Patents
Literature
295 results about "End-to-end delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
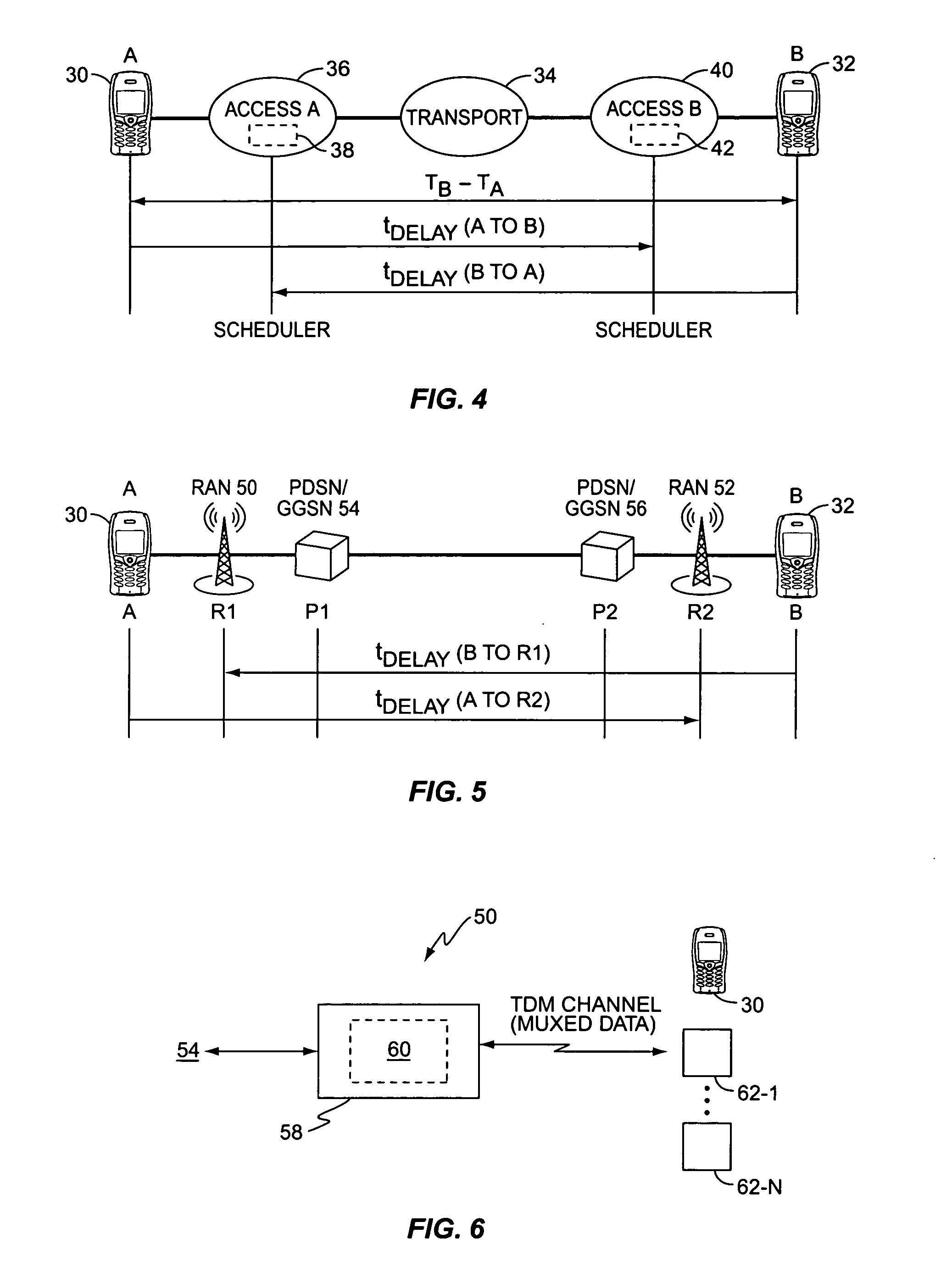
End-to-end delay or one-way delay (OWD) refers to the time taken for a packet to be transmitted across a network from source to destination. It is a common term in IP network monitoring, and differs from round-trip time (RTT) in that only path in the one direction from source to destination is measured.
Application aware rate control
InactiveUS20090164657A1Maximize qualityMaximizing conferencing qualityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPacket lossThe Internet
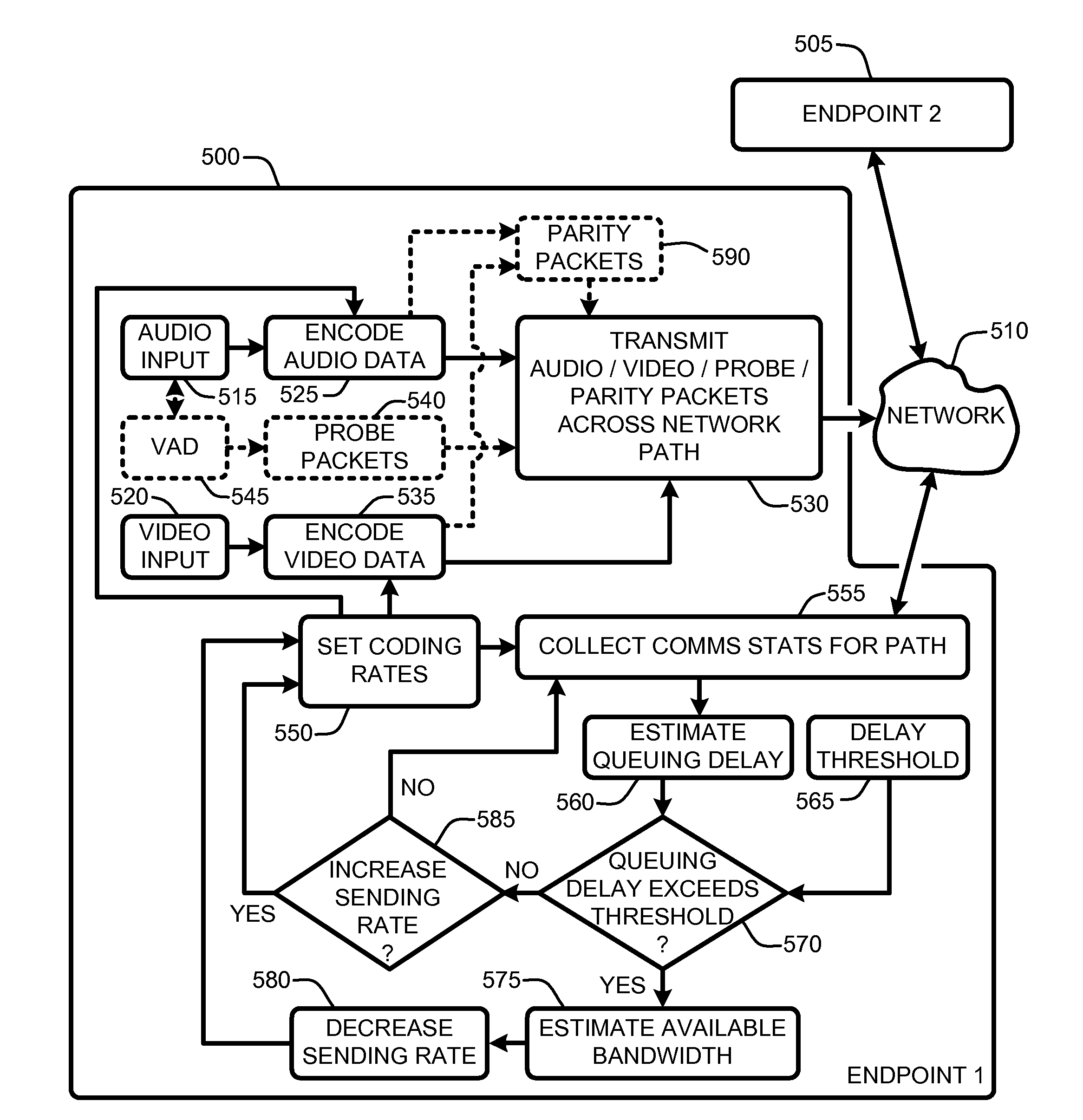
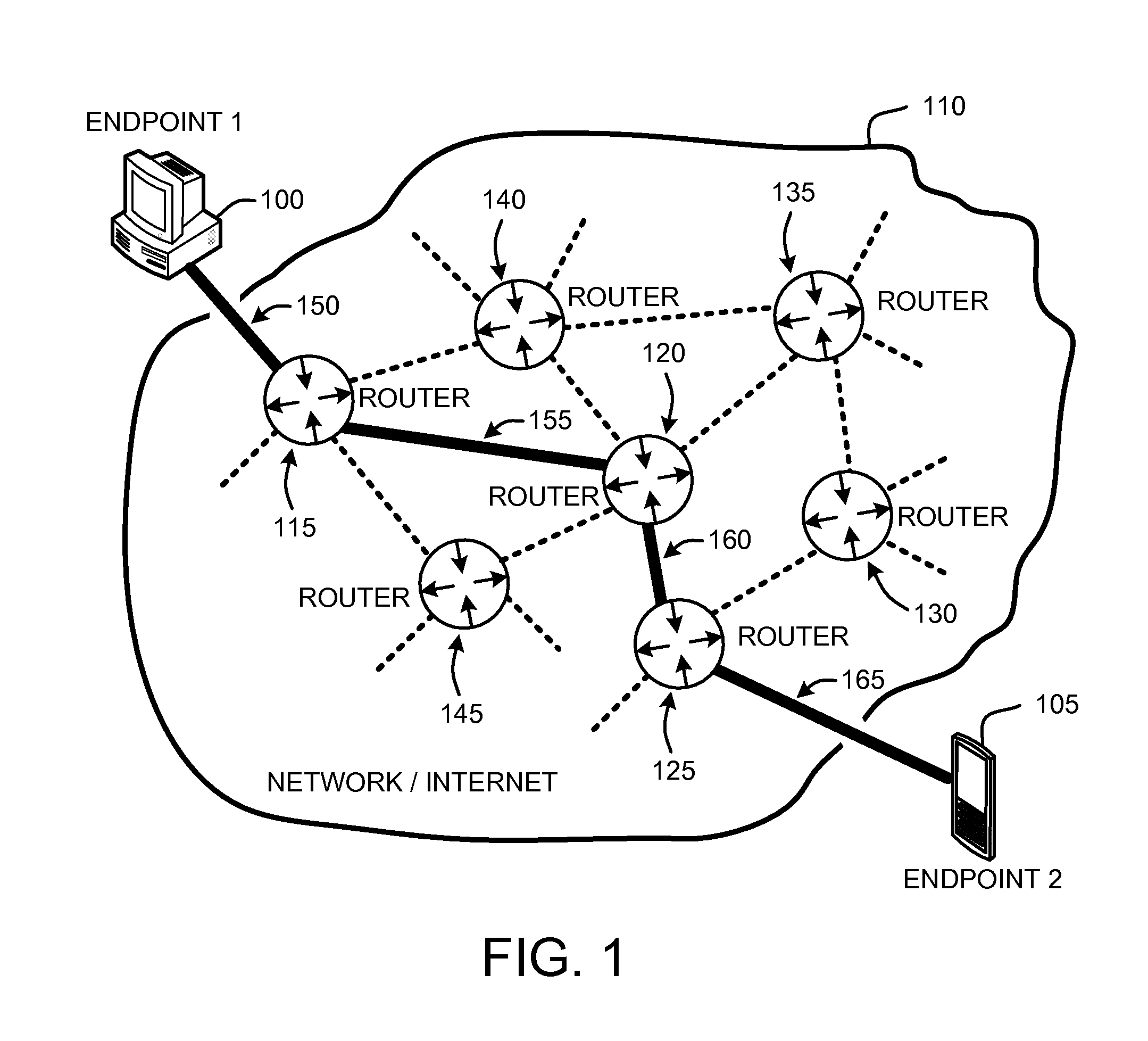
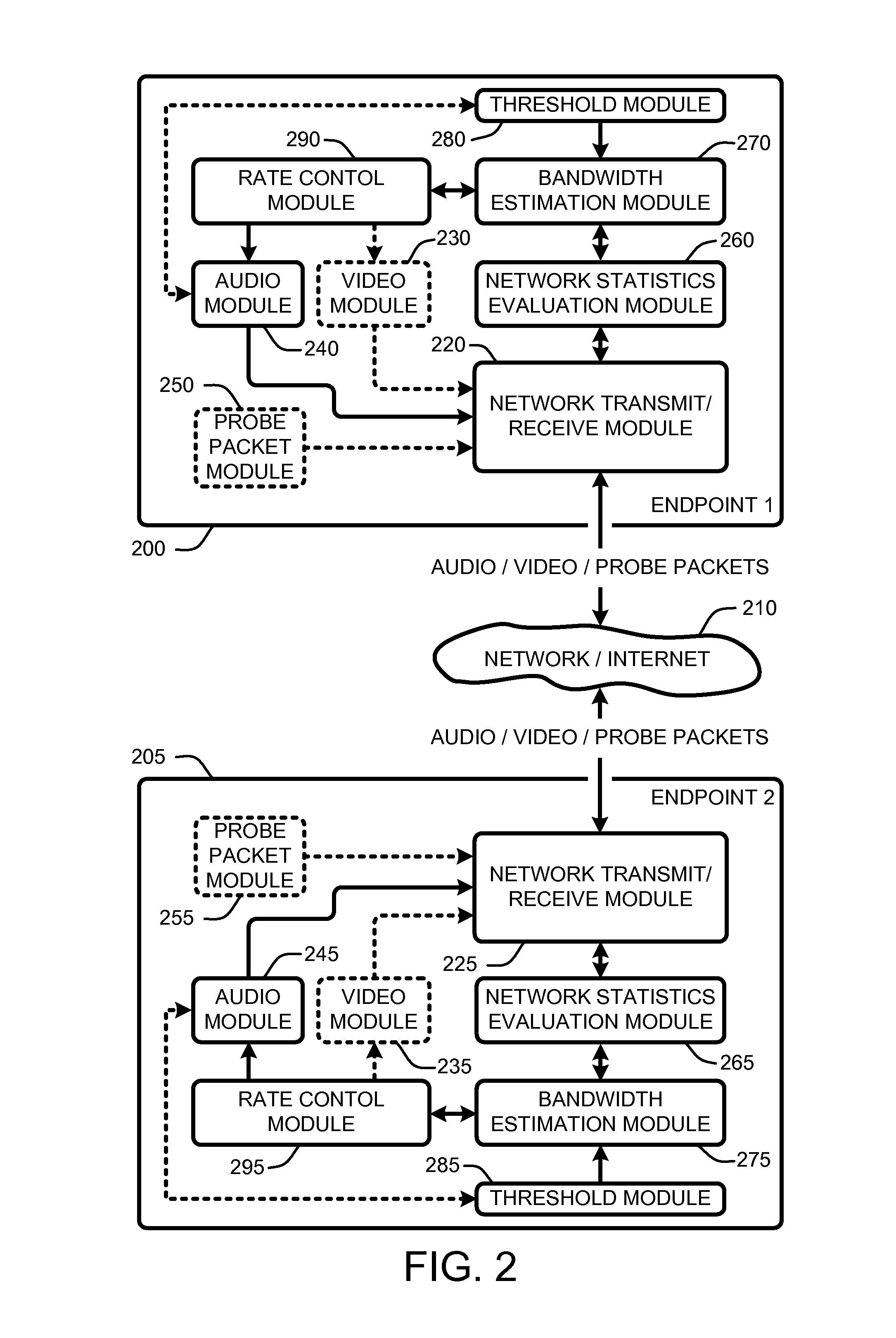
A “communications rate controller” provides various techniques for maximizing a quality of real-time communications (RTC) (including audio and / or video broadcasts and conferencing) over multi-hop networks such as, for example, the Internet. Endpoints in such networks generally communicate via a segmented path that extends through one or more routers between each endpoint. Maximization of conferencing quality is generally accomplished by providing in-session bandwidth estimation across segments of the network path between endpoints (i.e., communication / conference participants) in combination with a robust non-oscillating dynamic rate control strategy for maximizing usage of available bandwidth between RTC endpoints. Further, the dynamic rate control techniques provided by the communications rate controller are designed to prevent degradation in end-to-end delay, jitter, and packet loss characteristics of the RTC.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
