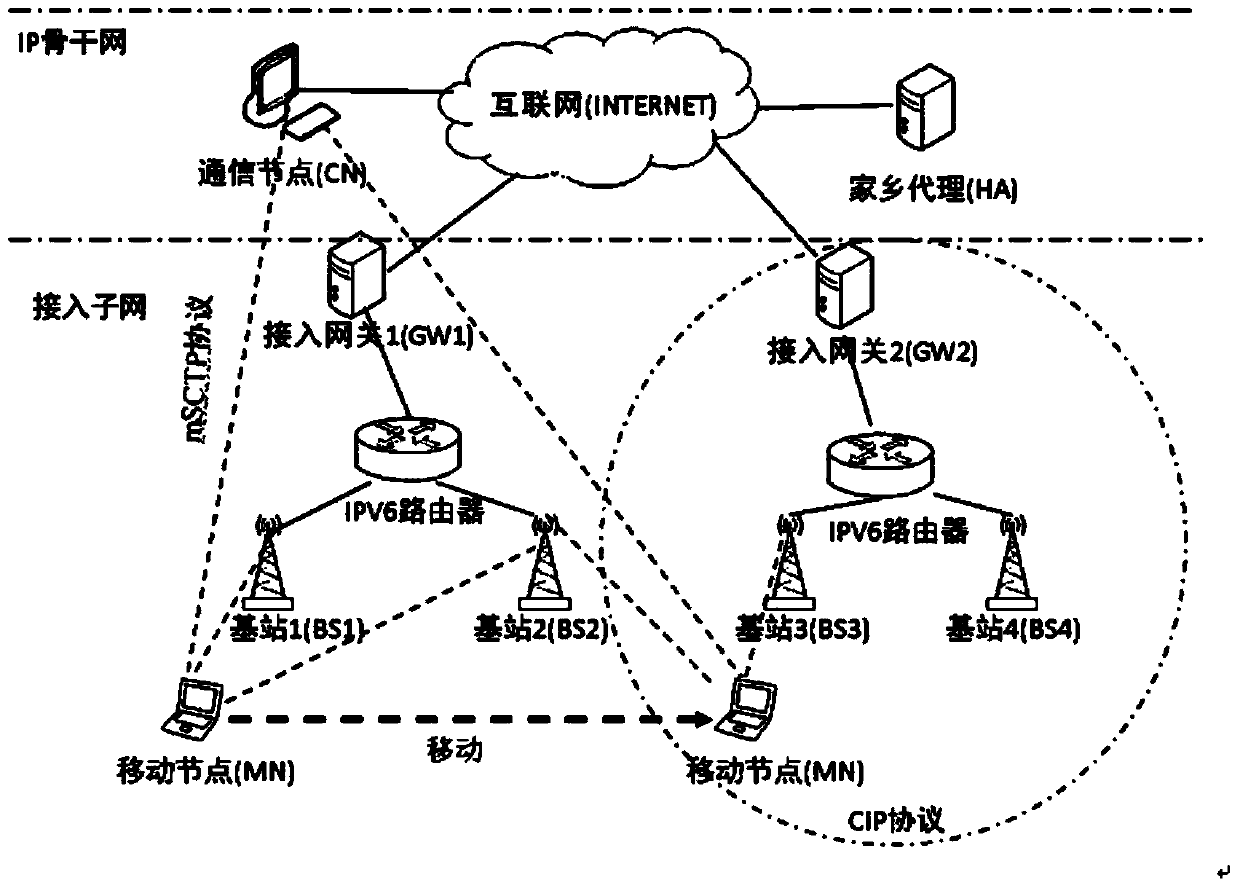
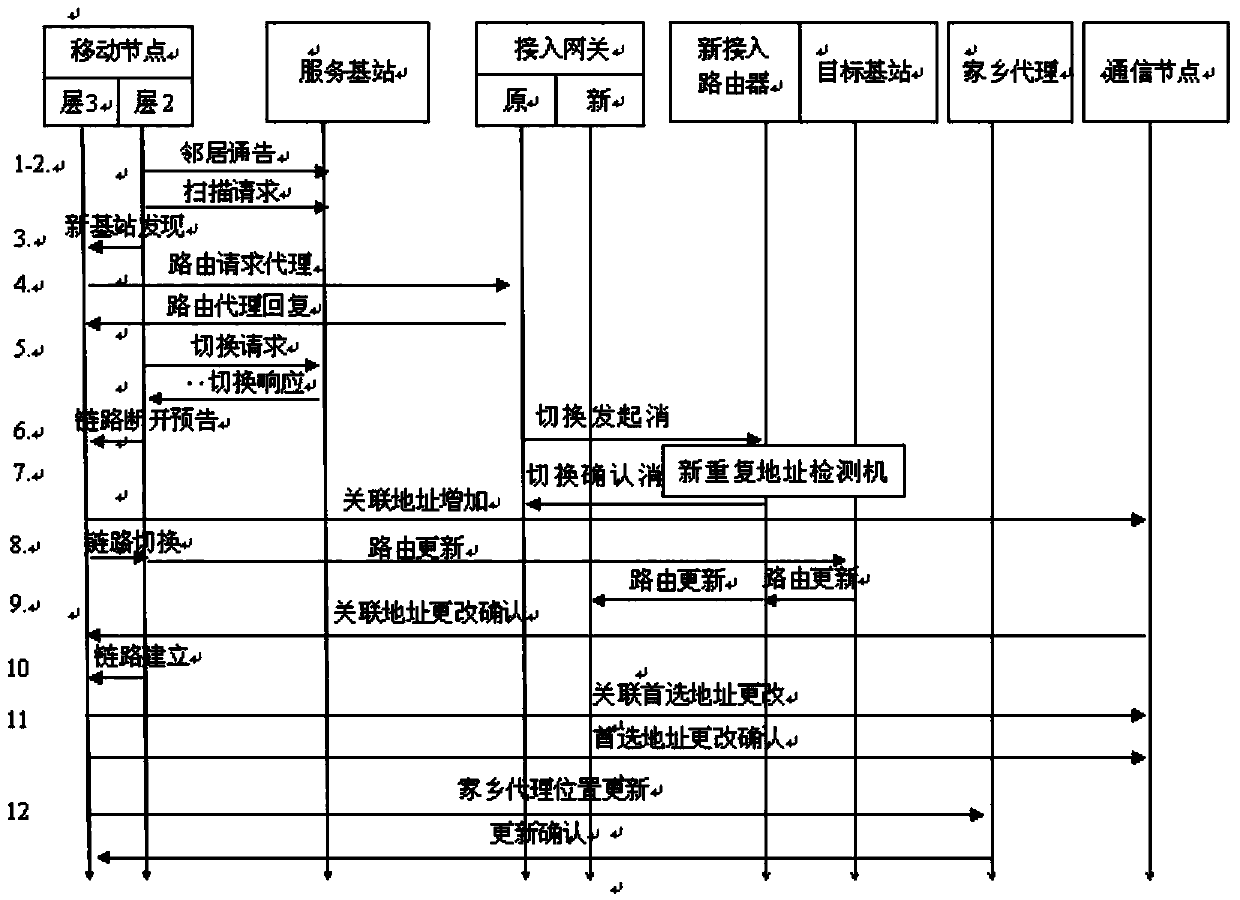
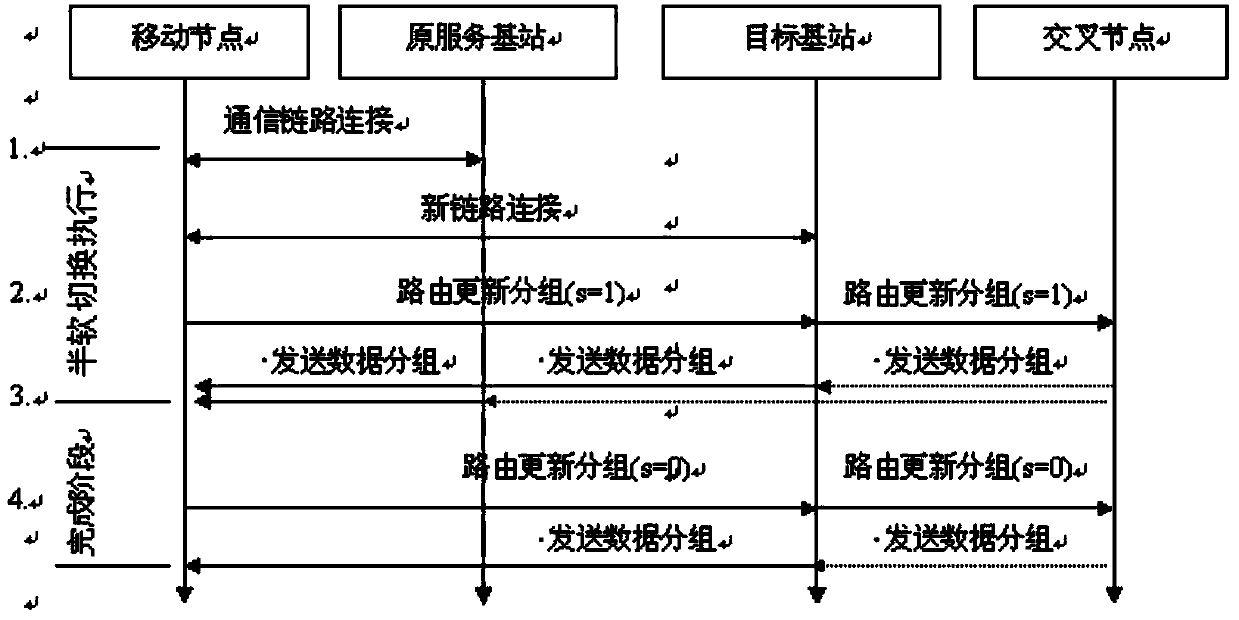
Hybrid fast handover (HFH) method adapted to mobile worldwide interoperability for microwave access (WiMAX) network
The invention discloses a hybrid fast handover (HFH) method adapted to a mobile worldwide interoperability for microwave access (WiMAX) network. According to the HFH method, fast handover between the movement of mobile sites in sub-networks and the movement of the mobile sites among the sub-networks is realized. The HFH method has the advantages that on the basis of fast handover over hierarchical mobile internet protocol version 6 (F-HMIPv6) handover, by the combination of a cellular internet protocol (CIP) and a mobile stream control transmission protocol (mSCTP), signaling overhead and handover delay during register updating and tunnel establishment of a home agent can be effectively reduced. By the adoption of a new fast duplicated address detection (F-DAD) mechanism, the handover delay caused by DAD can be effectively reduced, and by the introduction of a service scheduling buffer mechanism, packet loss in a handover process can be effectively reduced. The HFH method can be applied to a third-generation (3G) mobile WiMAX network and a fourth-generation (4G) long term evolution (LTE) network.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
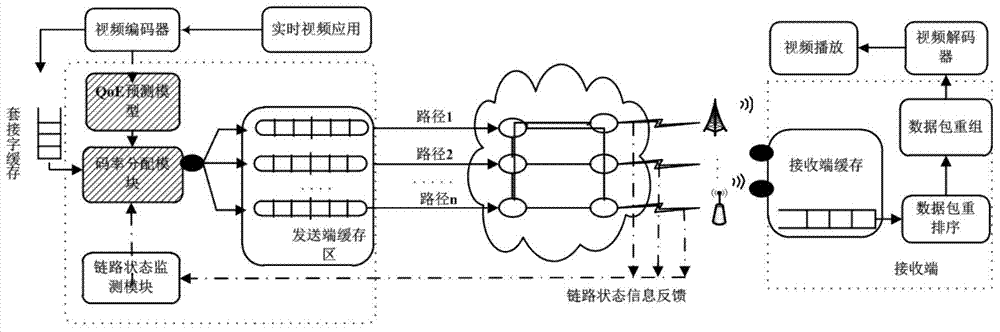
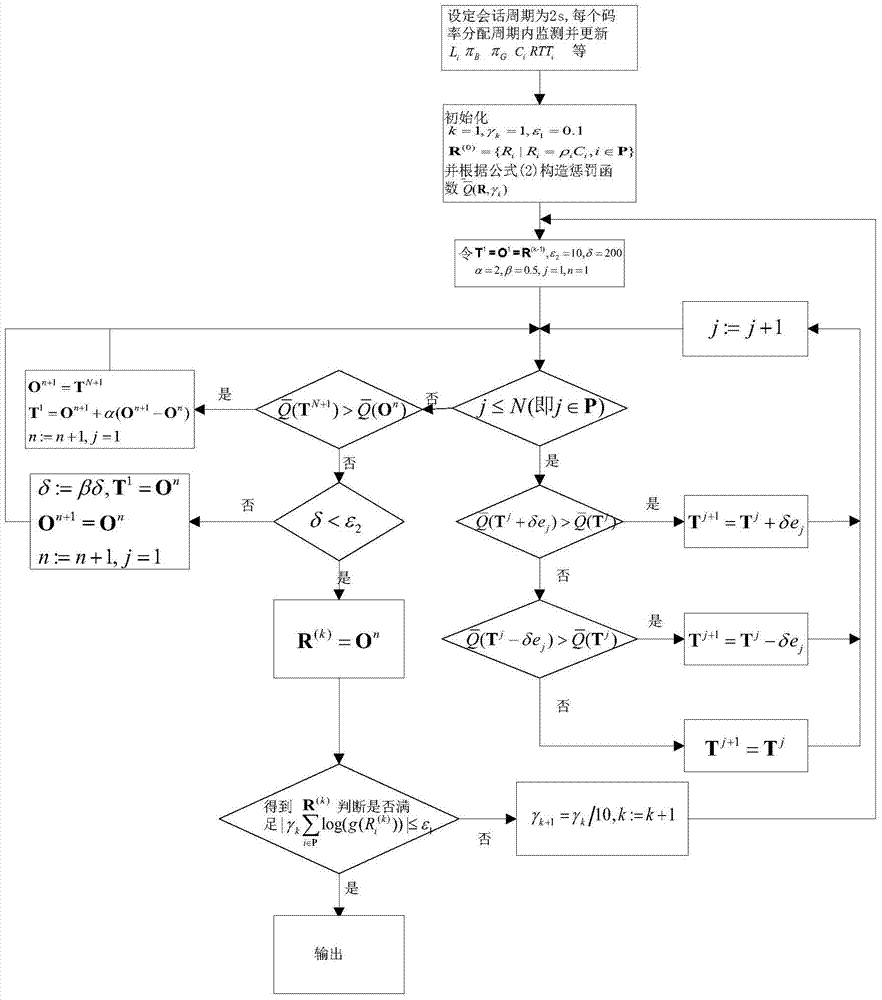
User experience quality-oriented code rate allocation method
InactiveCN104506453AGreat practicabilityImprove video qualityDigital video signal modificationSelective content distributionAcceleration factorTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a user experience quality-oriented code rate allocation method, which comprises the following steps of monitoring and updating a parameter in a code rate allocation session , setting the time length of the code rate allocation session, and performing initialization; structuring a penalty function, and executing subsequent steps on each specific gammak; initializing an intermediate variable T<1>=0<1>=R<k-1>, initializing a convergence standard epsilon2, a step length delta, an acceleration factor alpha and a retarding factor beta for the kth iteration, and setting values of iteration variables j and n to be 1; when j is less than or equal to N, if a condition shown in the original document is met, determining that T<j+1>=T<j>+deltaej, if a condition shown in the original document is met, determining that T<j+1>=T<j>-deltaej, otherwise determining that T<j+1>=T<j>; setting j:=j+1, and repeating the step until j is more than N; when j is more than N, if a condition shown in the original document is met, 0<n+1)=T<N+1), T<1>=0<n+1>+alpha(0<n+1>-0<n>, n:=n+1 and j=1, and if delta is smaller than epsilon2, returning R<(k)>=0<n>, detecting whether the returned R<(k)> is consistent with the convergence standard shown in the original document, and if the returned R<(k)> is consistent with the convergence standard, returning R<(k)>, and allocating the obtained optimal R<(k)> to each path.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
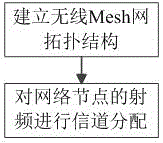
Channel allocation method in multi-radio frequency multi-channel wireless Mesh network
ActiveCN106170153AImprove throughputImprove latencyWireless communicationWireless mesh networkStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses a channel allocation method in a multi-radio frequency multi-channel wireless Mesh network. The channel allocation method comprises steps that a wireless Mesh network topological structure comprising orthogonal channels used for network allocation and a neighbor node set of various nodes are established; the channel allocation of the radio frequencies of the network nodes is carried out, and one node of the network is selected, and is set to be a current node, and by considering the current node and the channel allocation condition of the radio frequency of every node in the neighbor node set of the current node, different processing ways are selected according to the possible scene states of the two nodes, and therefore the channel allocation corresponding to different radio frequencies of all of the nodes is determined sequentially. The new channel allocation method in the multi-radio frequency multi-channel wireless Mesh network is advantageous in that objects of better inhibiting inter-channel interferences and improving the integral performance of the wireless Mesh network are realized.