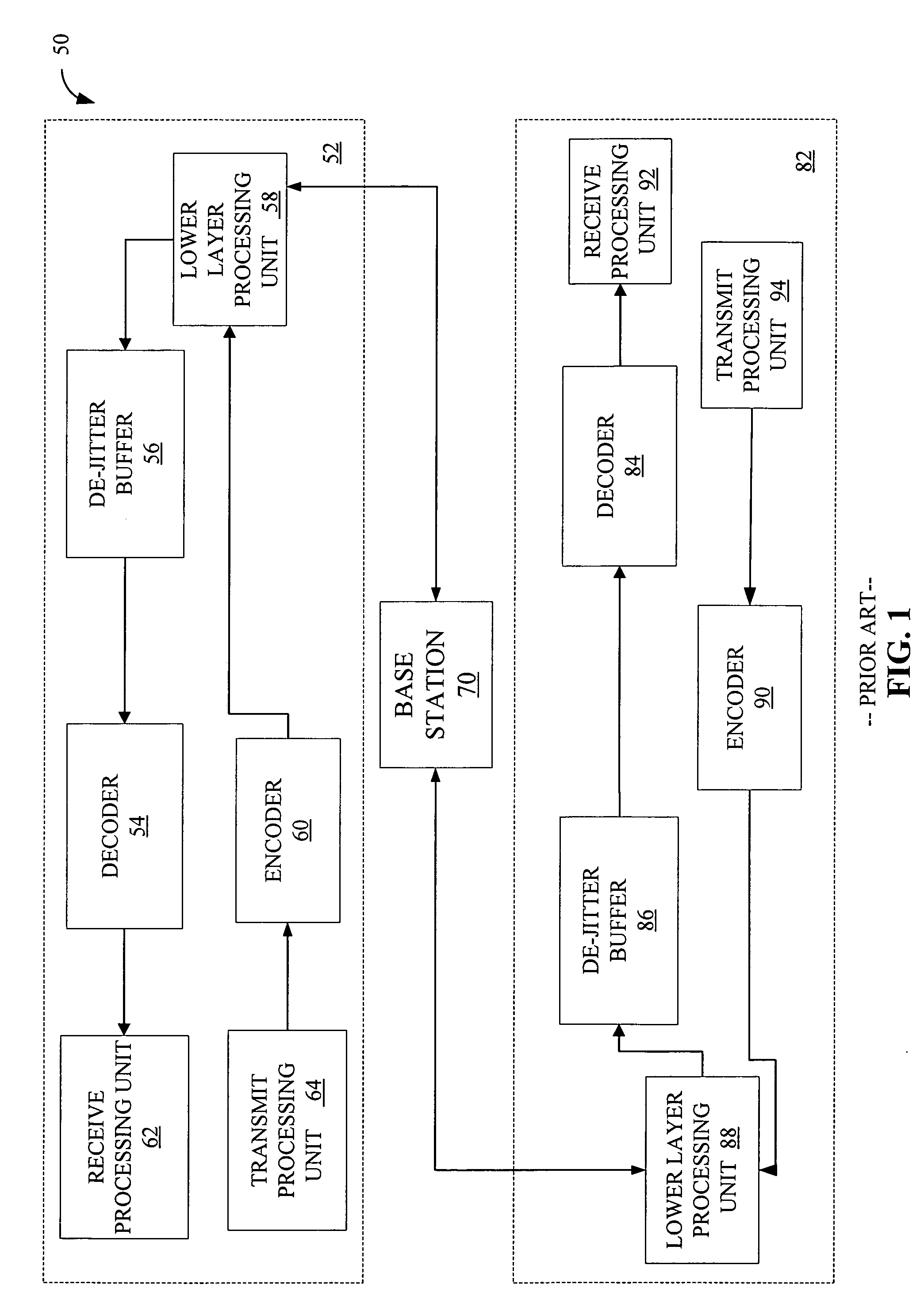
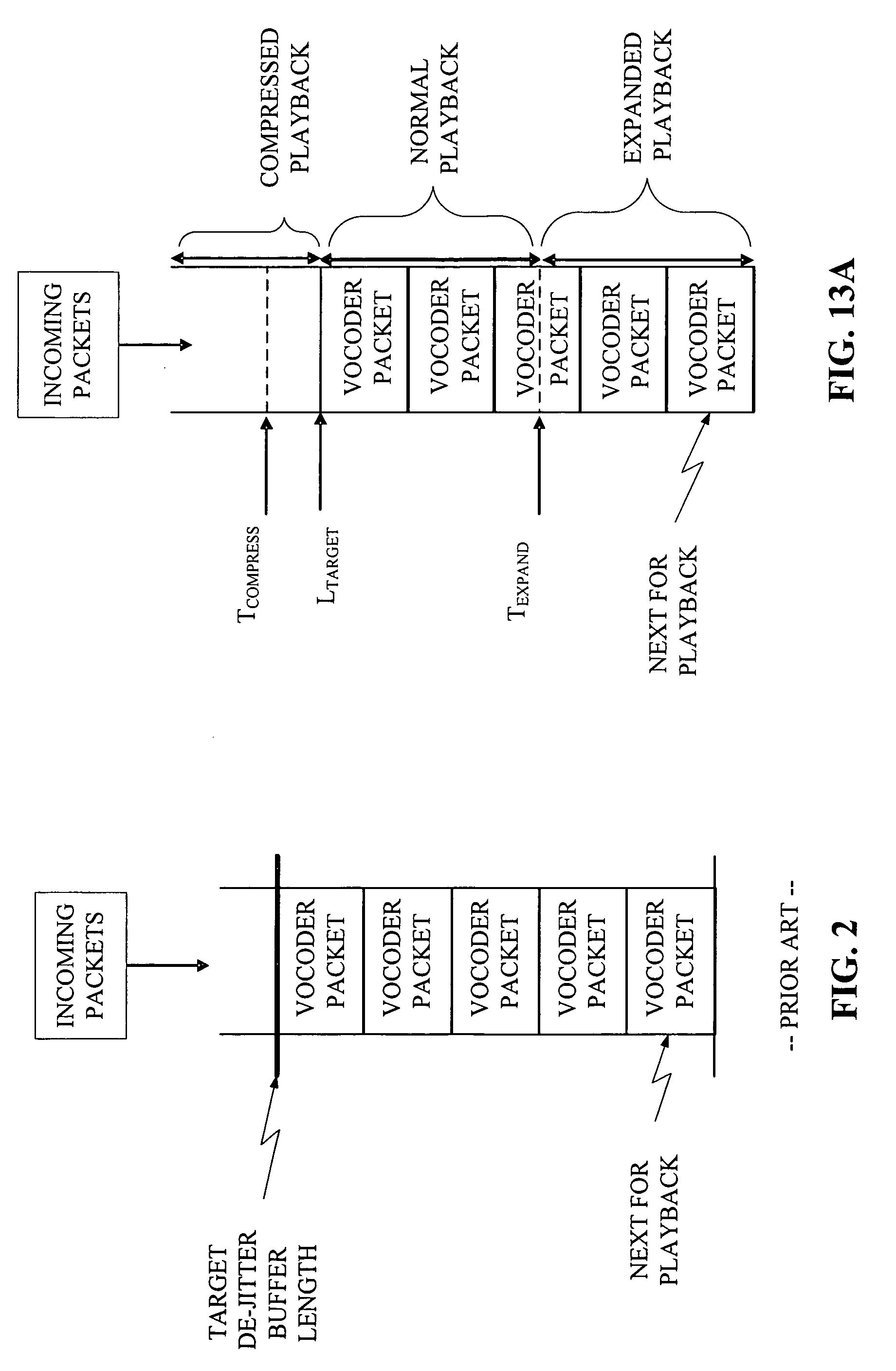
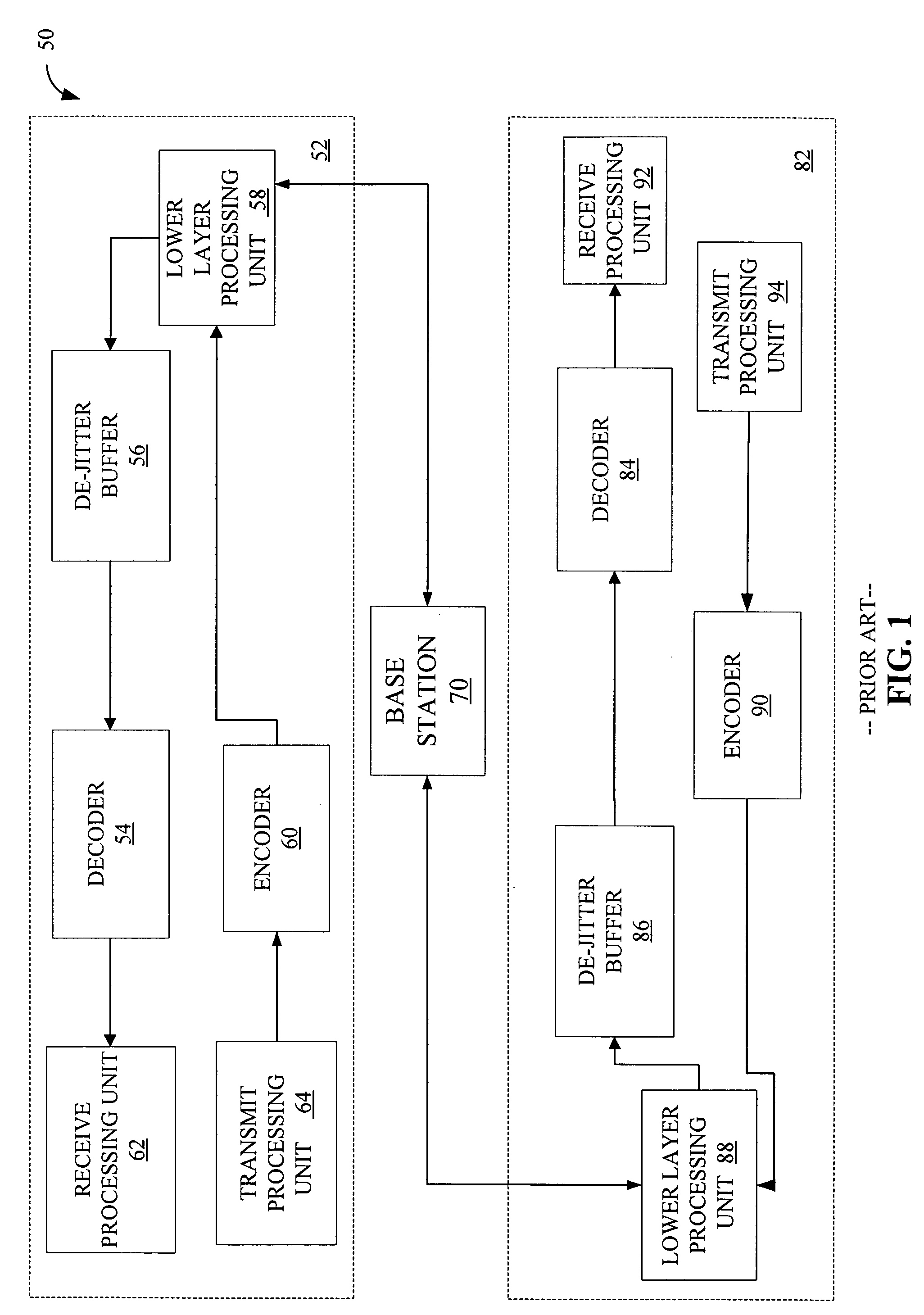
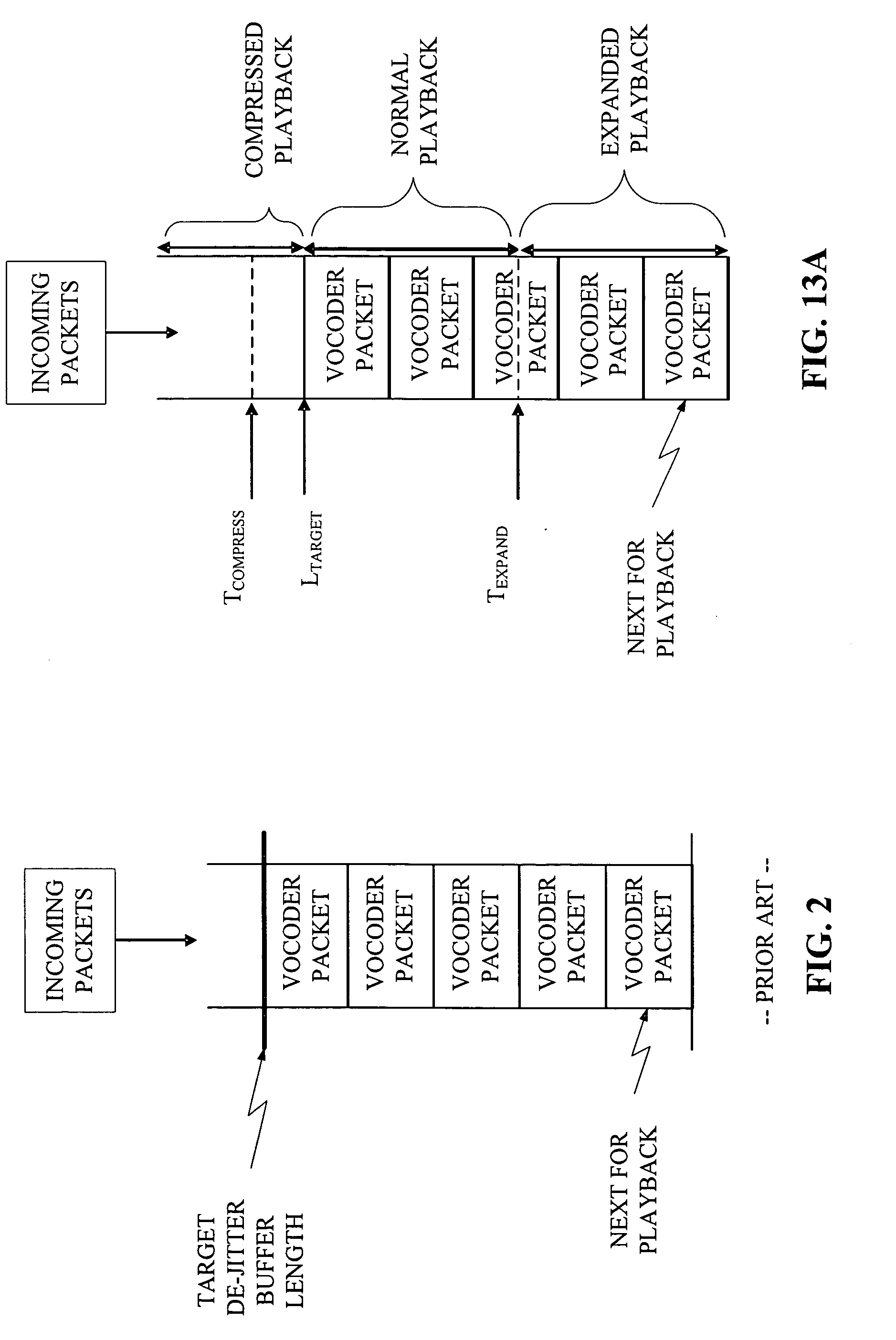
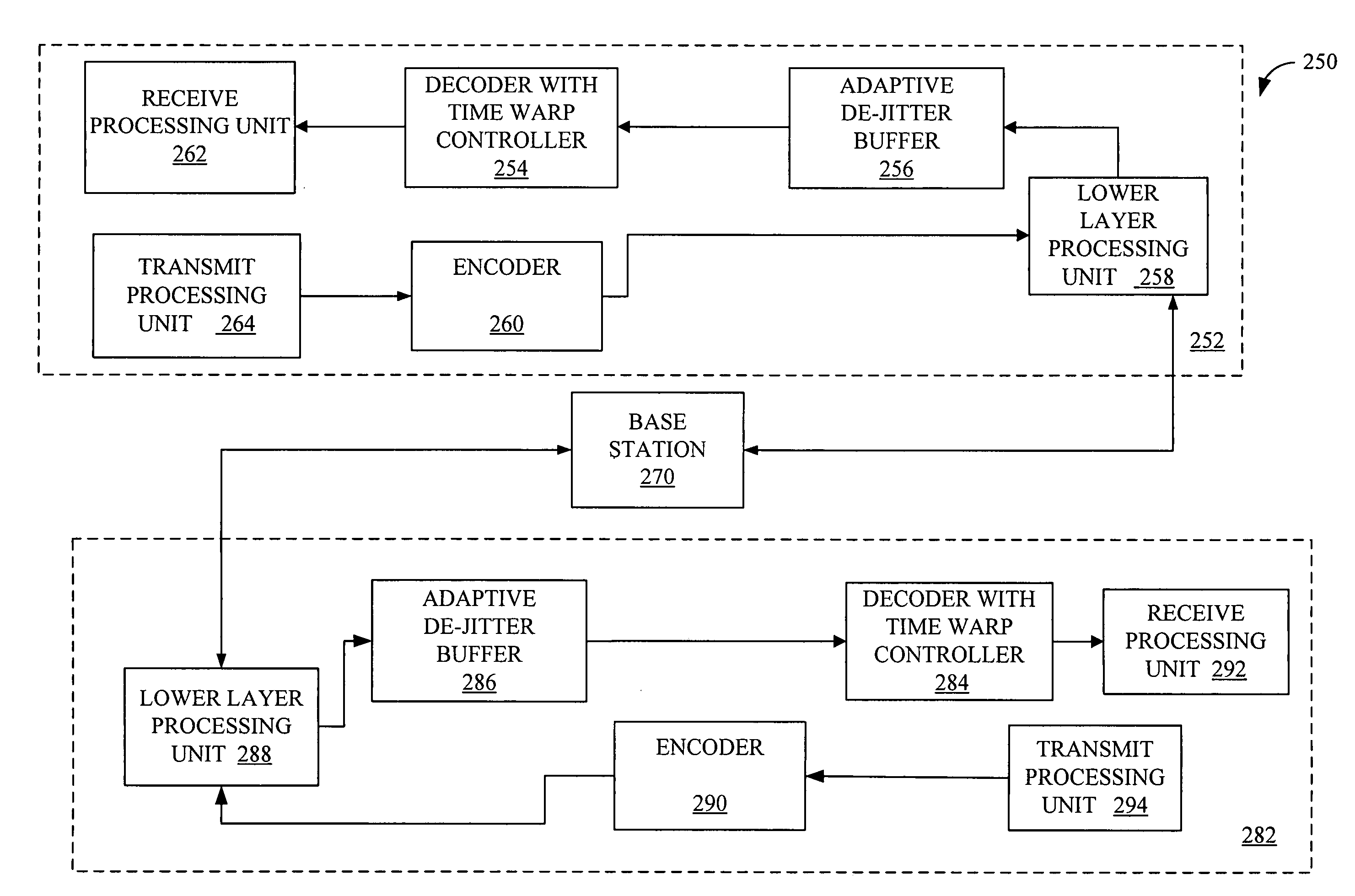
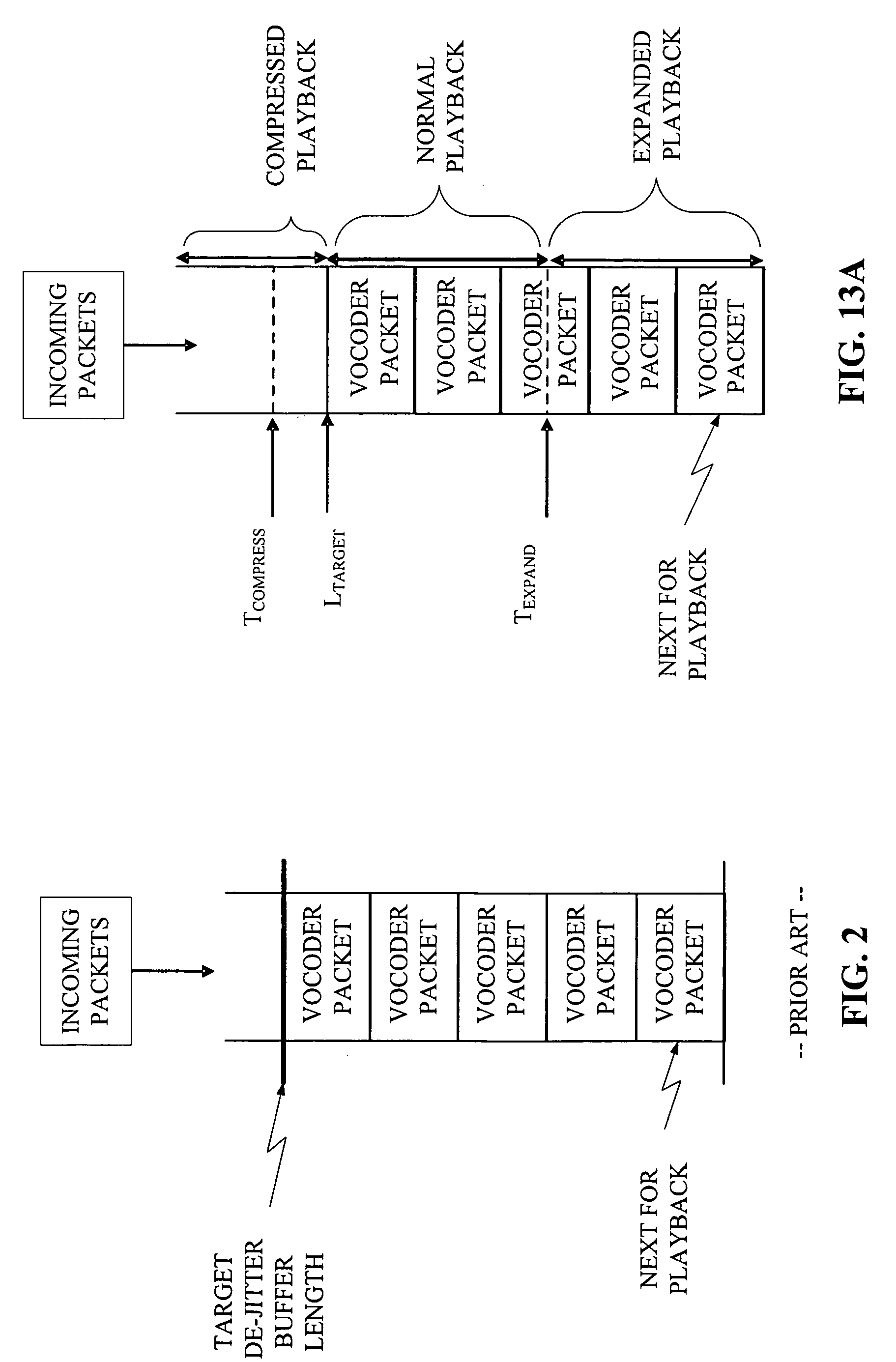
Method and apparatus for an adaptive de-jitter buffer
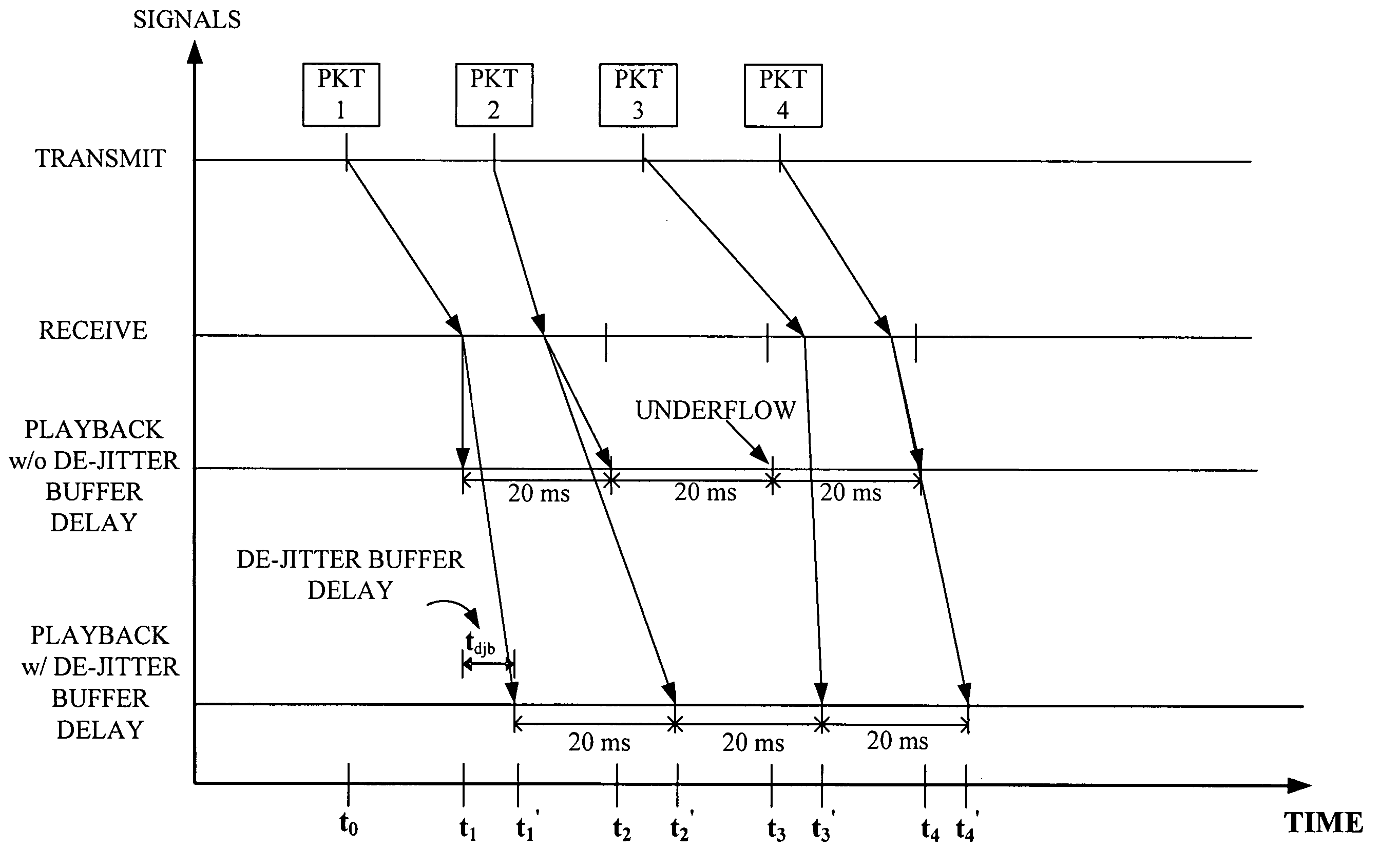
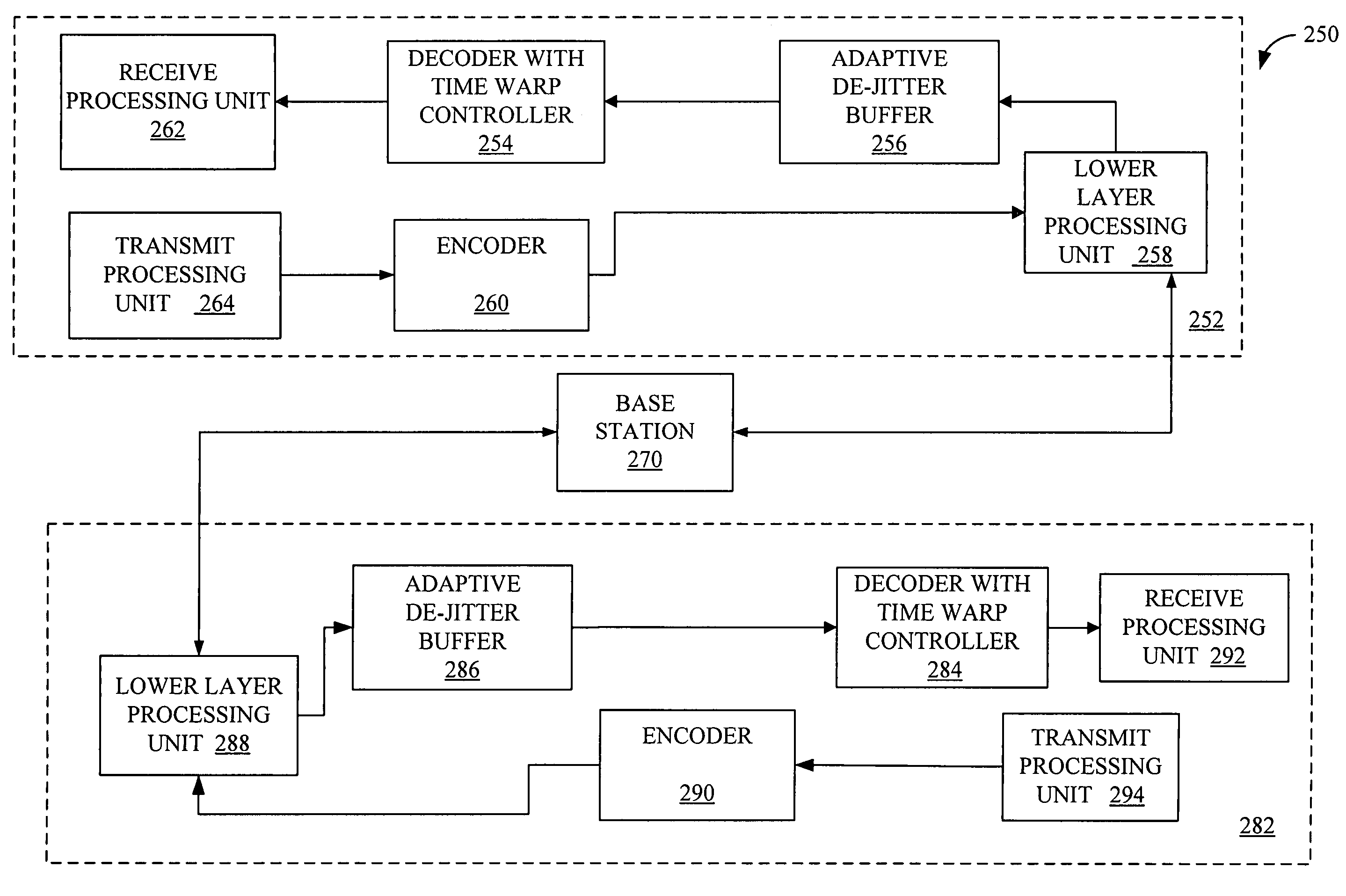
Adaptive De-Jitter Buffer for Voice over IP (VoIP) for packet switch communications. The de-jitter buffer methods and apparatus presented avoid playback of underflows while balancing end-to-end delay. In one example, the de-jitter buffer is recalculated at the beginning of each talkspurt. In another example, talkspurt packets are compressed upon receipt of all remaining packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Low delay picture coding
ActiveUS20150023409A1Lower end-to-end latencyEfficient preparationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionEntry pointLow delay
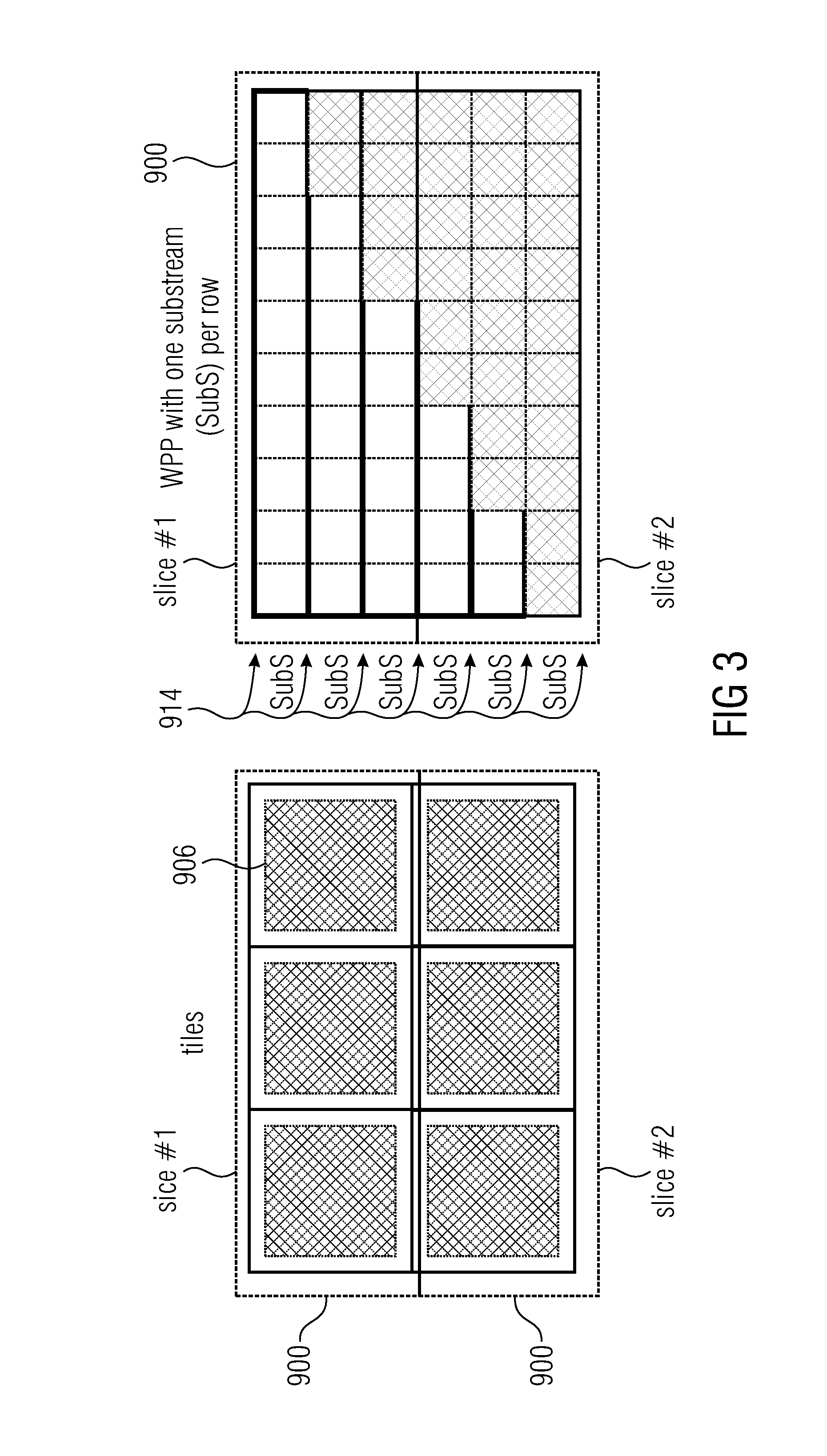
Parallel processing concepts such as wavefront parallel processing, are realized with a reduced end-to-end delay by giving up the usual slice concept according to which slices are either coded / decoded completely independent from areas of the picture outside of the respective slice, or at least independent from areas outside the respective slice as far as the entropy coding is concerned, namely in favor of slices of different modes, namely ones called dependent slices which allow for interdependencies across slice boundaries, and others which do not, called normal slices, for example. Combined with the aspect or not, WPP processing concept is made more efficiently by using the slices' start syntax portions to locate WPP entry points.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