Owner:陕西尚品信息科技有限公司
Self-organizing network medium access control method based on reinforcement learning
ActiveCN111601398ASimplify the interaction processEasy to implement interactive processWireless communicationNetwork mediaMedia access control
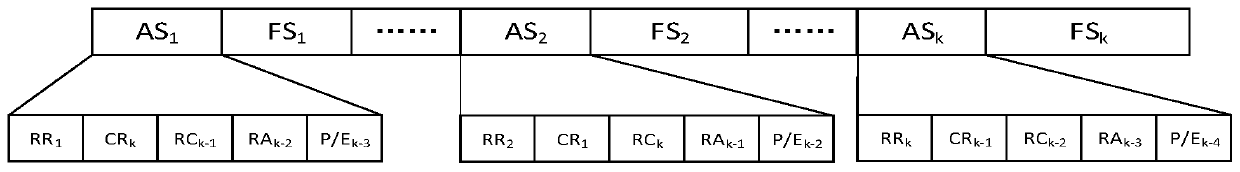
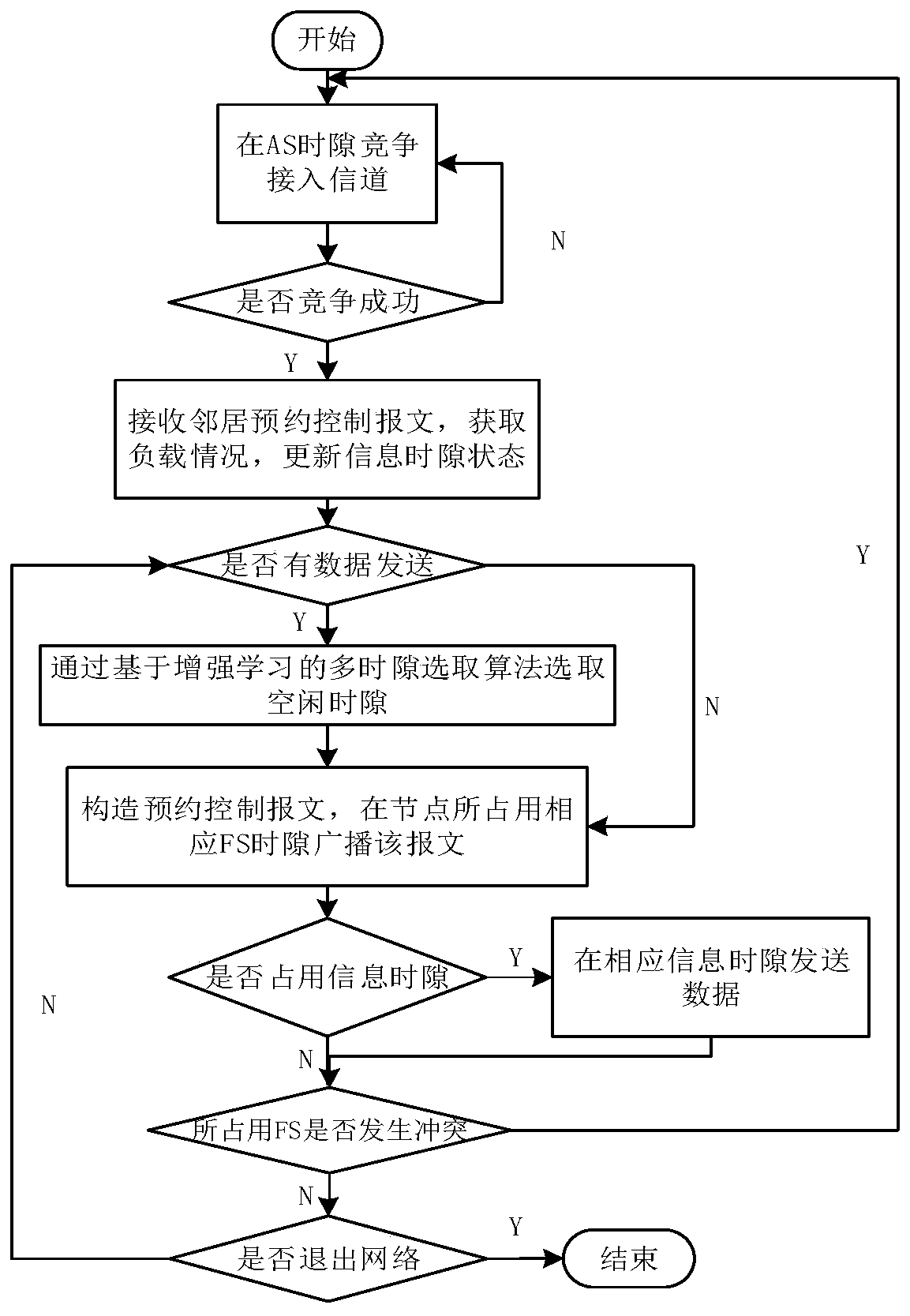
The invention discloses a self-organizing network medium access control method based on reinforcement learning, is applied to the field of wireless networks, and aims at solving the problem that in the prior art, distributed network node multi-time-slot selection in a dynamic TDMA medium access control method is generally not considered. According to the invention, a time slot interleaving schemeis adopted in the frame structure design, so that the requirement of the media access control method on the packet response delay performance of hardware equipment is looser; meanwhile, a multi-time-slot reservation mechanism is adopted, so that the network node only needs to send a control frame once and reserve information time slots of a plurality of subsequent periods in each period, the interaction process is simple and easy to implement, and the control overhead is low; and the selection probability of each section of time slot is adaptively adjusted based on a multi-time slot selectionalgorithm of reinforcement learning, and a more optimized time slot selection strategy is generated, so that the time slot competition conflict is reduced, the time slot allocation efficiency is improved, and the competition success rate, the transmission bandwidth, the transmission time delay, the packet loss rate and other performances of the medium access control method are further optimized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Outburst convergence control method, and corresponding device and communication device
InactiveCN101212389BAdjust in timeAvoid Continuous Excessive VariationsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksComputer scienceCommunication device