System And Method For Thinning Of Scalable Video Coding Bit-Streams
InactiveUS20070263087A1Flexibility in processingImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionExtensibilityComputer architecture
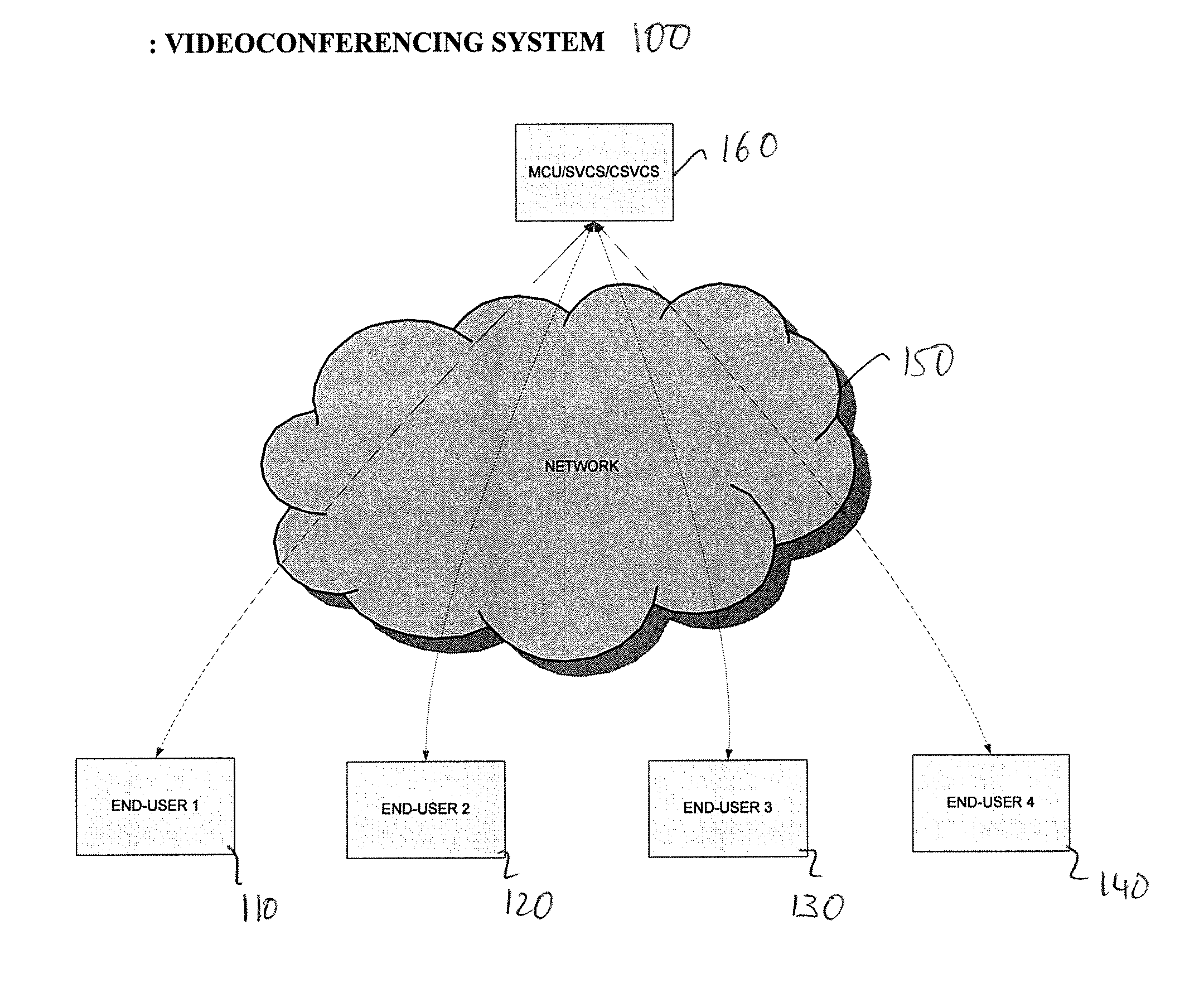
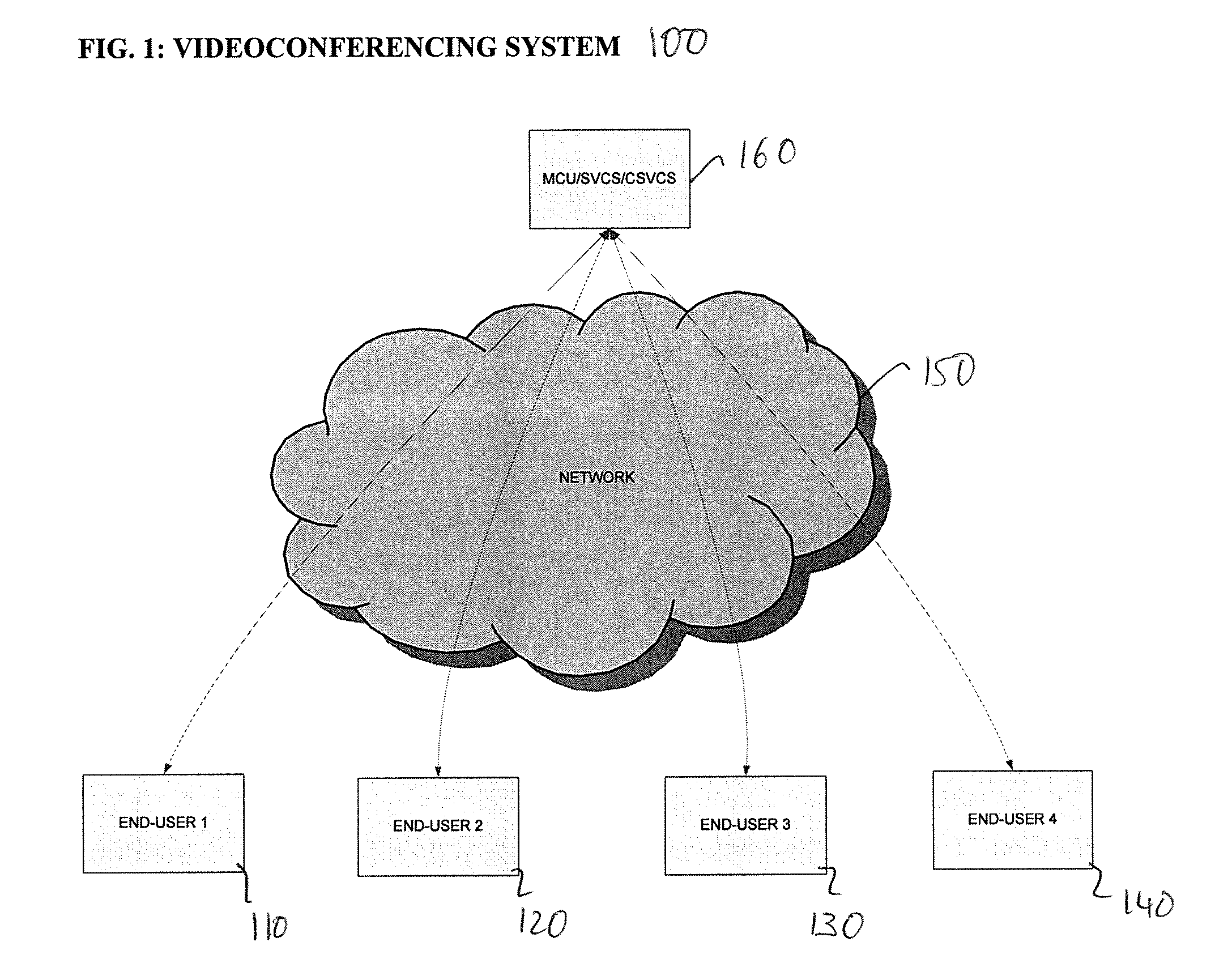
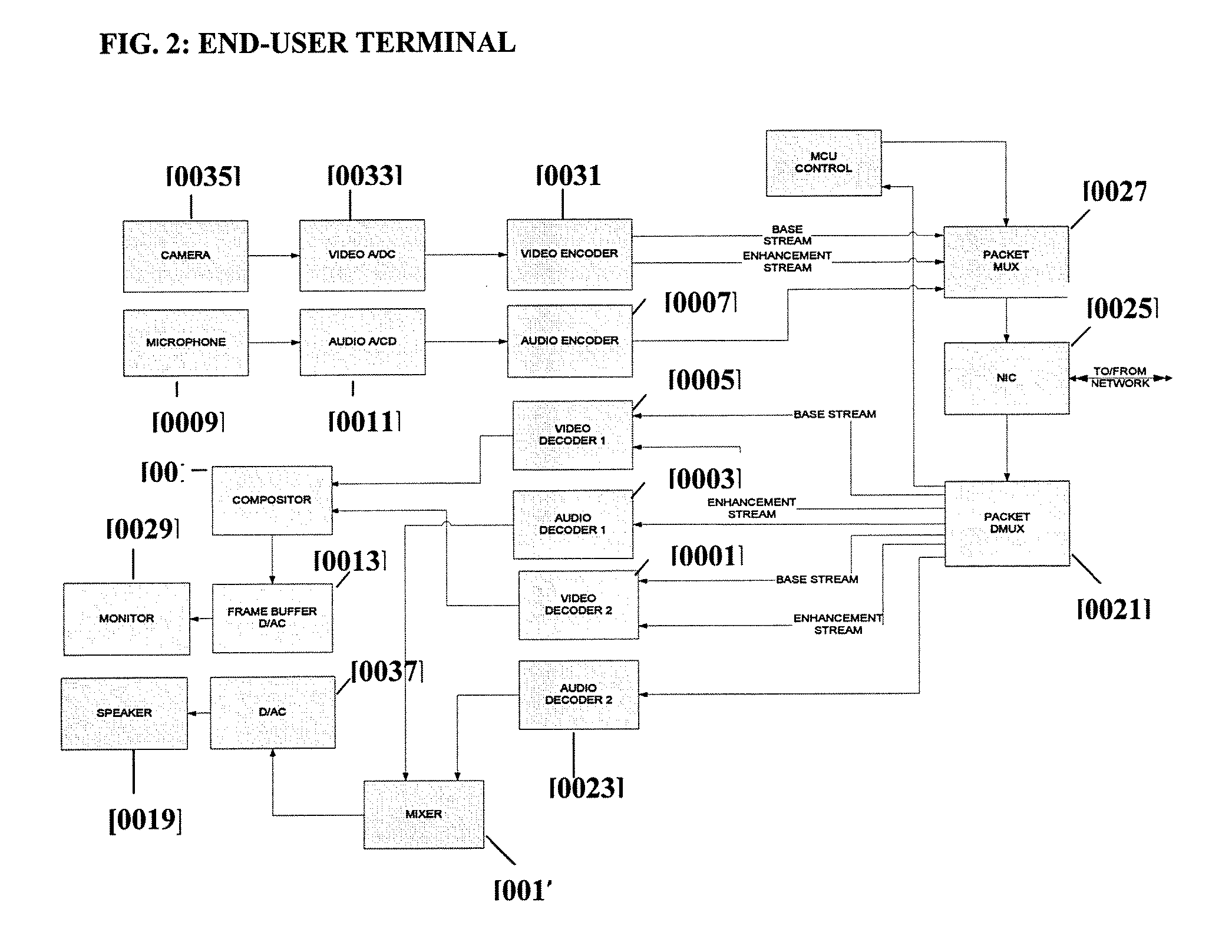
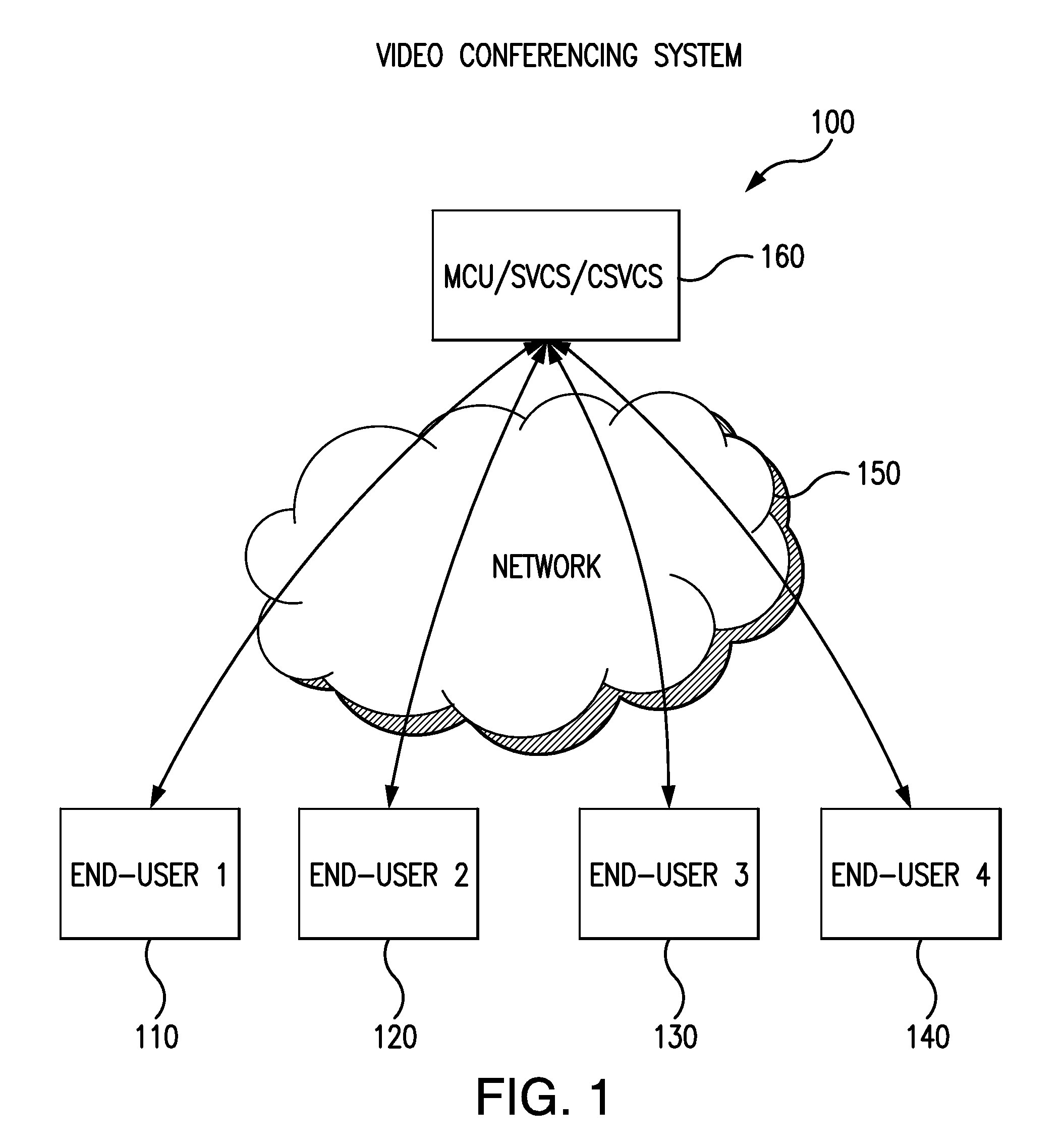
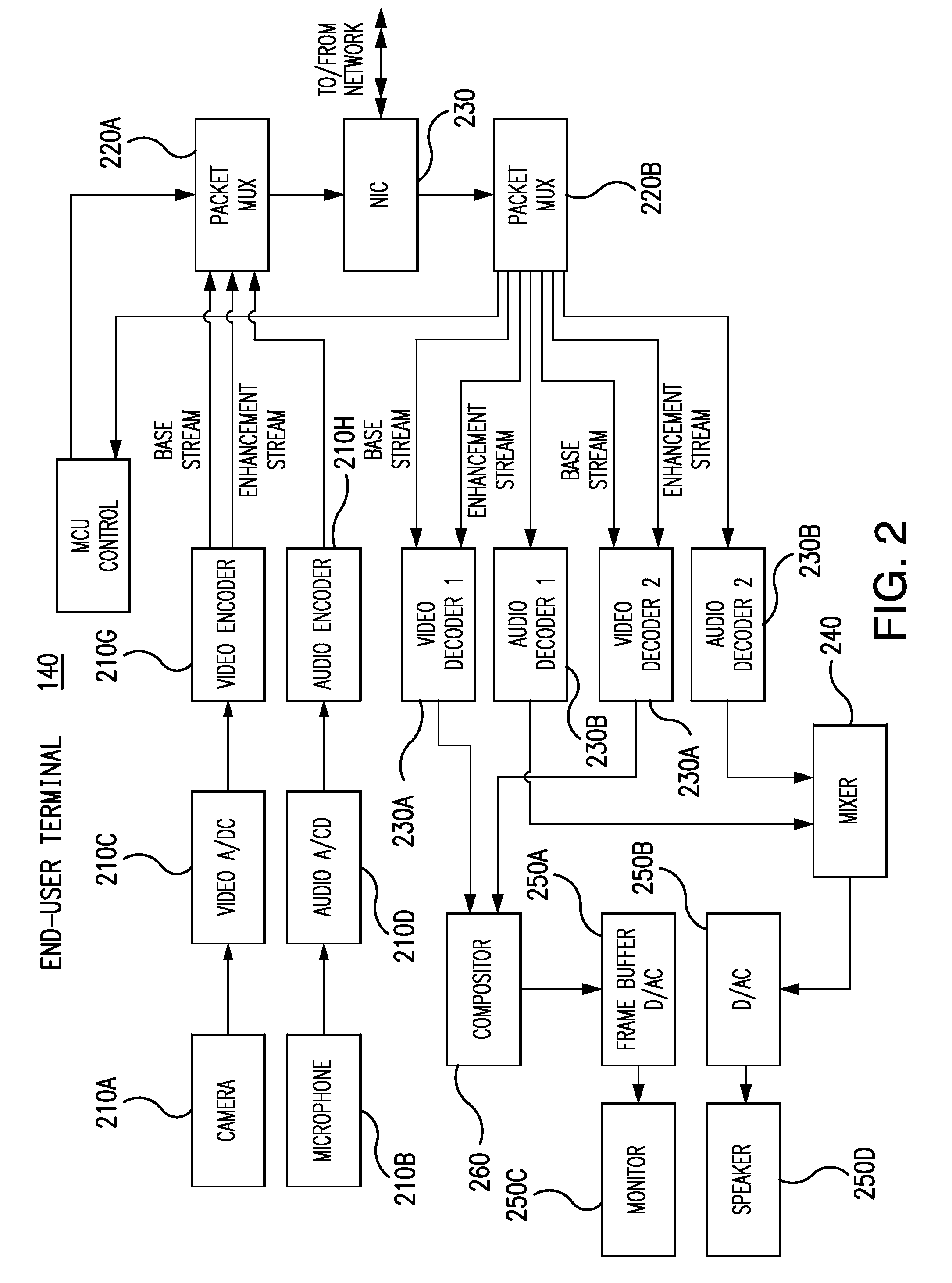
A system for videoconferencing that offers, among other features, extremely low end-to-end delay as well as very high scalability. The system accommodates heterogeneous receivers and networks, as well as the best-effort nature of networks such as those based on the Internet Protocol. The system relies on scalable video coding to provide a coded representation of a source video signal at multiple temporal, quality, and spatial resolutions. These resolutions are represented by distinct bitstream components that are created at each end-user encoder. System architecture and processes called SVC Thinning allow the separation of data into data used for prediction in other pictures and data not used for prediction in other pictures. SVC Thinning processes, which can be performed at video conferencing endpoints or at MCUs, can selectively remove or replace with fewer bits the data not used for prediction in other pictures from transmitted bit streams. This separation and selective removal or replacement of data for transmission allows a trade-off between scalability support (i.e. number of decodable video resolutions), error resiliency and coding efficiency.