The invention discloses a controlling method for a burst assembly, a corresponding device and a communication equipment thereof. A core of the method and the device in the invention includes the following steps: by comparing an assembly time with a time threshold set in advance, a change trend of carriers in a buffer queue is judged; if the change of the carrier burst is increased or reduced, a length threshold is directly increased or reduced; if the carriers are in an increasing trend, the threshold is randomly increased according to a certain probability; if the carriers are in a reducing trend, the threshold is randomly reduced according to a certain probability; if the carrier is normal, the length threshold is not adjusted, therefore, the length threshold can realize dynamic adjustment with the changes of the carrier. By adopting the method and the device provided by the invention, a delay from a business end to anther business end is assured, thus optimizing the performance of the network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Internetwork interference avoiding method based on nested composite superframe structure
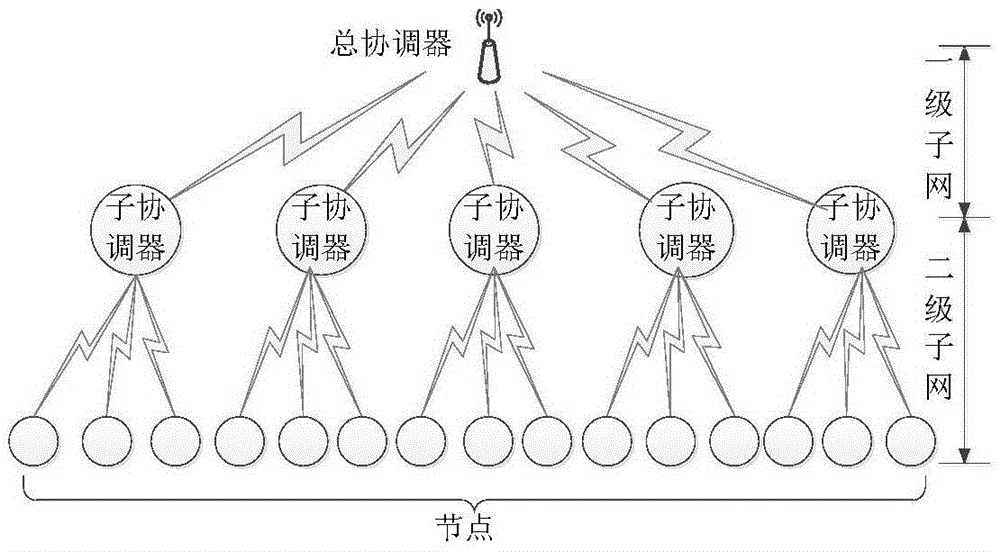
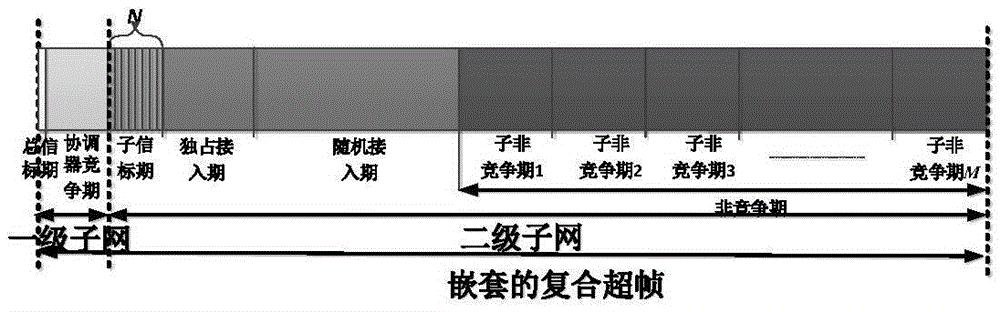
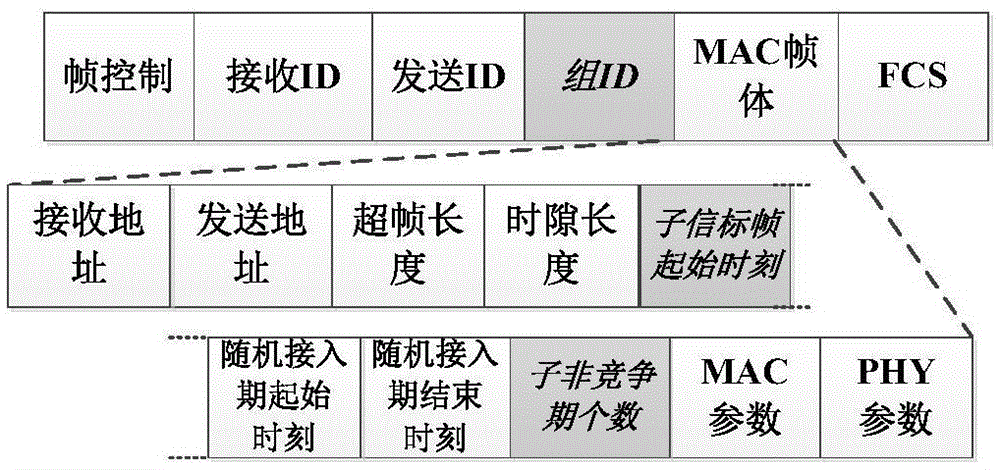
ActiveCN105611557AResolve interferenceAvoid interferenceWireless communicationPacket lossComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses an internetwork interference avoiding method based on a nested composite superframe structure. The method comprises the nested composite superframe structure, improved frame structures and a communication mechanism under the composite superframe. In adoption of the embodiment of the invention, the internetwork interference can be effectively avoided; and performances such as the packet loss probability and the throughput capacity can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Interference sensing cross-layer routing method based on node sending and receiving capacity
InactiveCN103108372BImprove average end-to-end latencyImprove throughputWireless communicationData streamPacket loss
The invention relates to an interference sensing cross-layer routing method based on node sending and receiving capacity. The method defines parameters for judging the sending and receiving capacity of a node based on an 802.11 medium access control (MAC) layer, and the two parameters can reflect that strength and weakness of interference of the periphery of the node and communication load degree born by the node, based on the fact, a MAC layer and a network layer are combined and a new routing criterion is defined, the new criterion is related to the number of surrounding active neighbor nodes, the number of data flow passing the nodes, capacity of node access channel and topology changing conditions around the nodes, and real conditions of the network can be further reflected. The interference sensing cross-layer routing method based on the node sending and receiving capacity aims to reduce interference, selects a path which is largest in bottleneck node comprehensive capacity or a path which is smallest in bottleneck link interference as far as possible, and the path which is largest in the bottleneck node comprehensive capacity or the path which is smallest in the bottleneck link interference is used as routing, and therefore average end-to-end delay and packet loss probability are reduced, and the throughput is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Collision-resistant random access method for satellite Internet of Things system in high-load scene
ActiveCN113422635AImprove throughputImprove packet loss rateRadio transmissionInstrumentsData packTelecommunications
The invention discloses a collision-resistant random access method for a satellite Internet of Things system in a high-load scene, which is used for improving the access effect of massive terminals of the satellite Internet of Things. The method comprises: a sending terminal determines the number of sent data packets and the sending interval of the data packets; and after receiving the data frames, a receiving end performs coherent accumulation on the time slot sliding windows one by one, determines a result of each coherent accumulation, performs signal separation processing when a signal separation condition is met, and repeats the process until all terminals are accessed or no separable data packets exist. According to the method, the system throughput under the high-load access condition can be effectively improved, and the method is suitable for the working scene of massive terminal access such as the satellite Internet of Things.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Hybrid random access method and device in satellite Internet of Things scene