Owner:VIDYO
Method and apparatus to support application and network awareness of collaborative applications using multi-attribute clustering
InactiveUS20050120105A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksQuality of serviceNetwork awareness
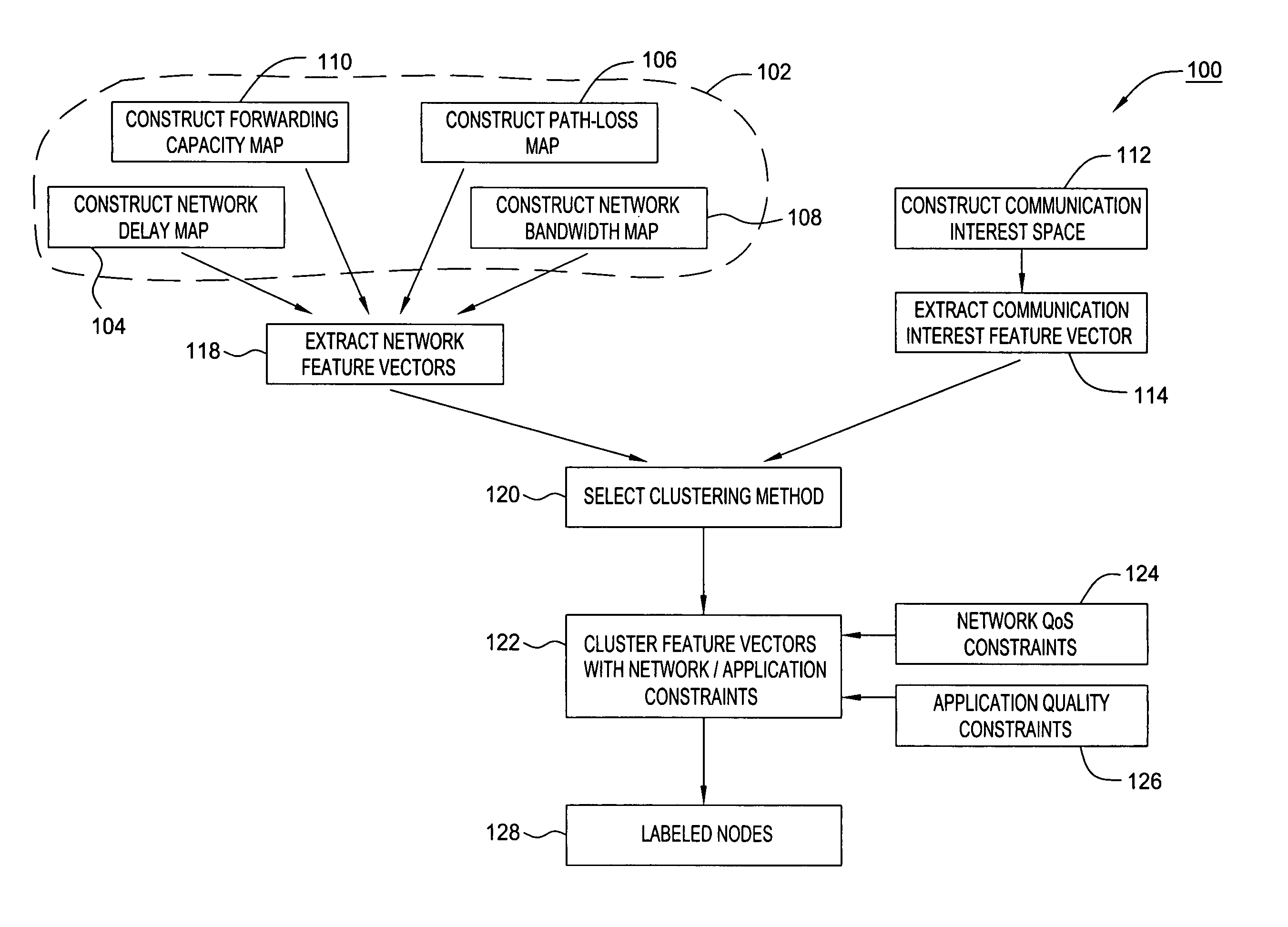
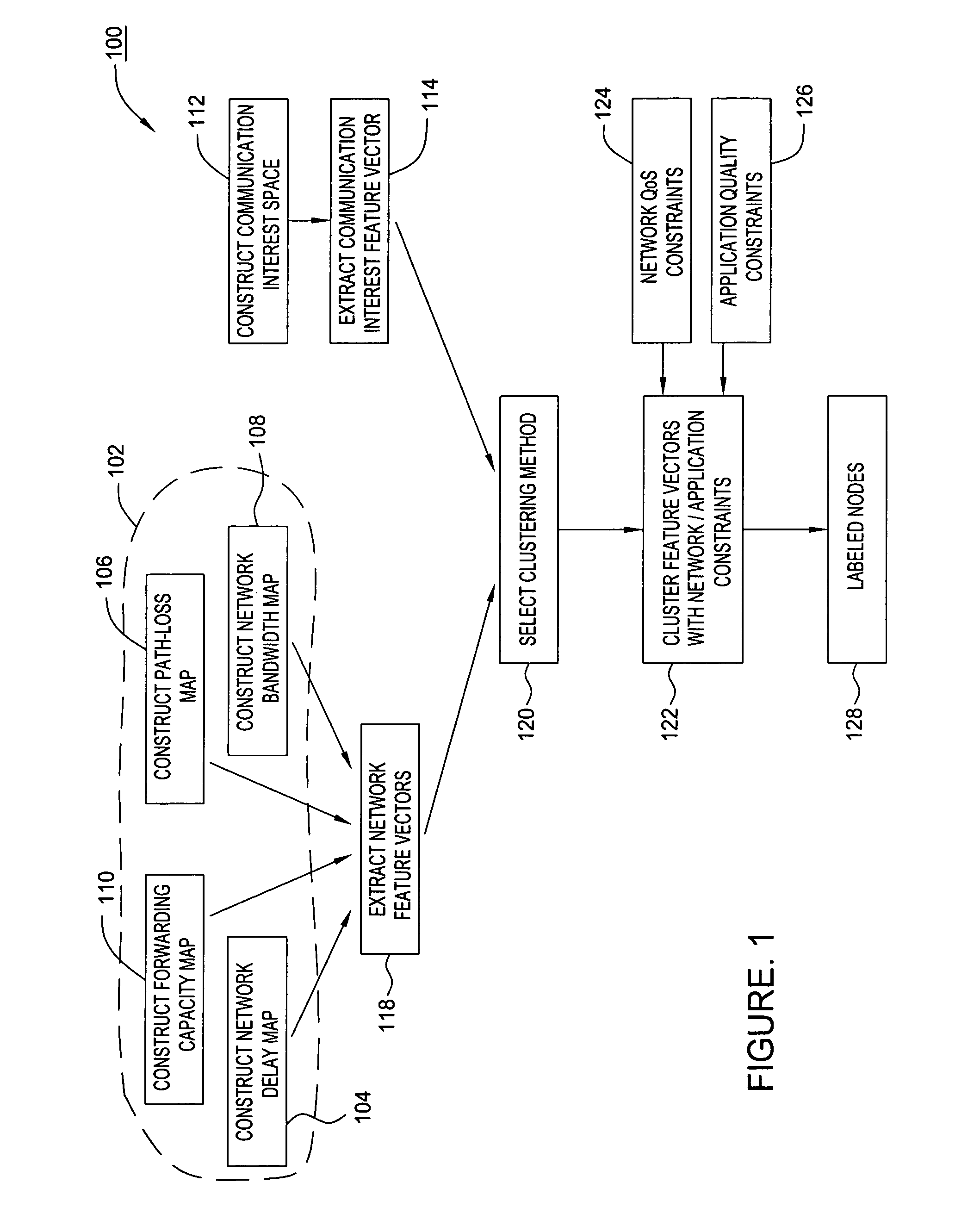
A method of clustering communication nodes based on network attributes such as network delays and forwarding capacity; on communication interest attributes; and on application attributes such as quality of service preferences / constraints (e.g. end-to-end delay constraints, bandwidth constraints) in providing communications between users and application servers. A multi-attribute communication feature vector is formed. That vector is comprised of network attributes (such as available bandwidth, client location attributes in the IP map), communication interests attributes (client request for content updates, client subscription to specific data items or to a set of proximal data sources in network space or application / virtual space) and quality of service requirements (such as delay and loss constraints is used to from efficient group communication mechanisms for distributed collaborative applications. Then the multi-attribute communication feature vectors are clustered. The clustering methods for multi-type attribute feature vectors are: iterative clustering using a generalized distance space with normalized attribute subspace metrics; fusion clustering, and nested clustering.
Owner:IBM CORP
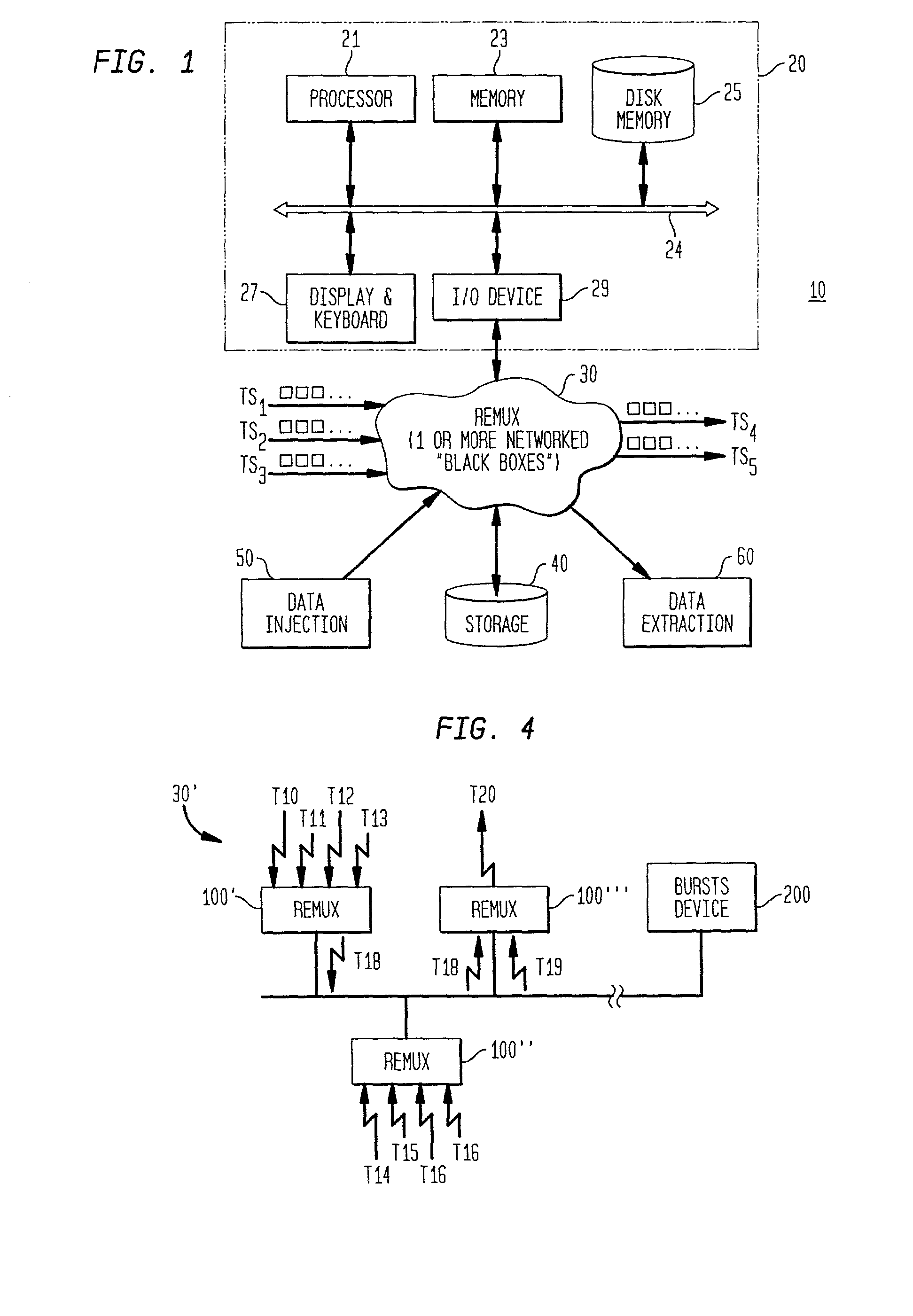
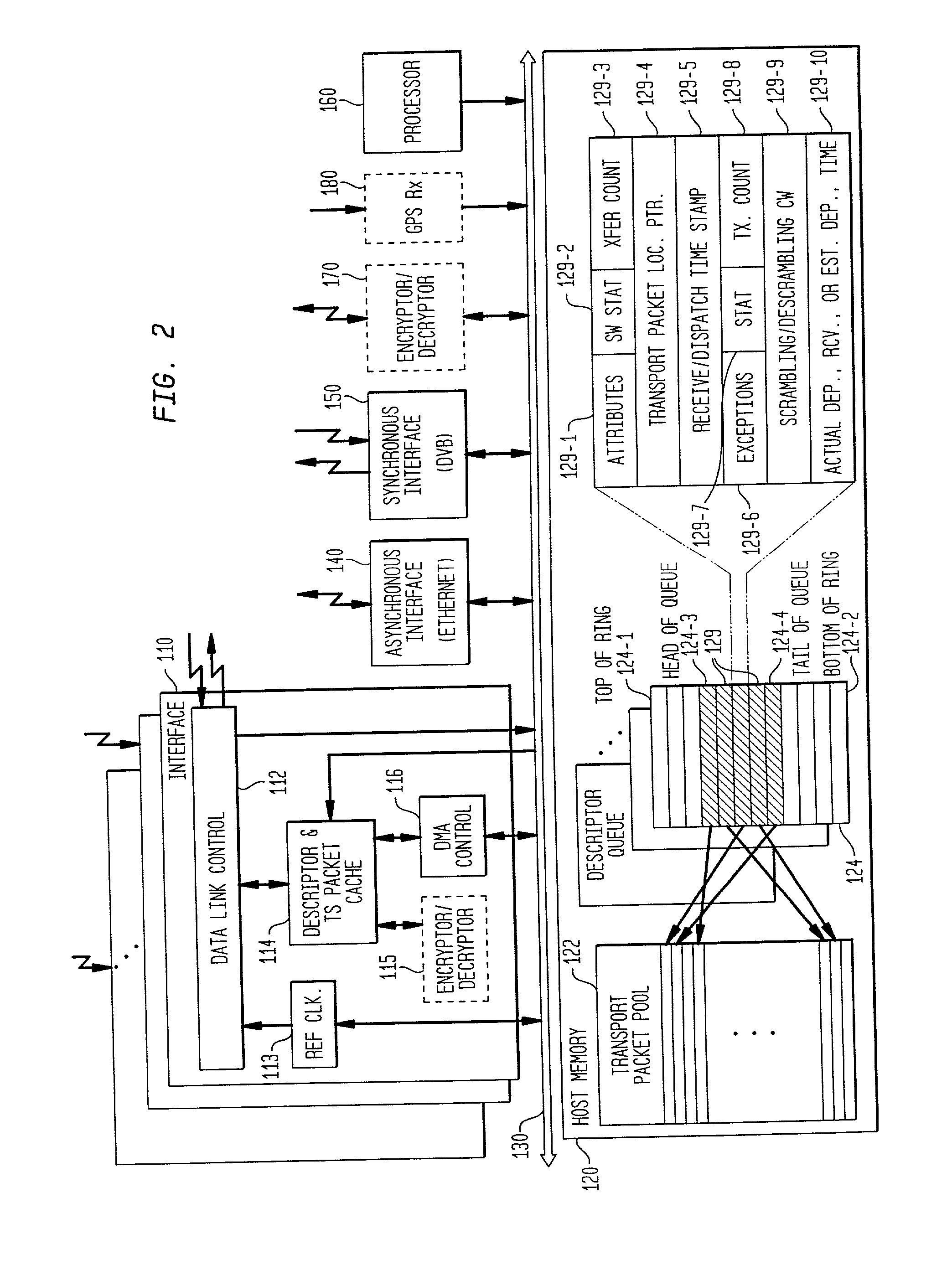
Network distributed remultiplexer for video program bearing transport streams
InactiveUS20020126711A1Flexible processIncrease flexibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexProgram clock referenceMultiplexing
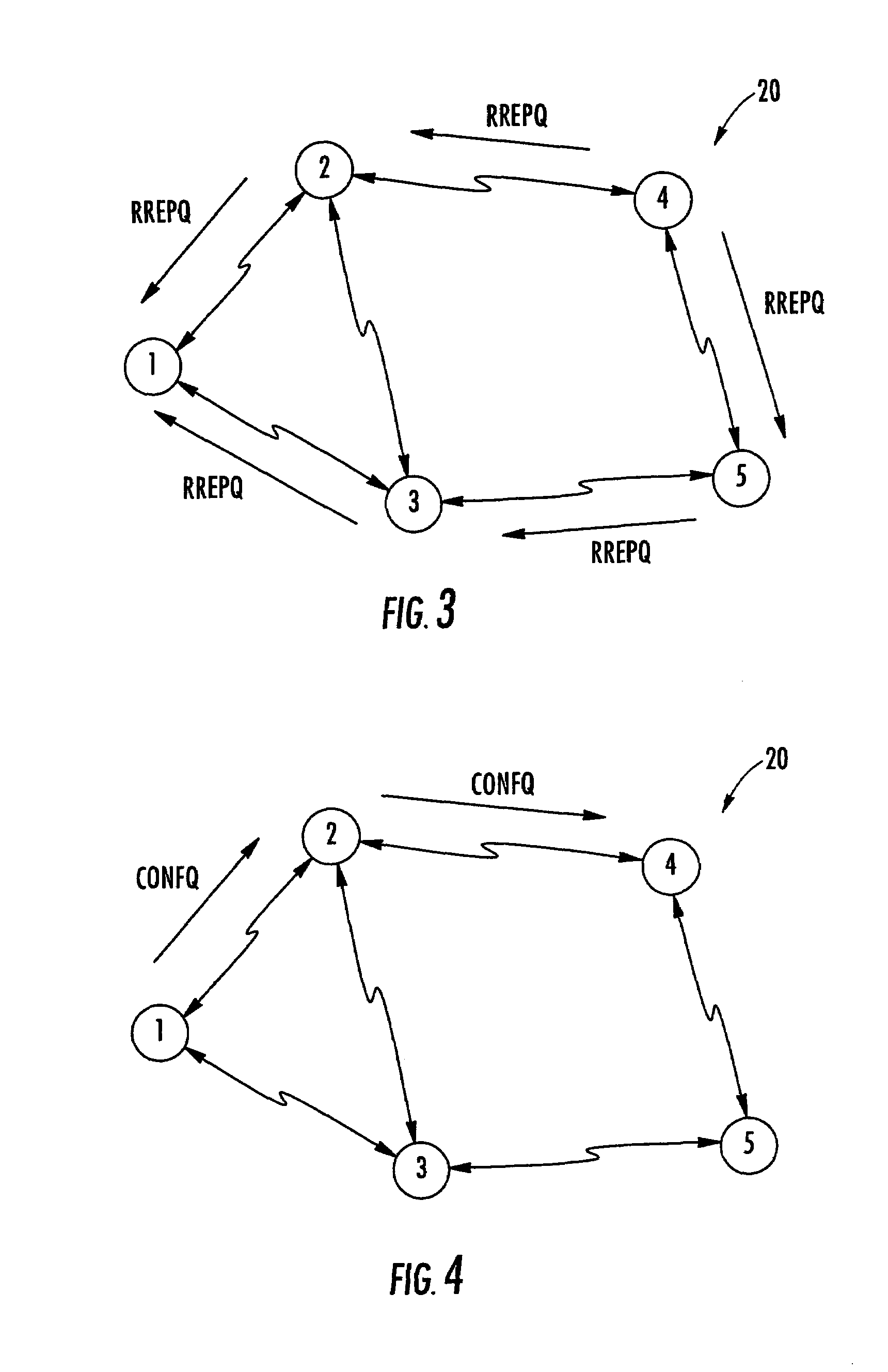
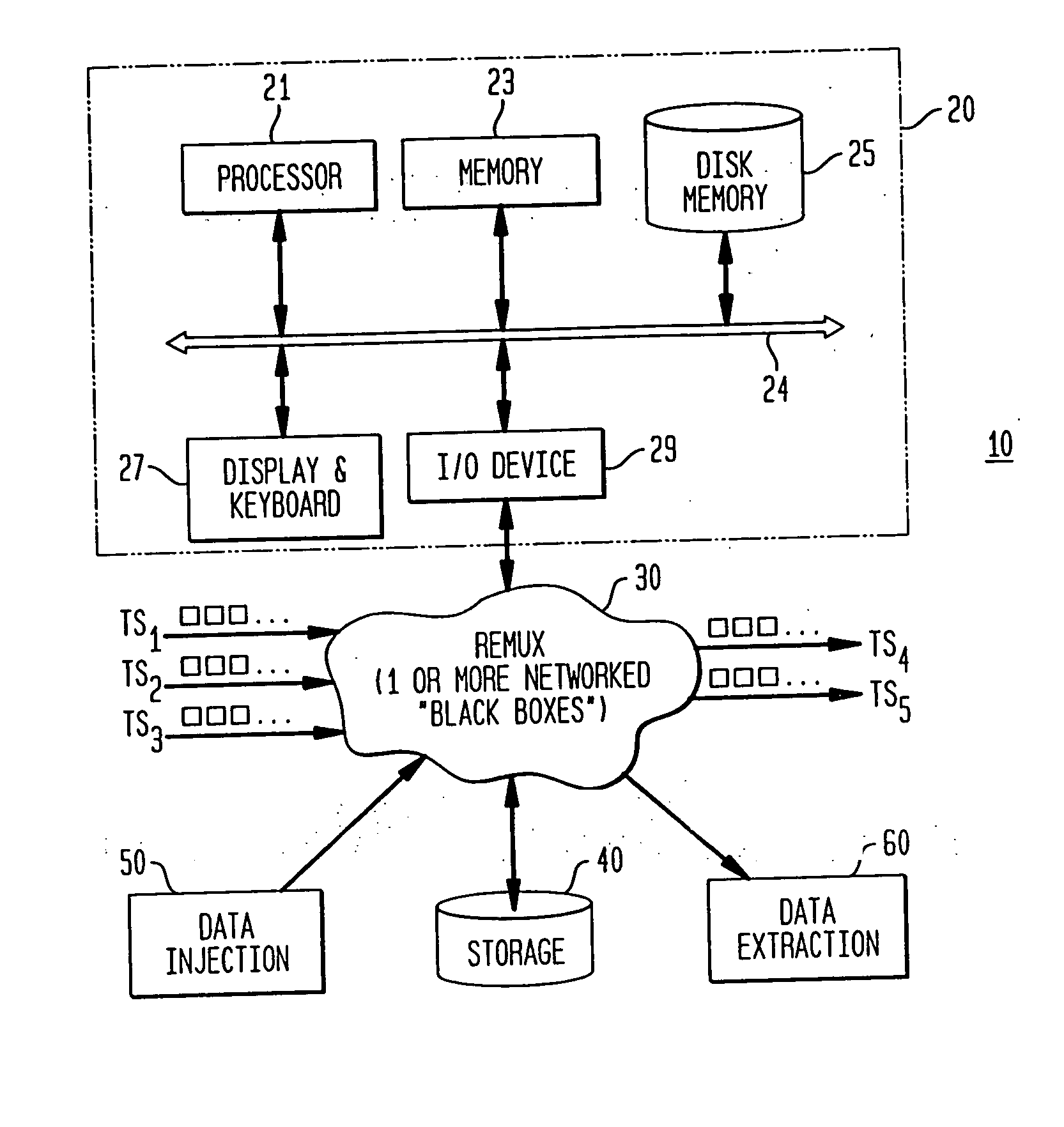
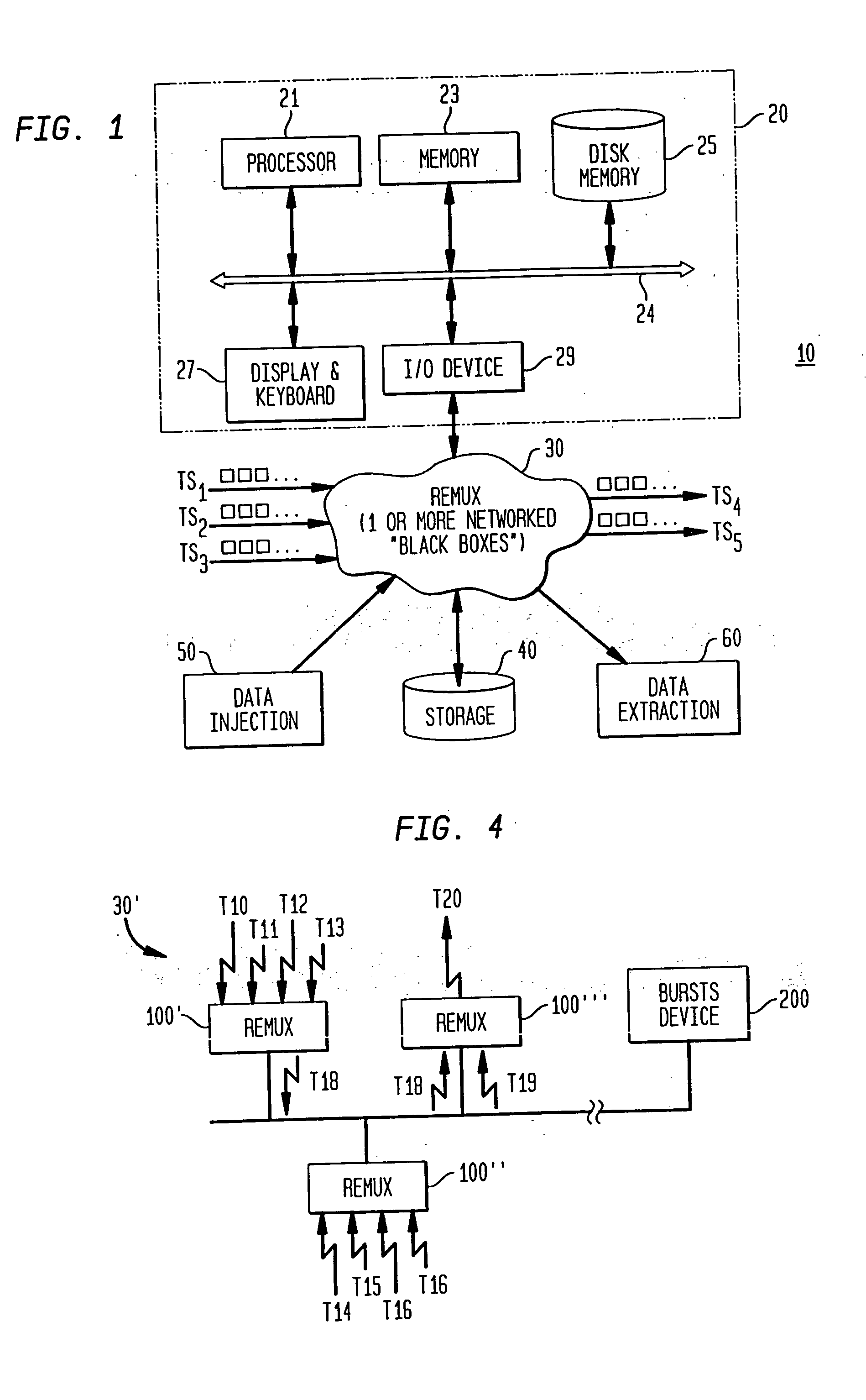
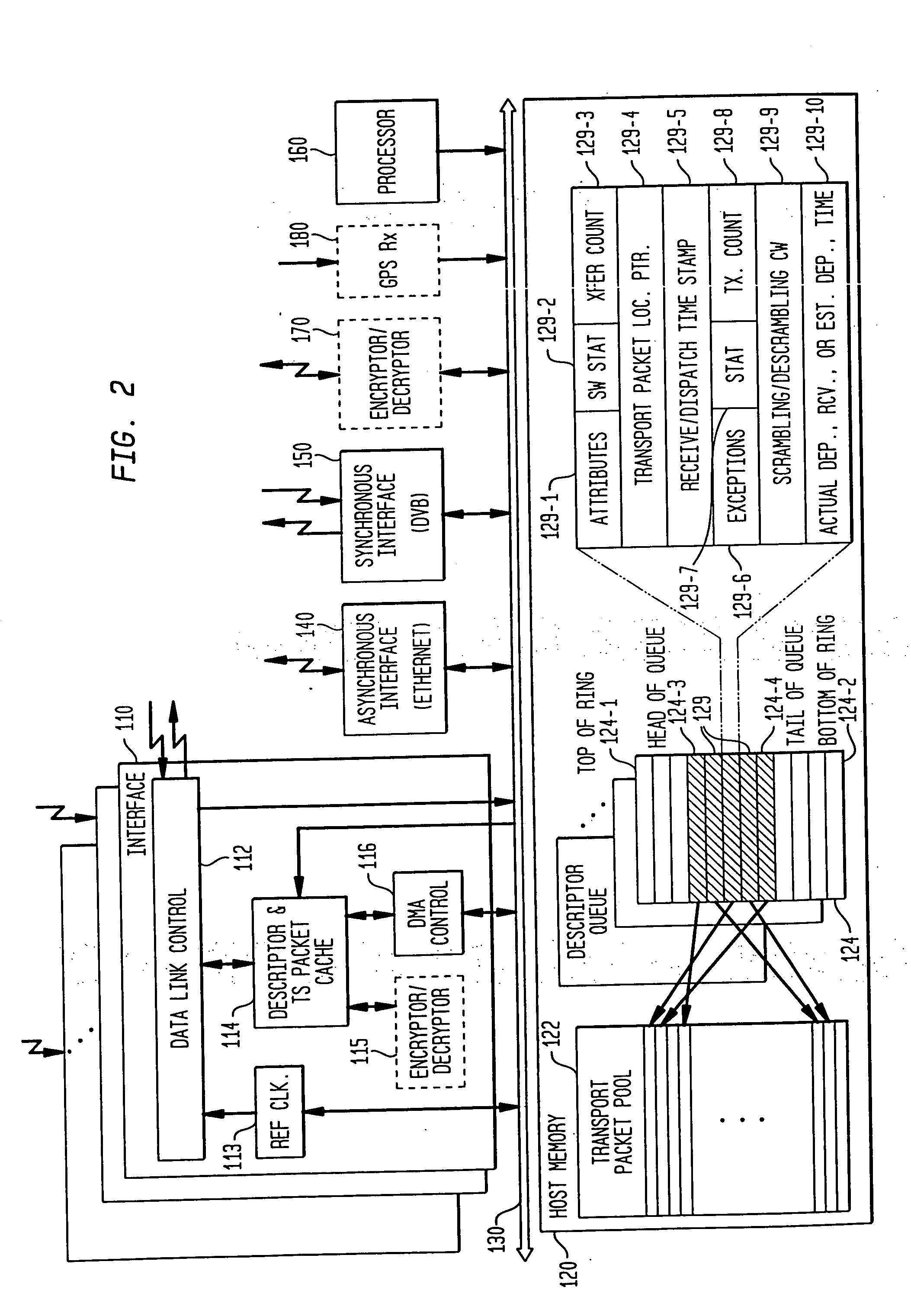
A method and system are provided for remultiplexing program bearing data. The remultiplexing method and system are applicable to MPEG-2 compliant transport streams carrying video programs. A descriptor based system is used for scheduling the timely output of transport packets wherein each descriptor records a dispatch time as well as a receipt time for each transport packet. The receipt time is used for estimating program clock reference adjustments, but final program clock reference adjustment is performed in hardware in relation to the precise output timing of each transport packets. A descriptor and transport packet caching technique is used for decoupling the synchronous receipt and transmission of transport packets from any asynchronous processing performed thereon. The descriptors can also be used for managing scrambling and descrambling control words (encryption and decryption keys). Remultiplexing functions may be distributed across a network. The remultiplexer can furthermore optimize the bandwidth of transport streams by replacing null transport packets with transport packet data to be inserted into the output transport stream. Program data transmitted via asynchronous communication links is re-timed and assistance is provided for outputting program data on such asynchronous communication links to reduce a variation in end-to-end delay incurred by the program data. Remultiplexing and program specific information can be searnlessly dynamically varied without stopping, or introducing a discontinuity in, the flow of outputted transport packets. A technique is also provided for locking multiple internal reference clock generators.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Method for scheduling transmissions in an ad hoc network
InactiveUS20080123682A1Lower end-to-end latencyNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionData sourceTrial and error
This invention relates to a method for scheduling and synchronizing all transmissions of data in an ad hoc network. Data is transmitted on a given path from a given source of the data to a given destination. Time is divided into cycles and in each cycle each node in the path transmits data belonging to the path during the same time slot reserved for that node and path. Time slots have arbitrary sizes, are reserved via trial and error, and the time slot schedule is iteratively optimized to reduce end-to-end delay using local coordination rules between nodes. The scheduling method can be used for wireless, wired, acoustic or optical networks.
Owner:YACKOSKI JUSTIN MICHAEL +1
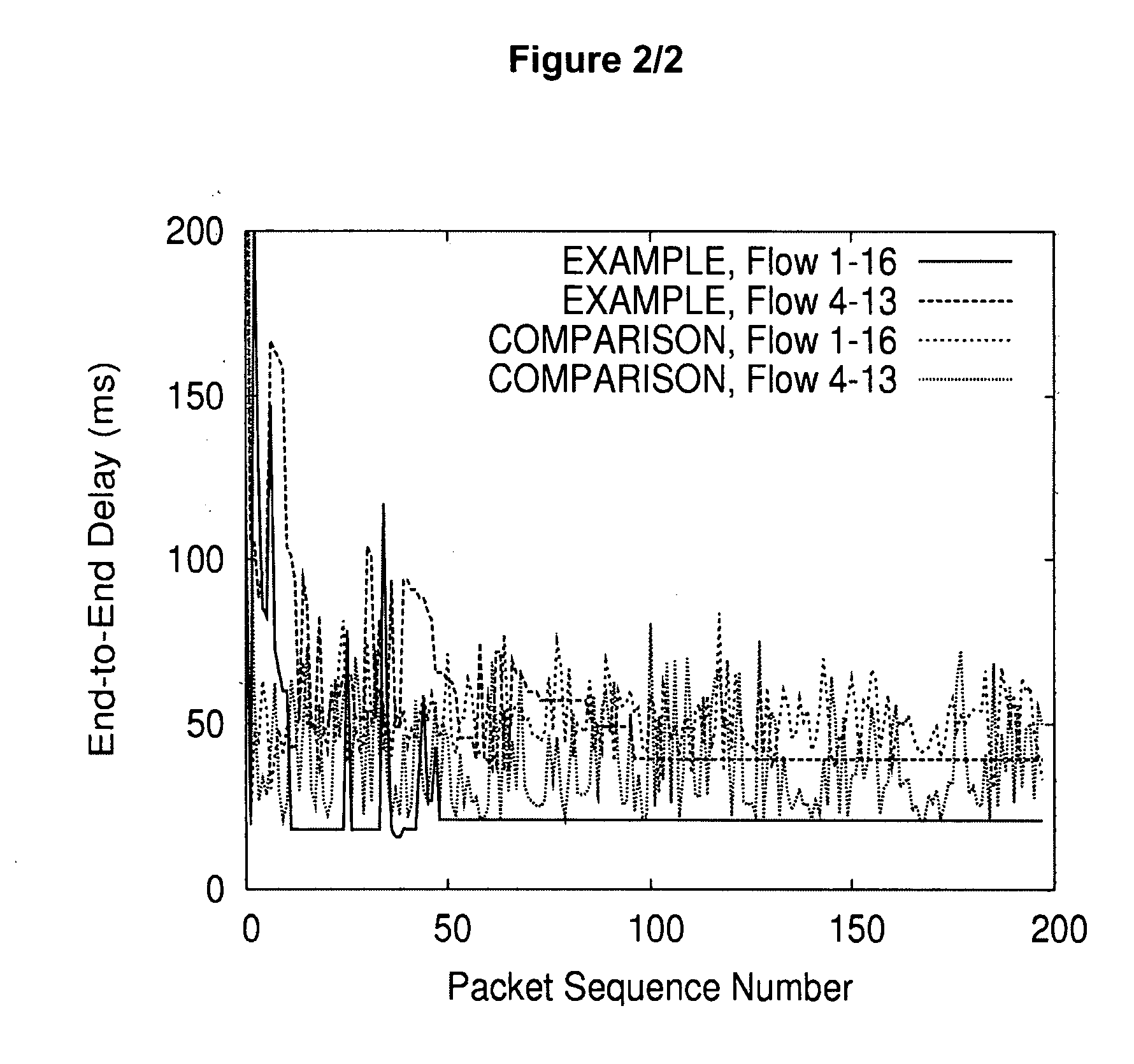
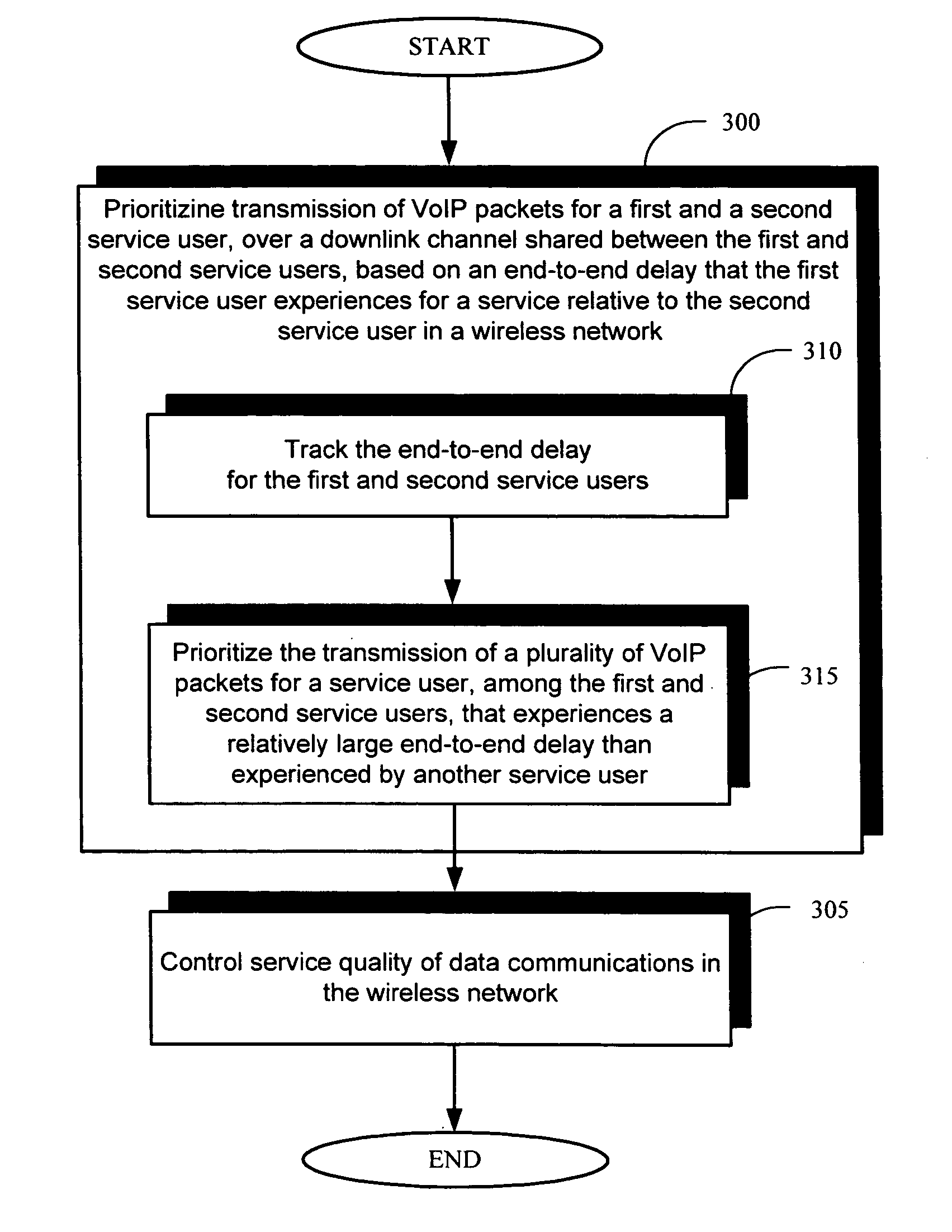
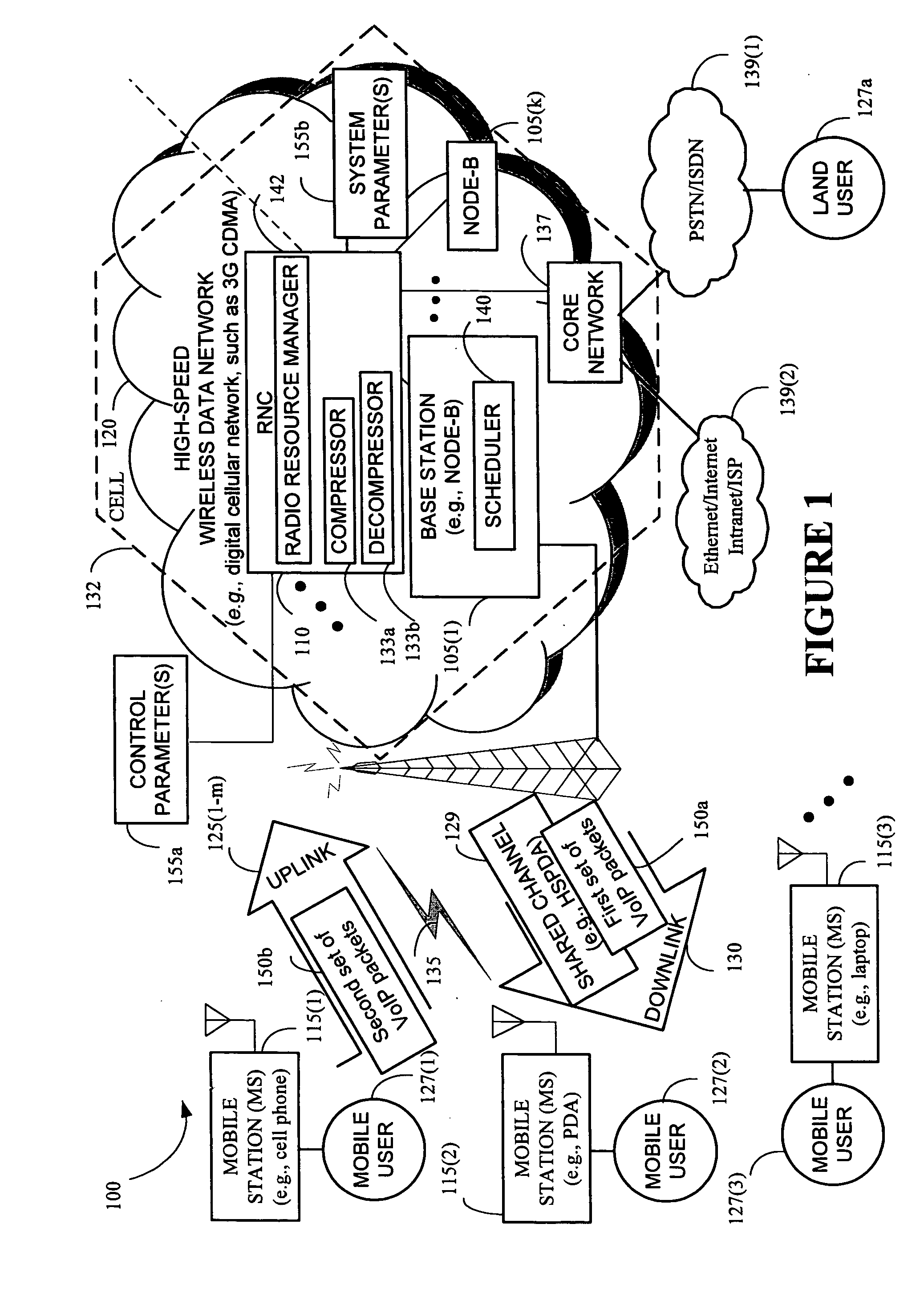
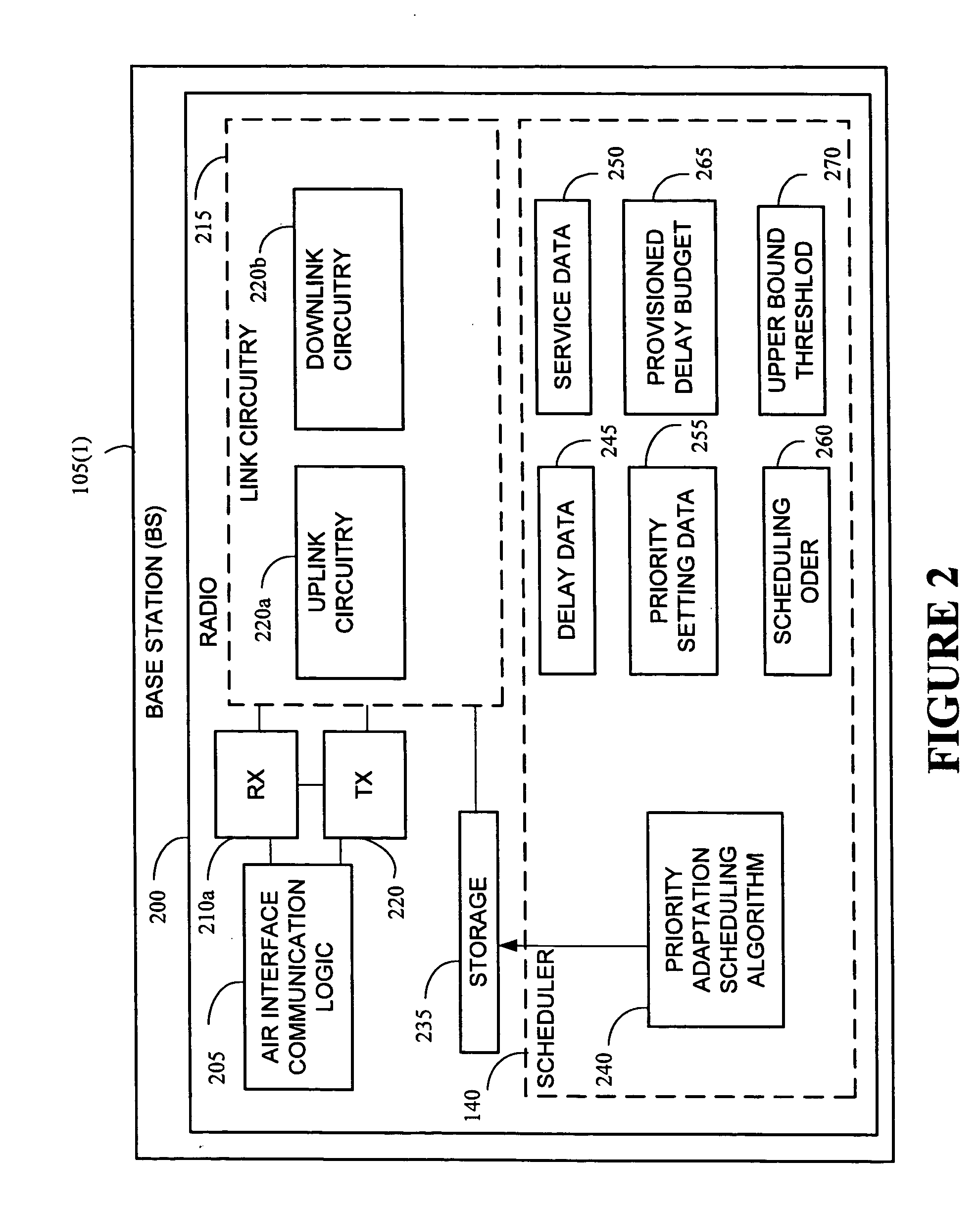
Controlling service quality of voice over Internet protocol on a downlink channel in high-speed wireless data networks
InactiveUS20070025264A1Lower quality of serviceError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceCommunications system
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for controlling service quality of data communications in a wireless network in which quality of service control for voice over internet protocol packets is provided on a downlink shared channel. A method is provided for a wireless communications between at least a first and a second service user. The method comprises prioritizing transmission of voice over internet protocol packets for the first and second service users over a shared downlink channel based on a first end-to-end delay that the first service user experiences relative to a second end-to-end delay that the second service user experiences. For example, such a priority adaptation may provide quality of service control for voice over internet protocol over a high-speed downlink packet access channel based on an end-to-end delay that a mobile-to-mobile user may be currently experiencing relative to a mobile-to-land user. In this way, a scheduler at a base station of a communications system may maximize use of voice over internet protocol capacity while maintaining an acceptable level of end-to-end delay for different users of mobile stations.