PendingCN114867129AImplement hybrid overlayMeet different business needsSynchronisation arrangementParticular environment based servicesTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
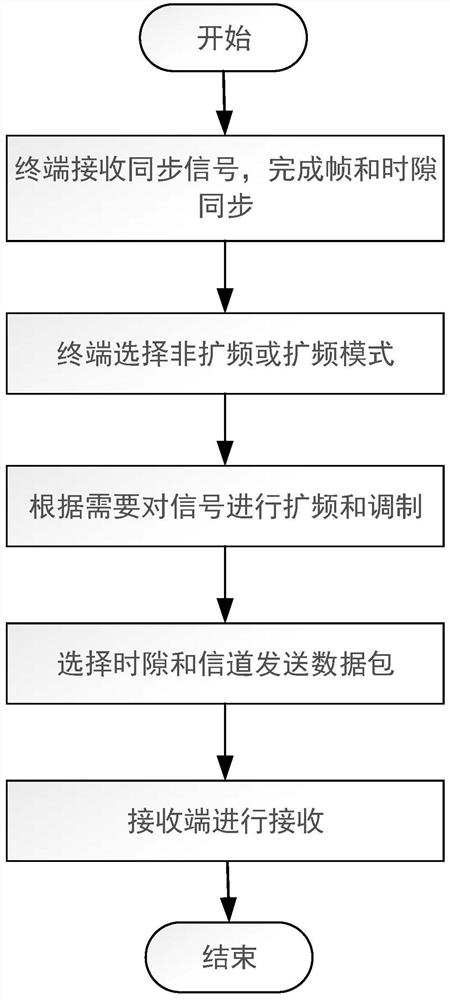
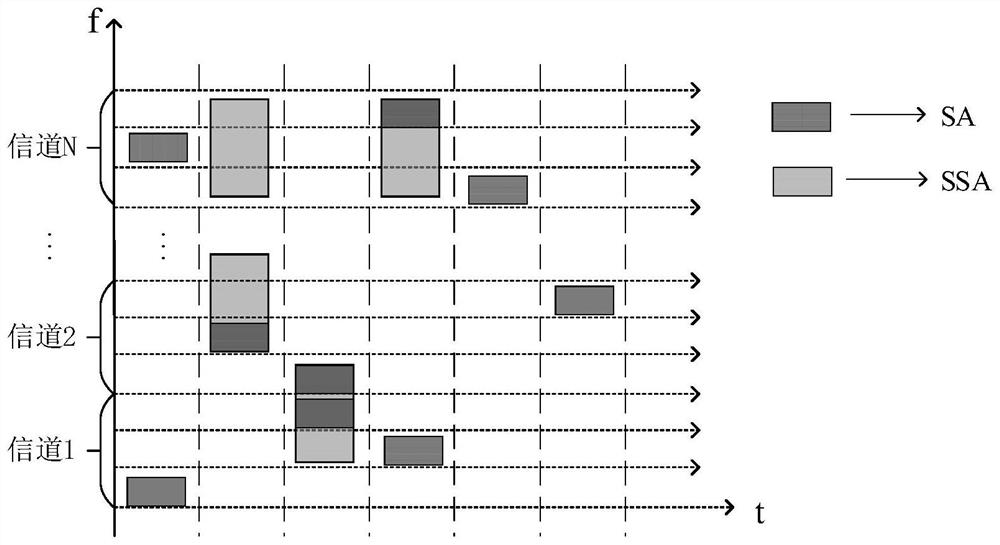
The invention discloses a hybrid random access method and device in a satellite Internet of Things scene, and the method comprises the steps: a terminal of a transmitting end receives a synchronization signal, and completes the synchronization of a frame and a time slot; according to the sending requirement of each terminal, determining that each terminal is in a non-spread spectrum mode or a spread spectrum mode, and the terminals of the sending end comprise a non-spread spectrum terminal and a spread spectrum terminal; carrying out carrier modulation on the non-spread spectrum terminal signal to obtain a non-spread spectrum data packet, and carrying out spread spectrum and then modulation on the spread spectrum terminal signal to obtain a spread spectrum data packet; and the non-spread spectrum terminal selects a channel and a time slot to randomly send the modulated non-spread spectrum data packet, and the spread spectrum terminal selects a channel and a time slot to randomly send the modulated spread spectrum data packet. According to the invention, two traditional random access modes, i.e., hybrid superposition of a non-spread spectrum random access mode and a spread spectrum random access mode in the same system, are realized, the throughput of the system can be improved, the service requirements of various terminals in an actual scene are met, and the method is suitable for the working scene of massive terminal access such as the satellite Internet of Things.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Supporting node mobility method based on node speed
InactiveCN101800592BFirmly connectedImprove connectivityEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementLine segmentEnergy consumption