Owner:RPX CORP
Unit and a method for handling a data object
InactiveUS20060104201A1Simpler and efficient wayError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital objectDatabase
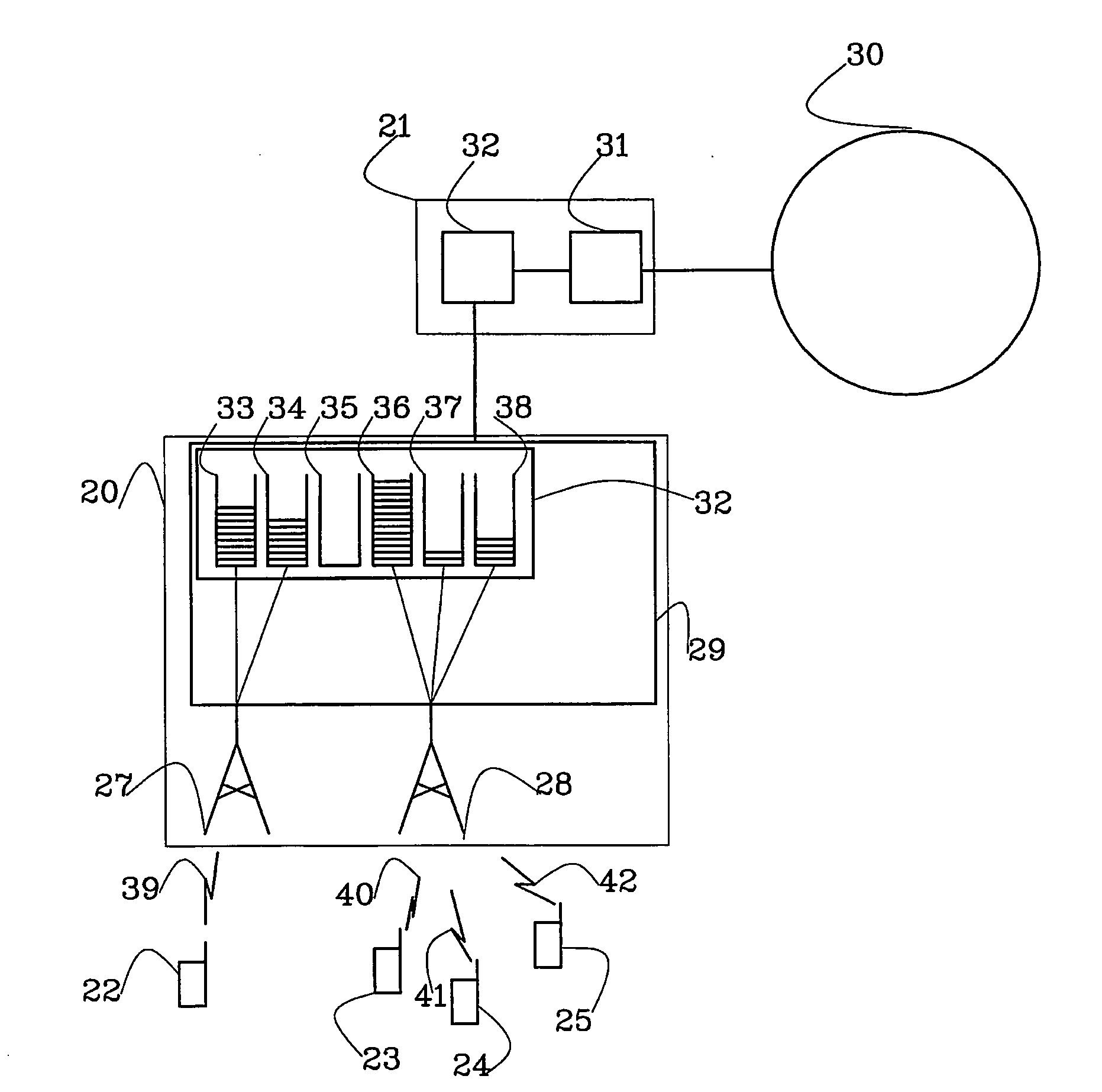
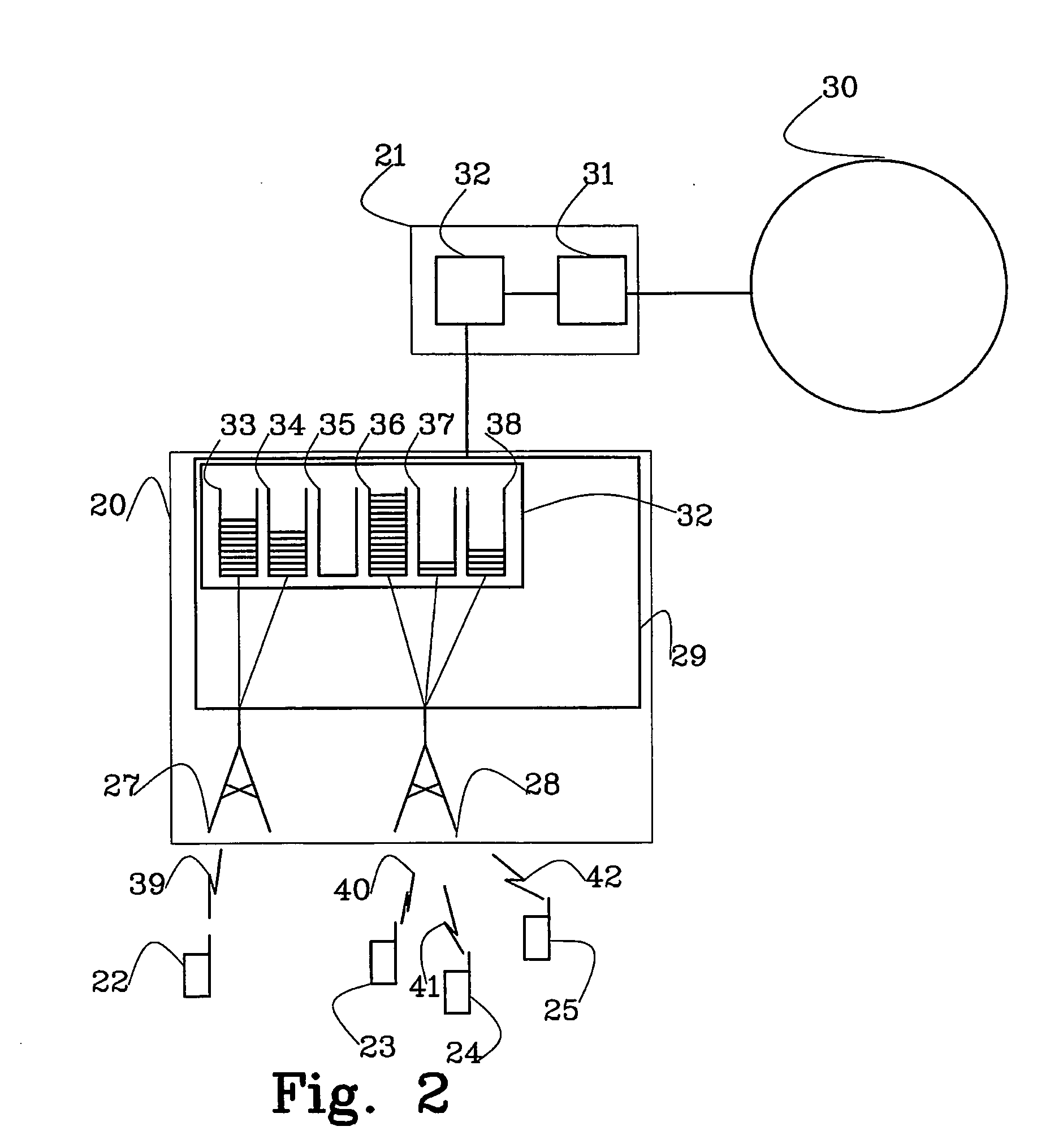
The present invention relates to a unit and a method for handling a data object that is to be transmitted over a link (39, 40, 41, 42), said data object being divided into at one least data unit. According to the invention the data unit that is in turn to be transmitted over the link (39, 40, 41, 42) should be handled differently depending on where a buffer fill level in a buffer (33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38) preceding the link (39, 40, 41, 42) is in relation to at least one buffer threshold (51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59) in order to minimise end-to-end delay.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for processing packetized data in a wireless communication system
Adaptive De-Jitter Buffer for Voice over IP (VoIP) for packet switch communications. The de-jitter buffer methods and apparatus presented avoid playback of underflows while balancing end-to-end delay. In one example, the de-jitter buffer is recalculated at the beginning of each talkspurt. In another example, talkspurt packets are compressed upon receipt of all remaining packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
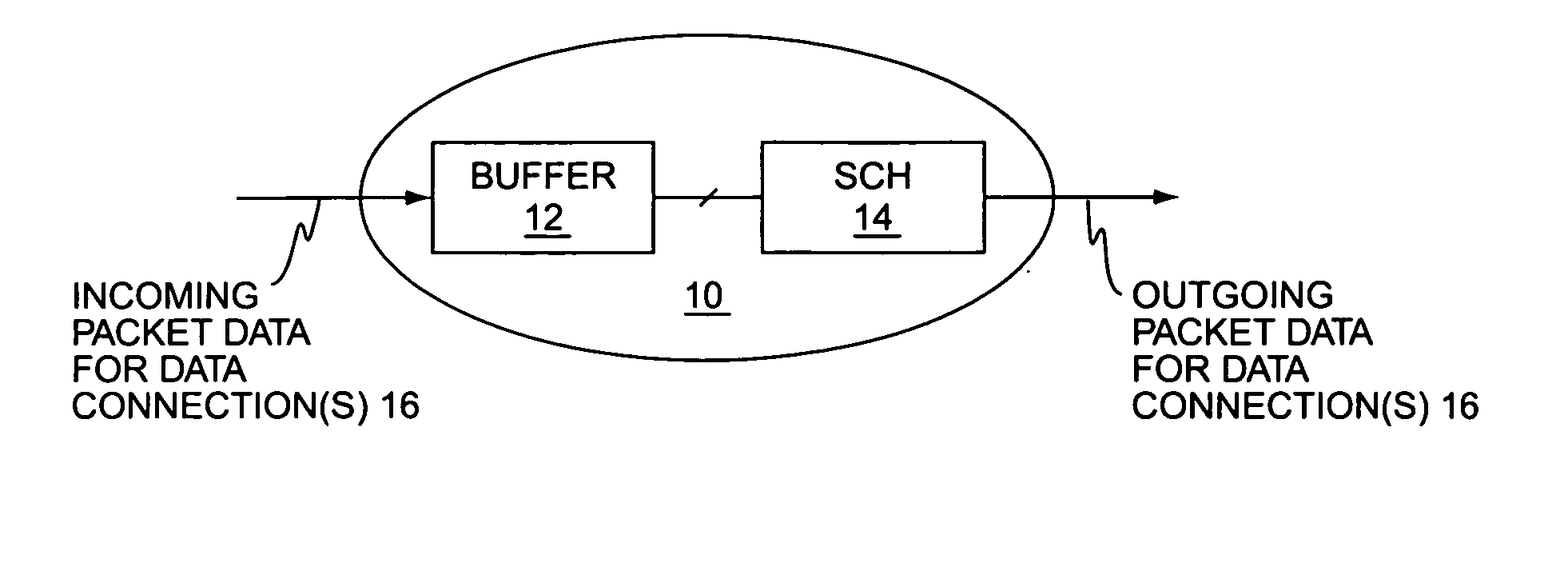
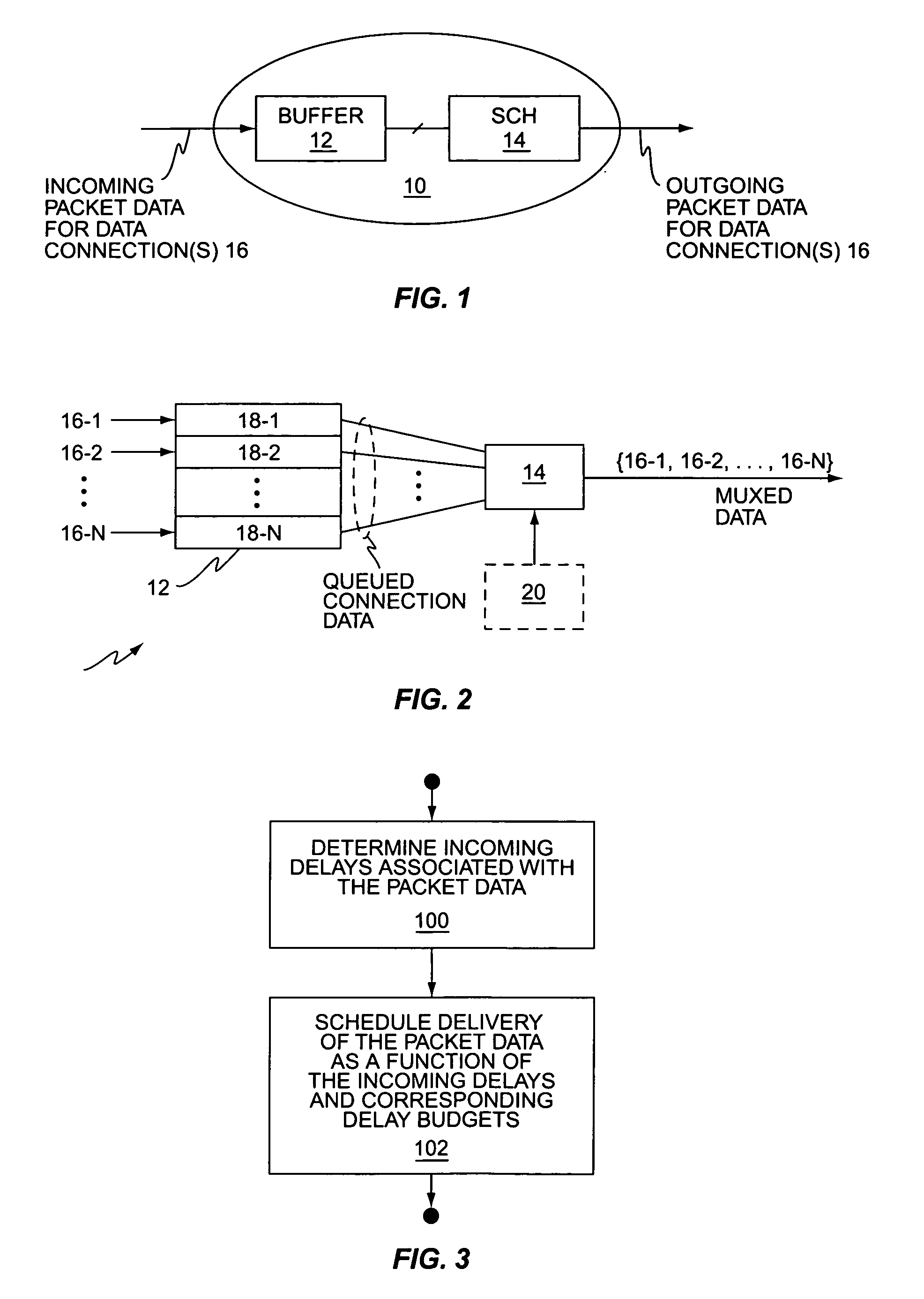
Method and apparatus for improving scheduling in packet data networks
InactiveUS20060268713A1Reduces and eliminates violationIncreases scheduler 's overall capacityError preventionTransmission systemsTemporal informationData connection
A method of scheduling packet data delivery by a communication network node uses knowledge of the incoming delays and corresponding delay budgets associated with the packet data to be scheduled. For example, a wireless communication network base station may serve a plurality of users via a time-multiplexed packet data channel, and may schedule the delivery of packet data targeted to individual ones of those users based on determining the allowable scheduling delays for the incoming packet data it receives for those users. The allowable scheduling delays for packet data received on a given data connection may be determined based on the incoming delays associated with that packet data and the corresponding end-to-end delay budget defined for that packet data. The incoming delays may be calculated from packet time information, e.g., timestamps, and / or may be estimated based on call type, network type, network distances / locations, network conditions, etc.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
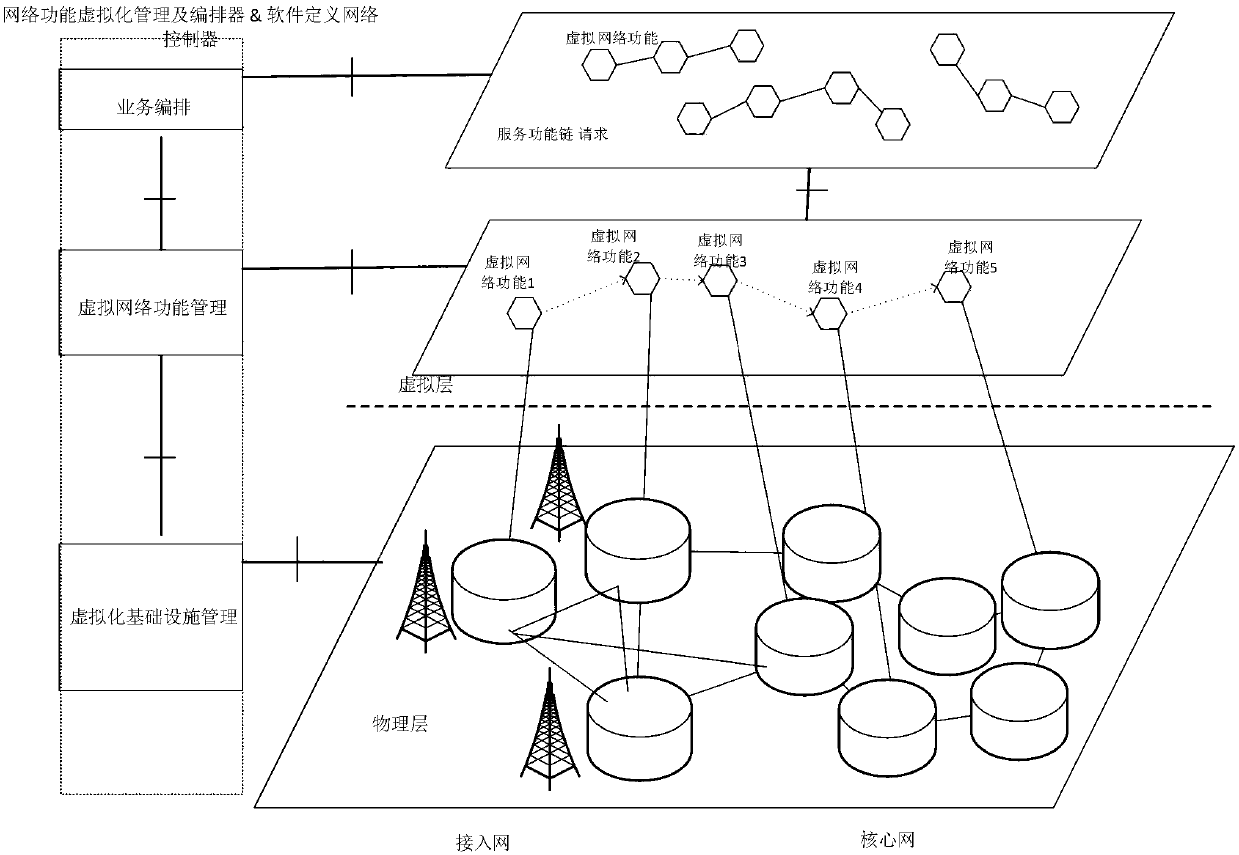
Service function chaining dynamic deployment method based on QoS (Quality of Service) guarantee
ActiveCN108260169AImprove reliabilityLoad balancingNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksQuality of serviceResource utilization
The invention relates to a service function chaining dynamic deployment method based on QoS (Quality of Service) guarantee and belongs to the technical field of mobile communication. According to themethod, on the basis of 5G network slicing, resources are flexibly configured through utilization of a software defined network and a network function virtualization technology. In order to improve the QoS of communication business in slice networks, a reliability requirement oriented service function chaining deployment model is established. According to the model, a service function chaining dynamic deployment scheme based on the QoS guarantee is designed with the purpose of minimizing the end-to-end delay. According to the scheme, node positions and reliability are taken into comprehensiveconsideration; virtual network functions are deployed through utilization of a novel node arrangement method, and the load of the networks is balanced. In a chaining mapping process, the QoS is improved through selection of the delay shortest path which satisfies a reliability requirement. According to the method, the end-to-end delay of the service function chaining is reduced, the deployment reliability is ensured, and a request acceptance rate and a resource utilization rate are improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Routing protocol design method based on link quality and node forwarding capacity
ActiveCN105657777AComprehensive assessmentAccurate and reliable reflectionNetwork topologiesNetwork packetRanking
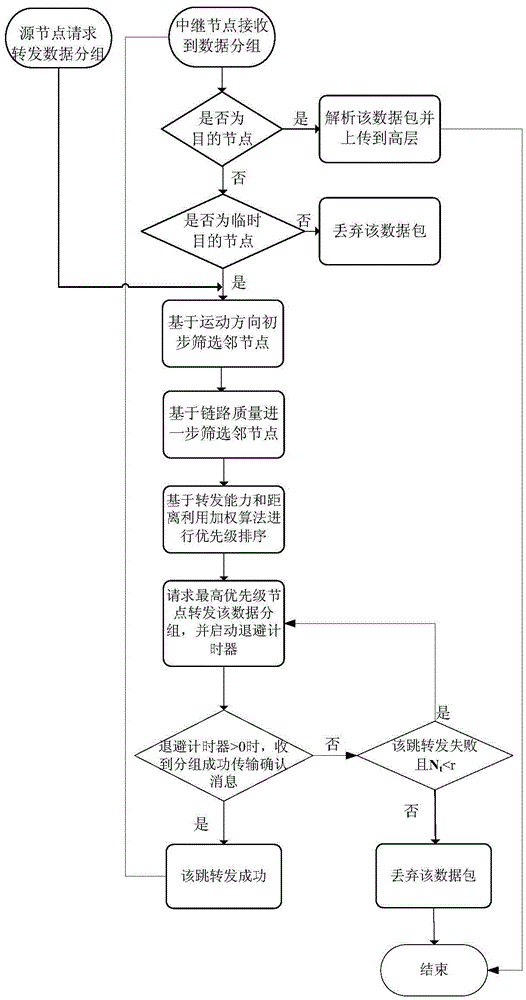
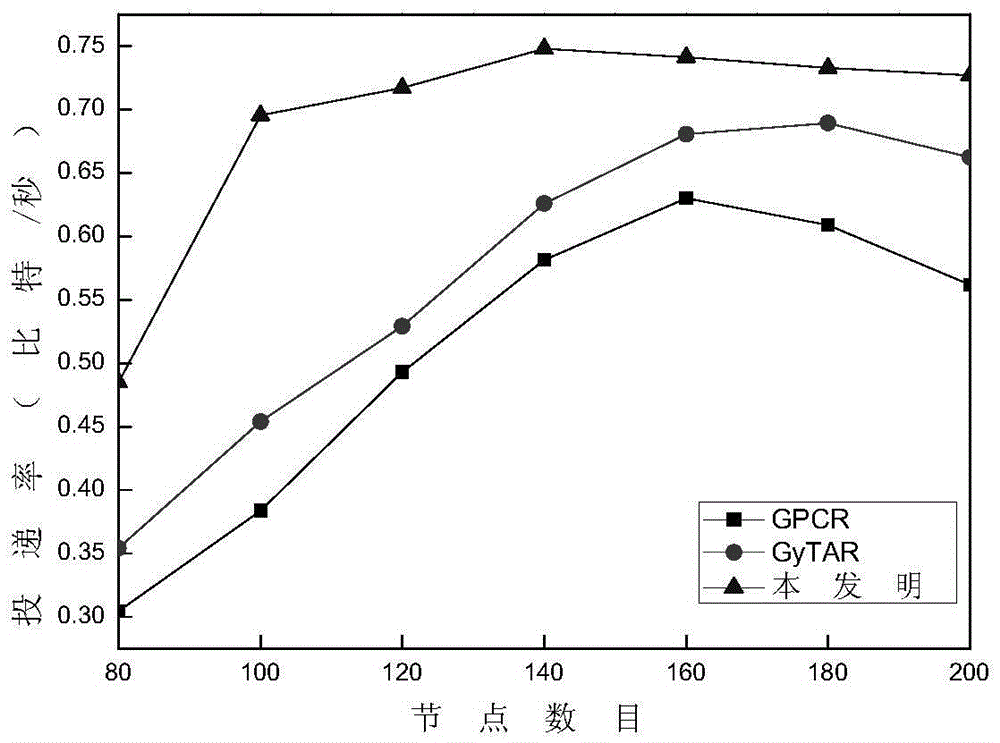
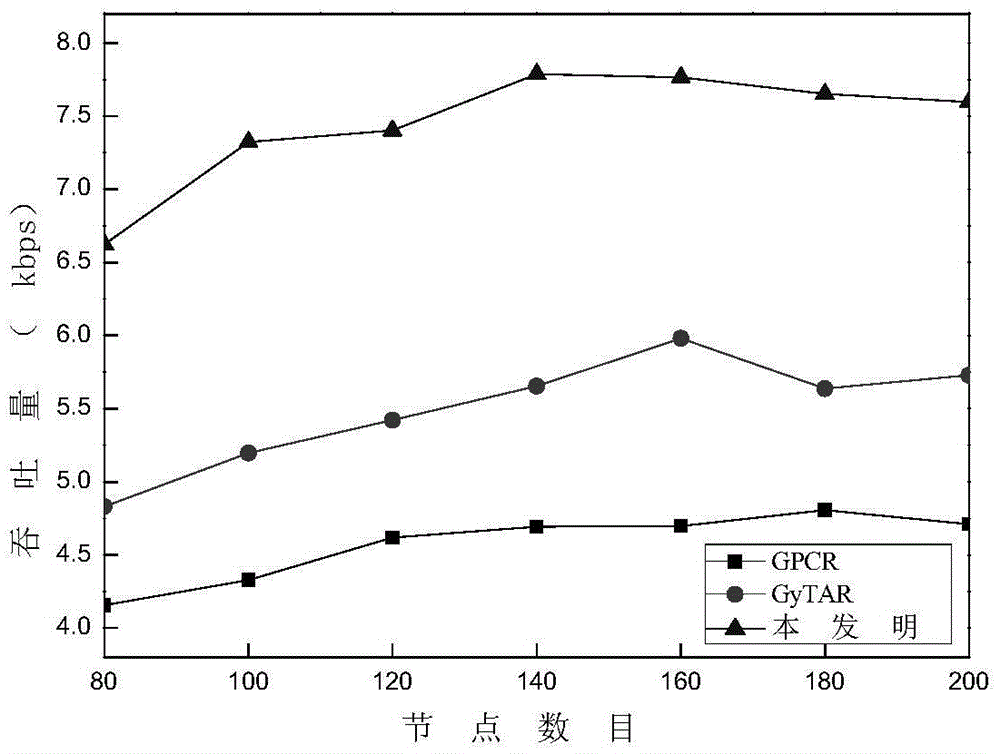
The invention discloses a routing protocol design method based on link quality and node forwarding capacity. The problems that in an existing routing protocol based on the geographic position, data grouping end-to-end transmission path selection is low in efficiency, consequently, the data grouping delivery rate is small, and network throughput is small are solved. The realizing scheme includes the steps that parameters which are related to node quality and include the motion direction, the distance, the link quality and internal forwarding capacity are calculated; then, candidate adjacent node set selection and node priority ranking are conducted through a screening mechanism and a weighting algorithm; based on a candidate adjacent node set and node priority information, an opportunity forwarding strategy is executed on data grouping. On the premise of ensuring acceptable data grouping end-to-end delay, the delivery rate of data packages and the network throughput are increased. The routing protocol design method can be applied to communication among vehicles in car networking, effective information exchange among the vehicles is achieved, and safety and efficiency of vehicle traffic are improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
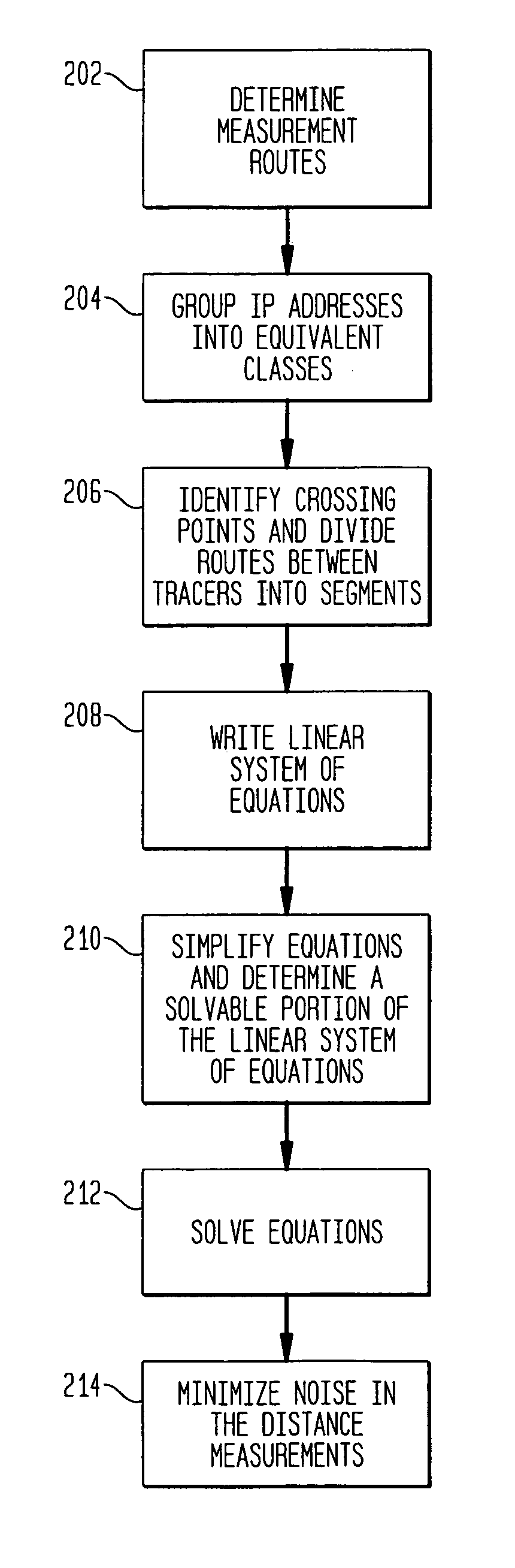
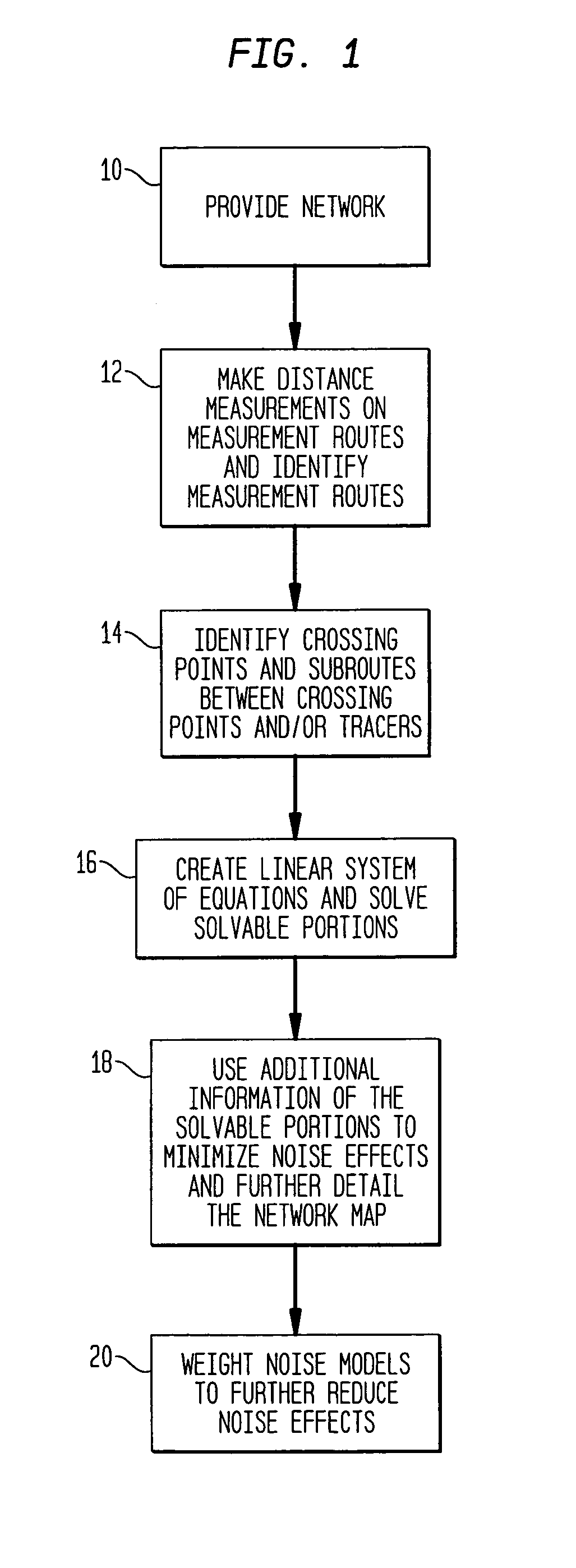
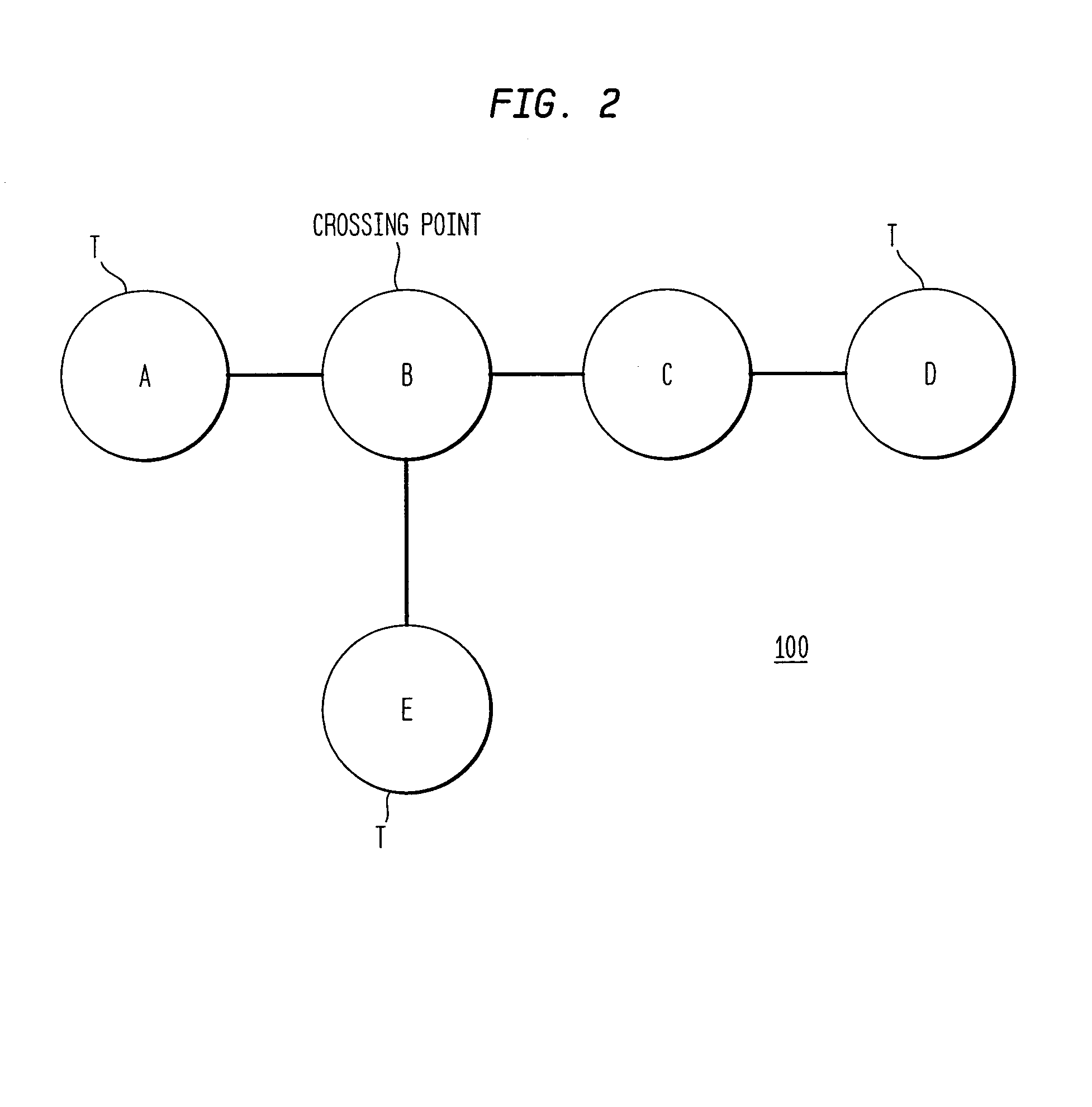
Method and apparatus for network mapping using end-to-end delay measurements
A method for mapping a network, in accordance with the present invention, includes providing distance measurements between tracers in the network, determining routes along which the distance measurements are made, and creating a system of equations which links the distance measurements between the nodes with a sum of the delays between the nodes which comprise the routes. Additional information is extracted about distances of subpaths of the routes to provide additional details to a map of the network. The additional information provides a capability of estimation of distances between nodes without tracers.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
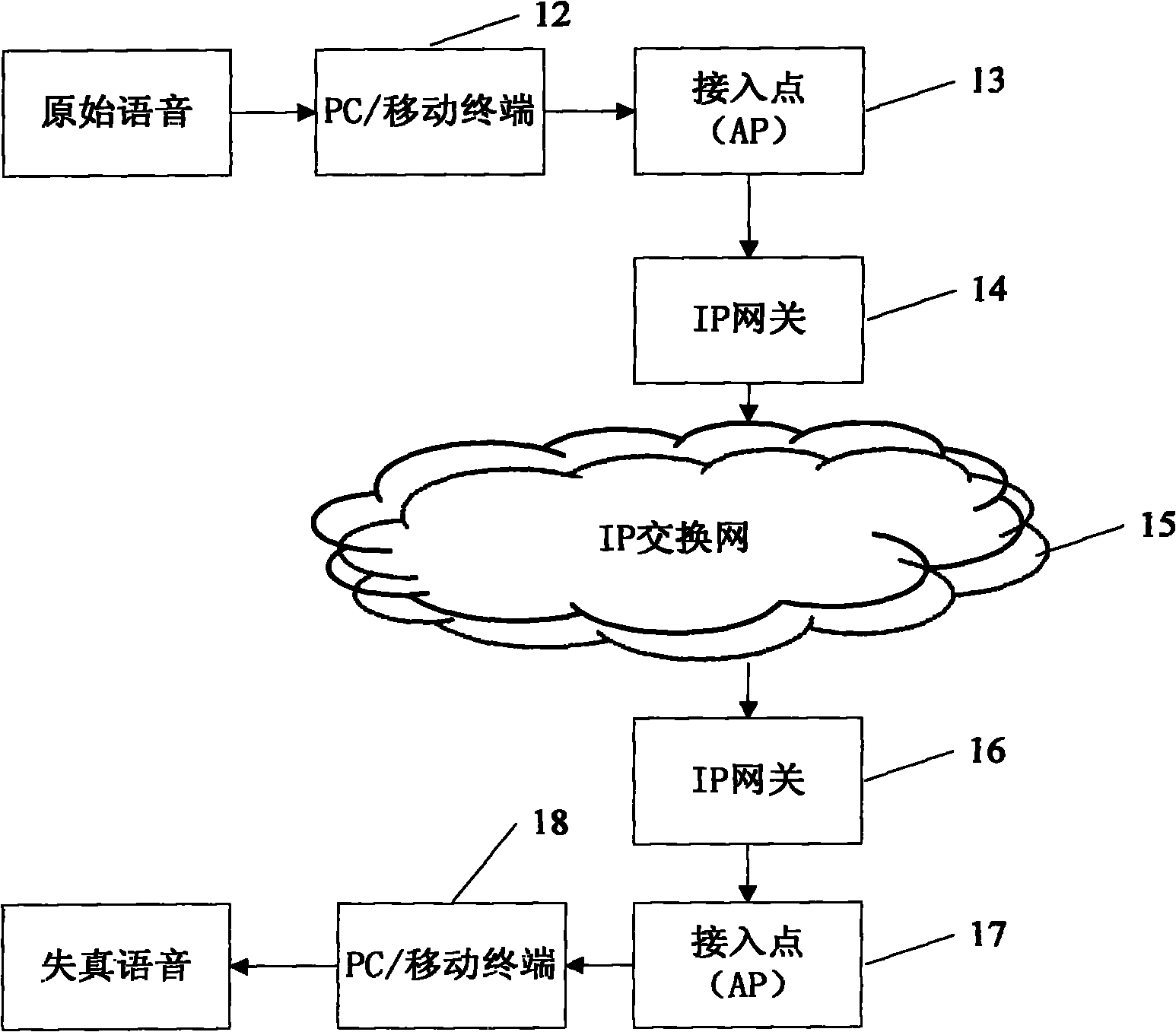
Objective evaluation method for VoIP speech
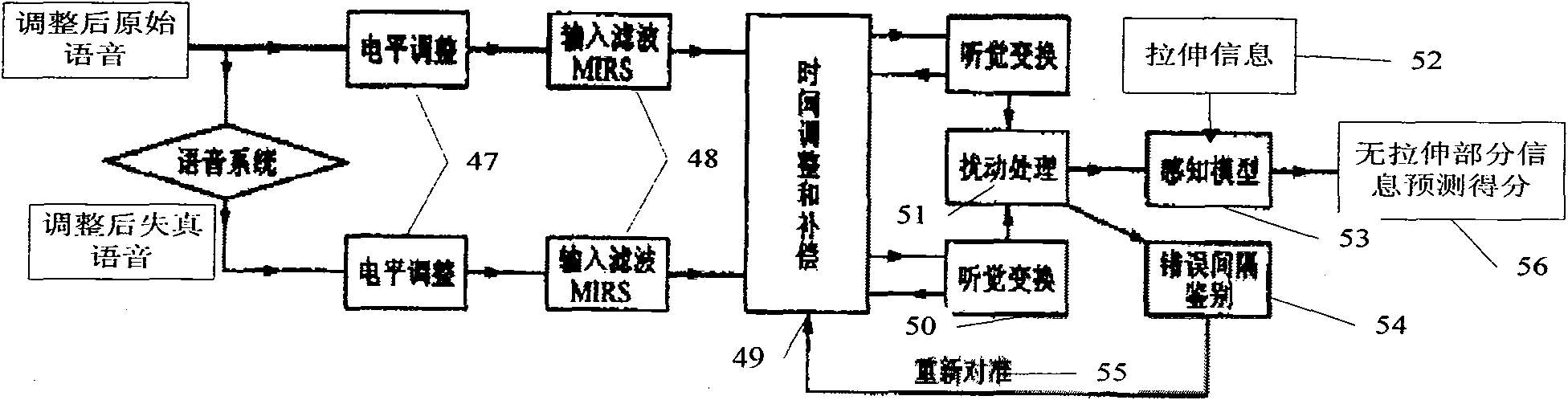
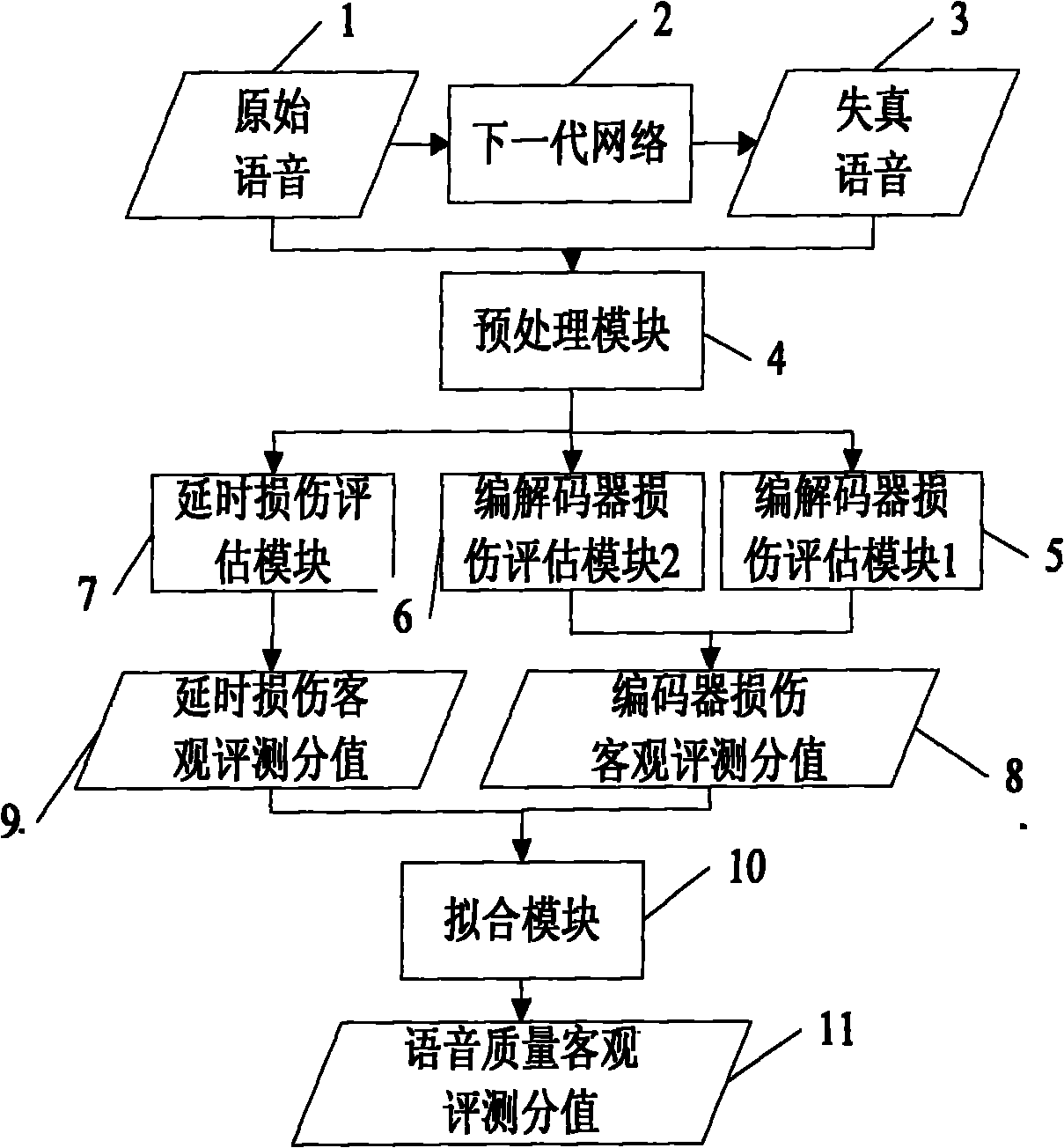
The invention discloses an objective evaluation method for VoIP speech, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring original speech at a transmitting end of VoIP; acquiring distortion speech introducing damage at a receiving end; differentiating the original speech and the distortion speech through a pre-processing module to acquire statement information, calculating coder / decoder damage of aligned statements by using a coder / decoder damage assessment module A, calculating the quality damage of the stretched or compressed statements by using a coder / decoder damage assessment module B, and evaluating the influence of end-to-end delay and internal delay on the speech by using a delay damage assessment module; and finally acquiring an objective evaluation score of speech quality by using a fitting module. The method evaluates the speech quality by using a network coder / decoder, an adaptive jitter buffer and the like, is more accurate compared with the method only using perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ), considers the delay damage, and also can evaluate the session quality. Meanwhile, compared with the correlation degree with a subjective score acquired by an E model, the method is more suitable for objectively evaluating the speech with network damage.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
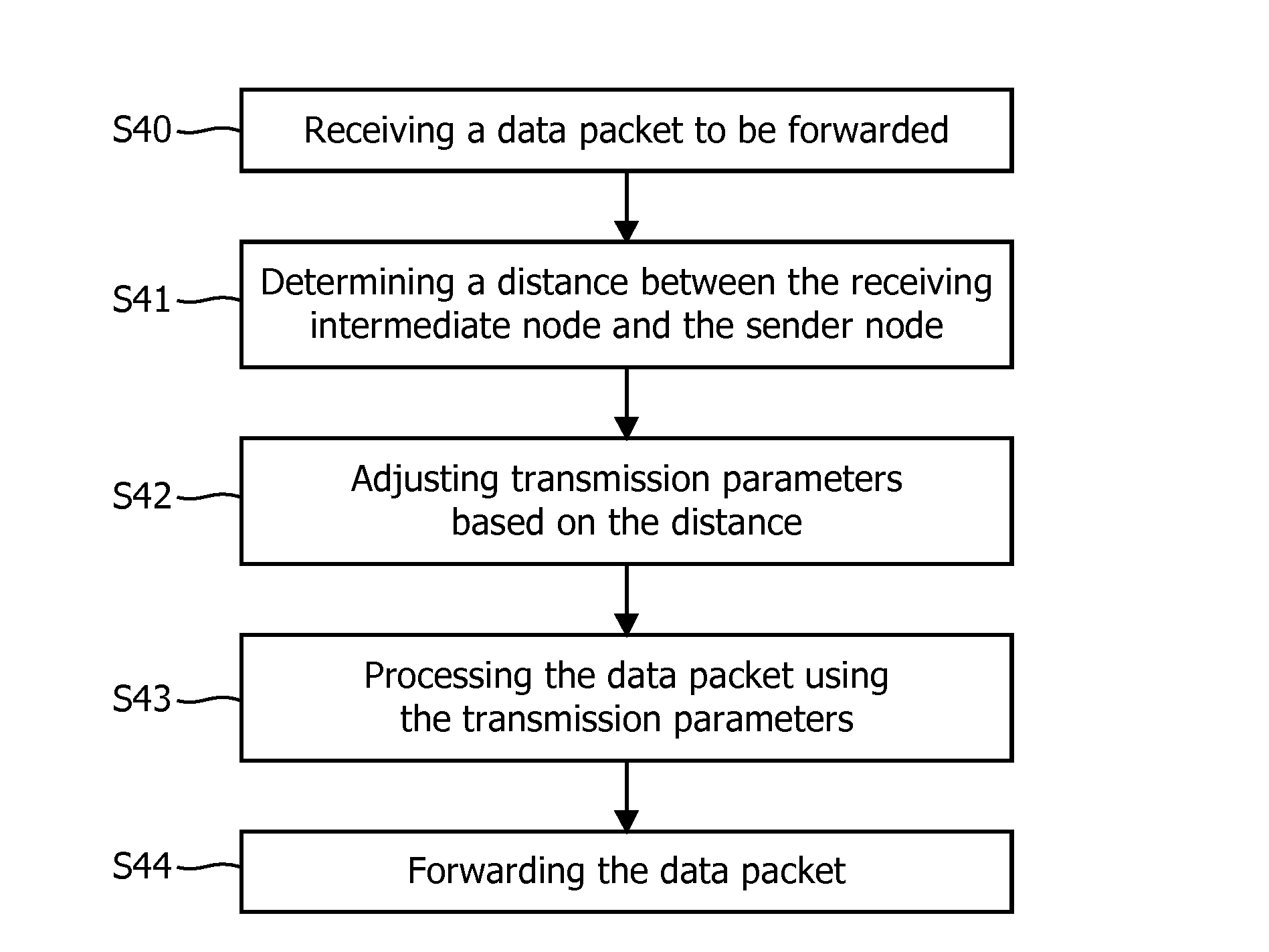
Device and method for delay optimization of end-to-end data packet transmissions in wireless networks
ActiveUS20130188562A1Minimize and homogenizeImprove scalabilityNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless commuication servicesWireless mesh networkWireless network coding
For reducing and homogenizing an end-to-end delay of data packet transmissions in a large-scale wireless mesh network, a device, a system and a method are provided for controlling data packet transmission in the wireless network, wherein transmission parameters of an intermediate node are adjusted based on a distance between the intermediate node and a sender node.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Wireless Mesh intelligent power grid routing mechanism with QoS perceiving and loading balancing