The invention discloses a supporting node mobility method based on node speed, a new neighbor node is obtained through judging whether a mobile synchronization frame MSYNC which is sent by a mobile node is replied or not by the method, the distance between the new neighbor node and the mobile node is obtained by the new neighbor node by receiving the strength of a MSYNC signal, meanwhile, whetherreplying MACK or not to the mobile node is determined through a judgment condition; after the judgment condition is met, the time interval for sending the MSYNC next time by the mobile node is calculated by the new neighbor node through the static neighbor information of the new neighbor node and the state information of the mobile node. The judgment condition is that: an included angle of a directed line segment and the moving direction of a mobile node m is bigger than 90 degrees, and the distance between the mobile node m and a new neighbor node n is less than a transmission range R. The energy consumption which is caused by frequent periodicity neighbor searching is avoided by the method in the invention, the scheduling information of a new cluster is quickly obtained when the mobile node moves among clusters, and mass lost packages which are caused by the differences of period scheduling are reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Dynamic Routing Method of Stereo Heterogeneous Network in Emergency Scenario Based on UAV
ActiveCN111263419BImprove operational efficiencyEasy and intuitive deploymentNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionPathPingSimulation
The present invention is based on the dynamic routing method of the three-dimensional heterogeneous network in the emergency scene of the UAV. The method can adapt to the fusion network of dynamic topology changes, and the UAV is used as the relay node to form the relay node, and the nodes in the same area do not communicate. , the node communication in different areas is routed through the UAV node relay, and the ground node is only used as the end node in the route. In each communication process, the method includes the following steps: Step A: respectively Nodes model the scene; step B: improve the link weight on the basis of the traditional OLSR protocol, and select the routing path as cost=α×ETT+β×E i +(1‑α‑β)×T as the benchmark; Step C: The core idea of the OLSR routing protocol is to select the MPR set to reduce routing overhead. The improved LBMRE‑OLSR abandons the classic MPR set selection algorithm, The selection of the MPR set is based on the node's expected transmission time, node energy and node congestion degree.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
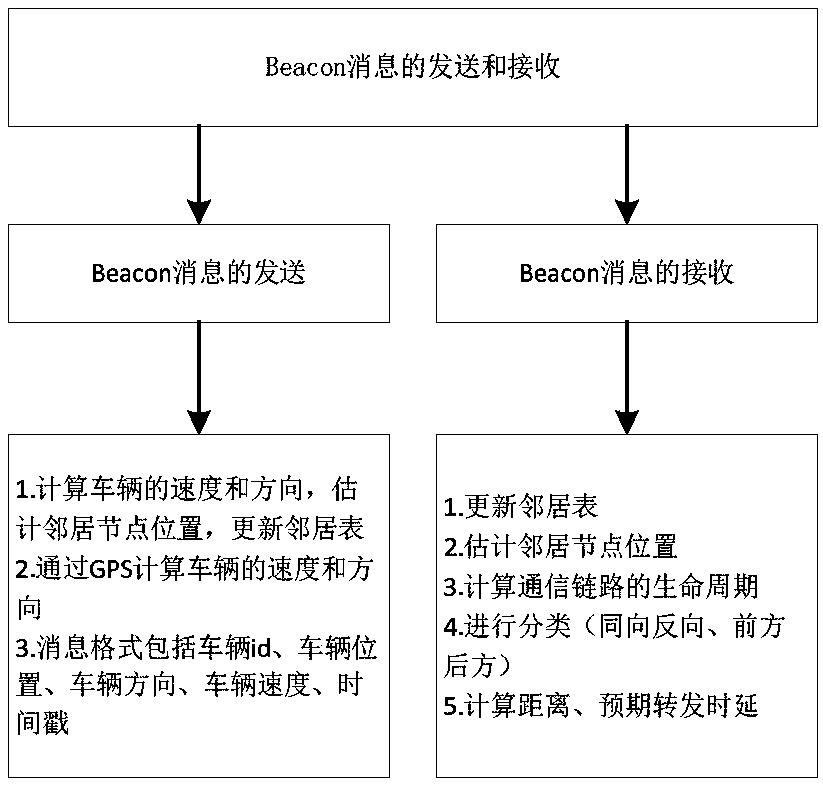
Adaptive service data distribution method based on opportunistic communication in the Internet of Vehicles environment
ActiveCN107302576BReduce overheadEffective distributionData switching networksAdaptive servicesIn vehicle
An adaptive service data distribution method based on opportunistic communication in the Internet of Vehicles environment. Adjacent vehicles or RSUs receive Beacon messages to judge the validity of the messages. If the forwarding conditions are met, the expected forwarding delay is calculated and the expected forwarding delay value is added to the field. Return RREP. After the last hop vehicle or RSU receives the RREP from its adjacent object, it executes the RREP response processing process and returns RREQ to the optimal next hop selected from the candidate object set. After receiving the RREQ, the candidate object judges whether All data packets arrive at the target location, if not all reach the target location, the forwarding vehicle or RSU will restart a new round of broadcasting until all data packets reach the target vehicle. The invention realizes the effective distribution of service data in the Internet of Vehicles environment, and improves the packet loss rate, reduces the number of retransmissions, delay and network overhead and other network performance under the condition of ensuring that other indicators are not damaged.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
A Cross-Layer Vehicle Network Routing Method Based on Link Transmission Capability
ActiveCN107105388BImprove stabilityImprove average end-to-end latencyParticular environment based servicesNetwork topologiesPacket lossProtocol design
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com