ActiveCN104661260AReduce end-to-end latencyImprove delivery rateNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh level techniquesService flowPacket collision
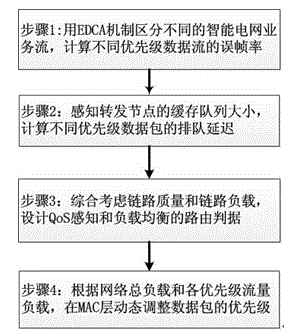
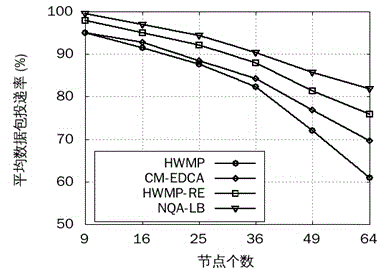
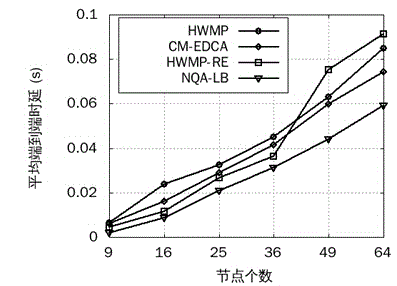
The invention provides a wireless Mesh intelligent power grid routing mechanism NQA-LB with QoS perceiving and loading balancing. The mechanism comprises four steps: firstly differentiating intelligent power grid service flows with different QoS requirements through an EDCA mechanism, and calculating the frame error rate of different service flows according to the data packet collision rate of the EDCA mechanism; secondly, calculating data packet queuing delay with different priorities of the queue length of forwarding node cache and the successful transmission probability of data packets; then designing the routing metric of QoS perceiving and loading balancing by comprehensively considering the data frame error rate and queuing delay of different service flows, and selecting an optimal path with less load for the service flow with different QoS demands; finally dynamically adjusting the data packet priority on an MAC layer according to network total loading and loading conditions of all priority service flows. The mechanism can more accurately perceive the link quality of the MAC layer, guarantees the QoS demands of different service flows of a power grid, further increases the data packet delivery rate and average throughput capacity, and reduces the end-to-end delay of all service flows.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method and apparatus for dynamically reducing end-to-end delay in multi-hop wireless networks in response to changing traffic conditions
InactiveUS20060039286A1Reduces mean end-to-end network transmission delayReduce transmission delayError preventionTransmission systemsLength measurementTraffic conditions
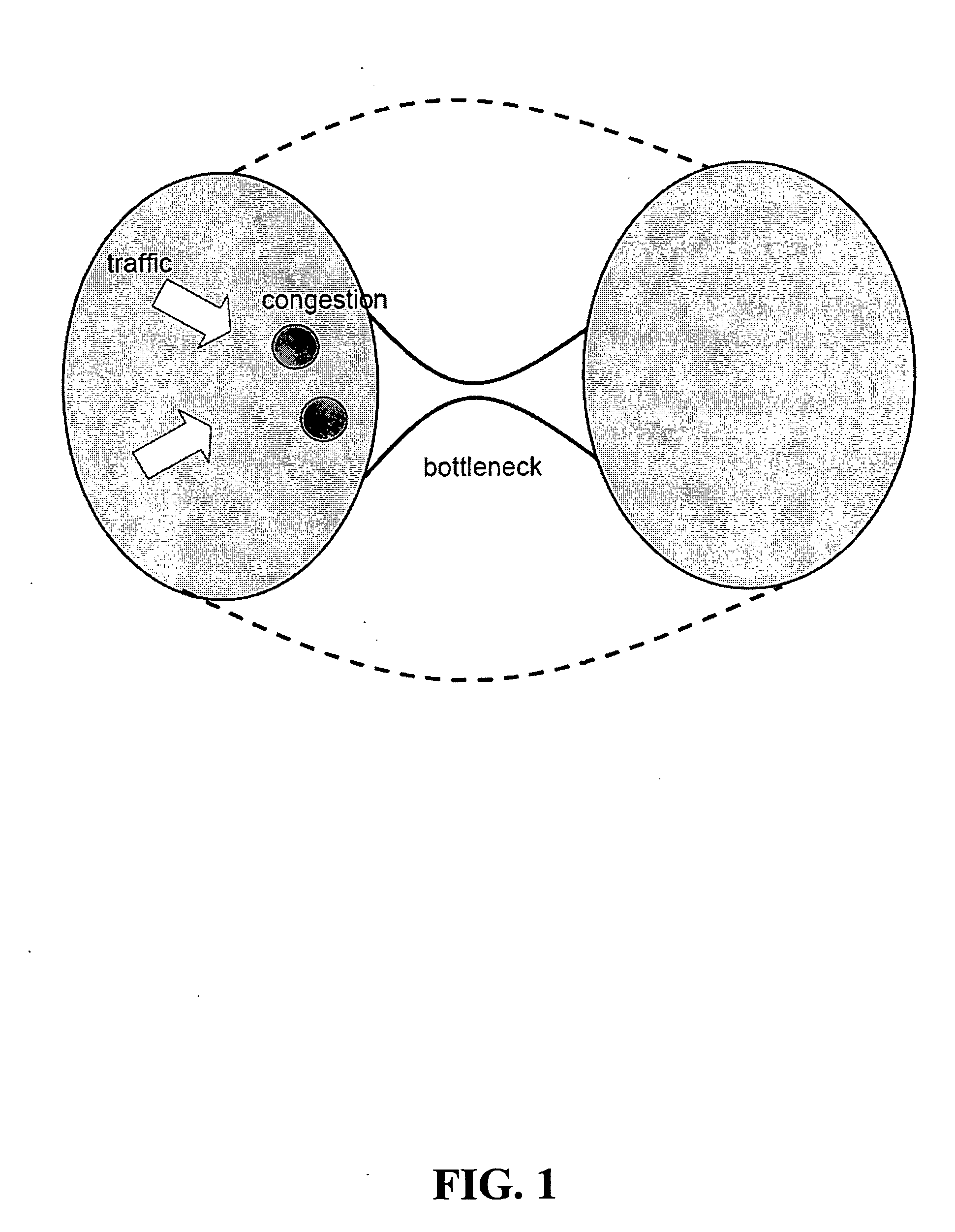
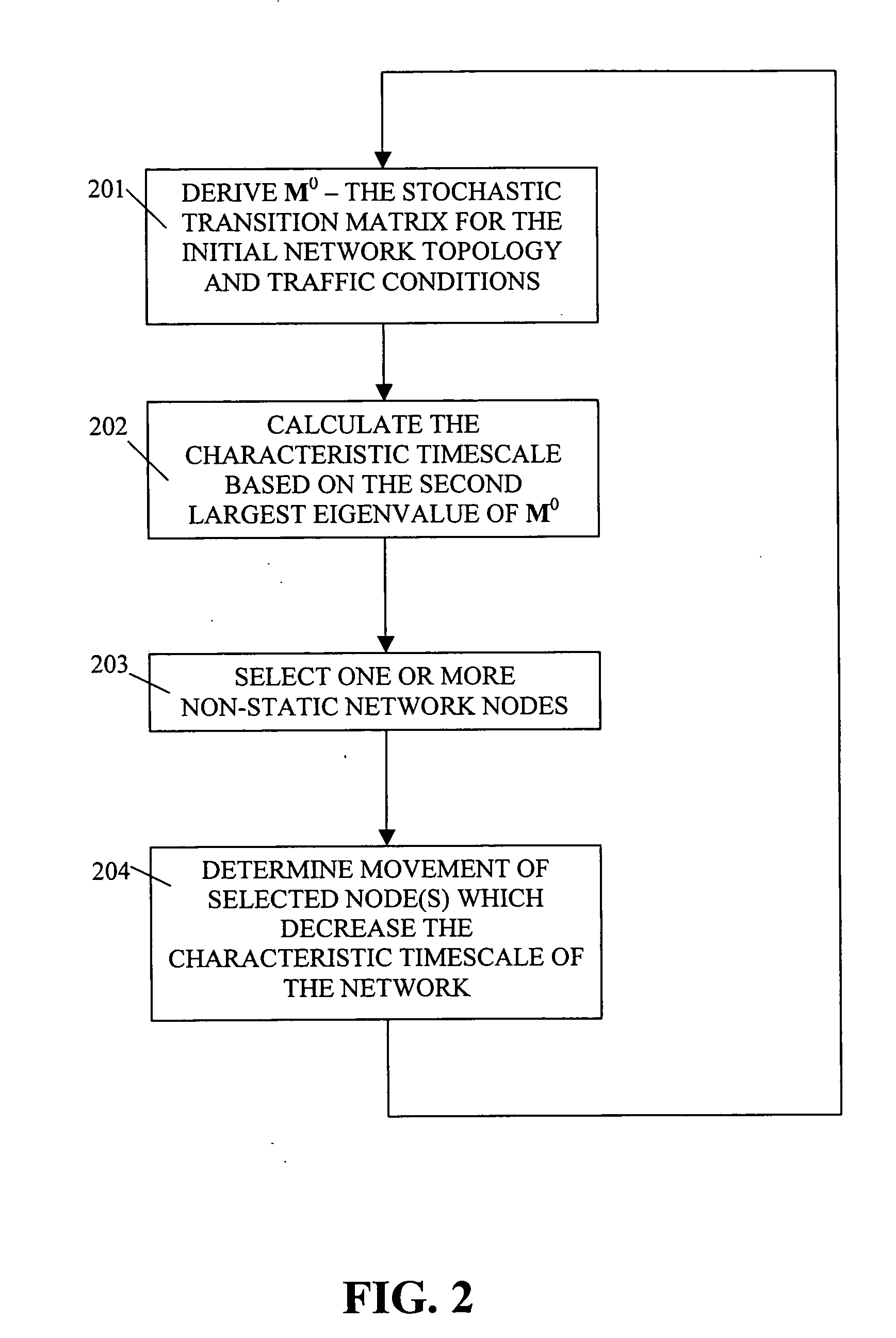
A method and apparatus for deforming the network topology of a multi-hop wireless network dynamically (i.e., in real time), in response to changing network traffic conditions and in order to advantageously reduce mean end-to-end network (transmission) delay. Two illustrative embodiments of the invention deform the network topology dynamically in response to traffic conditions (i) by changing the network connectivity between the existing network nodes and (ii) by adding one or more new nodes (and associated connections thereto and therefrom) to the network. In both cases, the traffic conditions may be fed into the algorithm in real time as, for example, a set of queue length measurements. Then, in response, the network is advantageously reorganized into a configuration that reduces the mean end-to-end network transmission delay.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
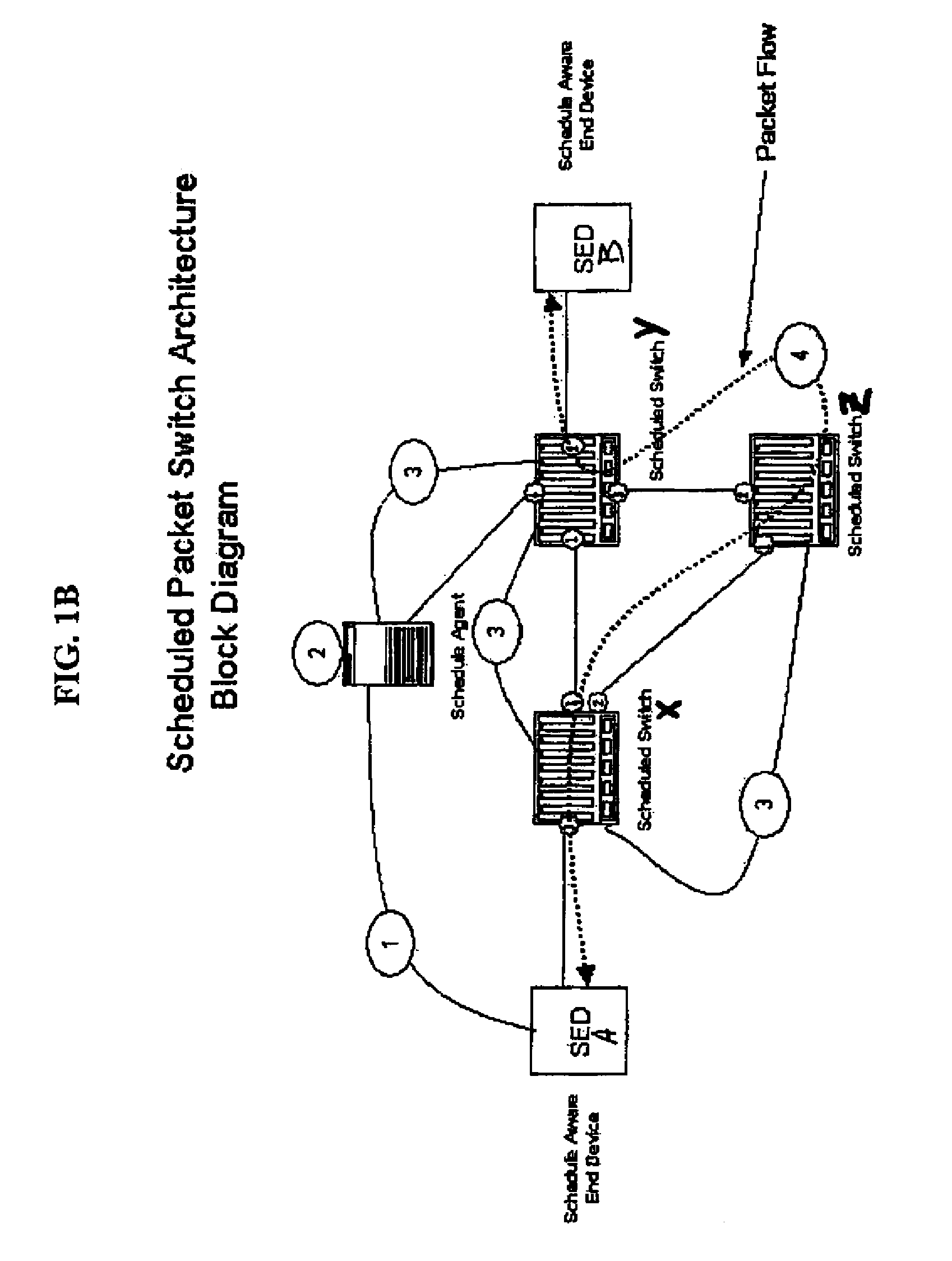
Method for achieving high-availability of itineraries in a real-time network scheduled packet routing system
ActiveUS8477616B1Reduce needGuaranteed bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsAppointment timeTopology information
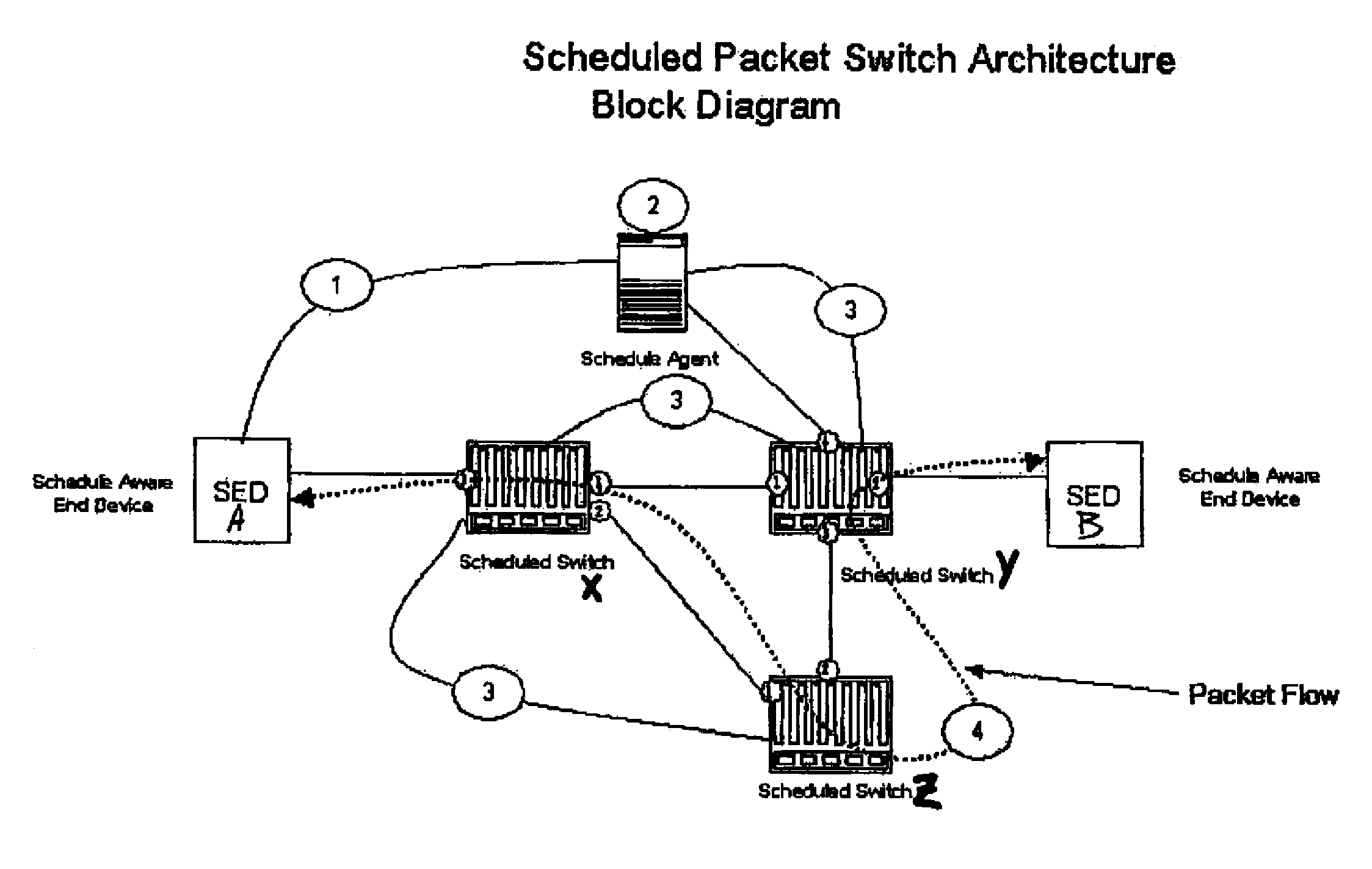
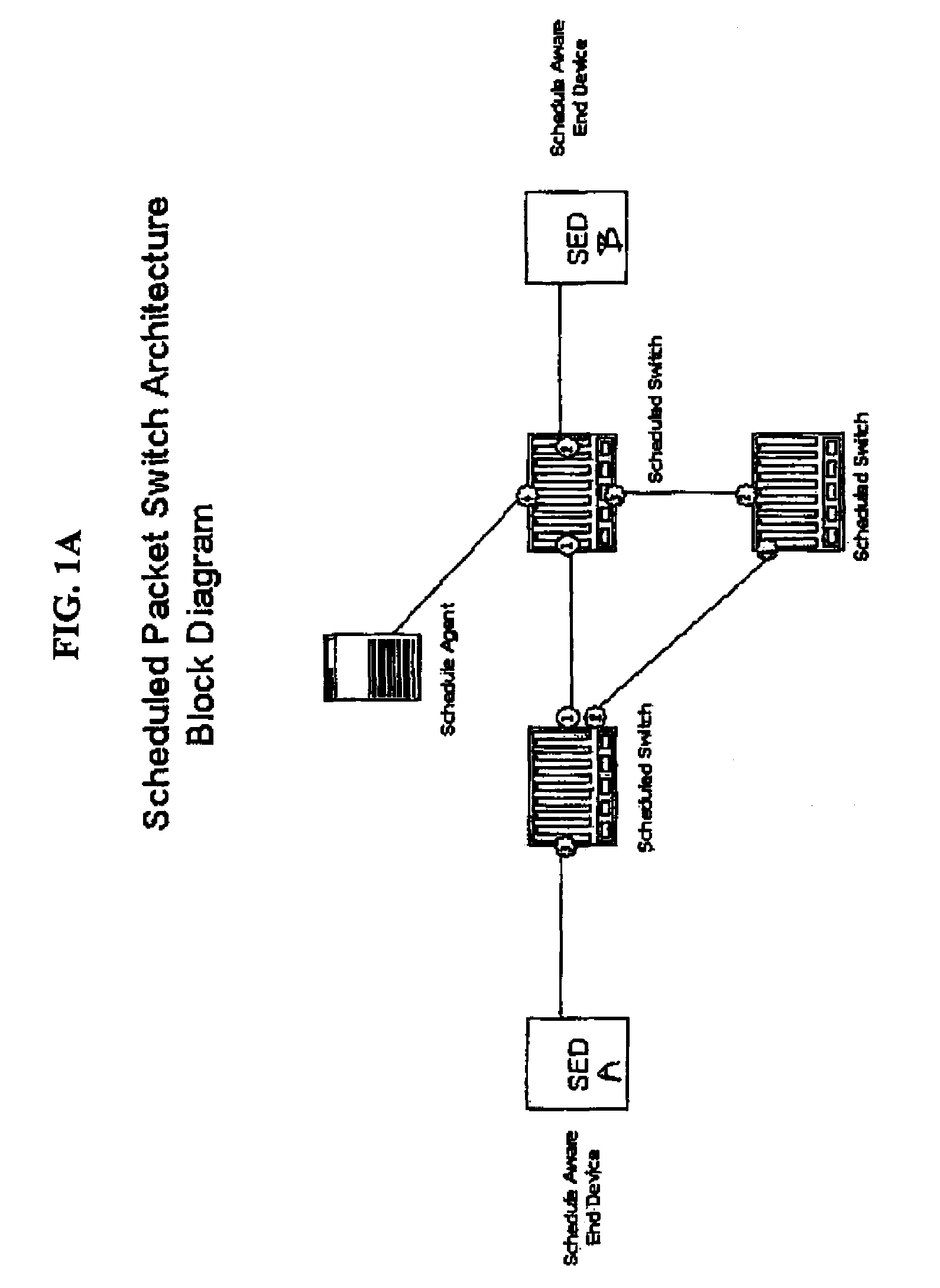
A system using scheduled times for transmission at each link guarantees bandwidth for transmitting data across a packet network. A scheduling agent determines availability of data paths across a network according to pre-selected criteria and real-time network topology information. Precise schedules are determined for transmission and reception appointments for data packets to traverse each link and switch in the network including compensation for transmission delays and switch latencies, resulting in a fixed packet flow itinerary for each connection. Itineraries are communicated to schedule-aware switches and endpoints and appointment times are reserved for transmission of the scheduled data packets. Scheduled packets arriving at each switch are forwarded according to their predetermined arrival and departure schedules, rather than their headers or contents, relieving the switches from making real-time routing decisions. Any unscheduled transmission times remain available for routing of unscheduled packets according to their IP headers. Real-time transmission of data can be guaranteed in each scheduled path, and schedule selection criteria may be adjusted according to network utilization and tolerable setup delay and end-to-end delay.
Owner:AVAYA INC
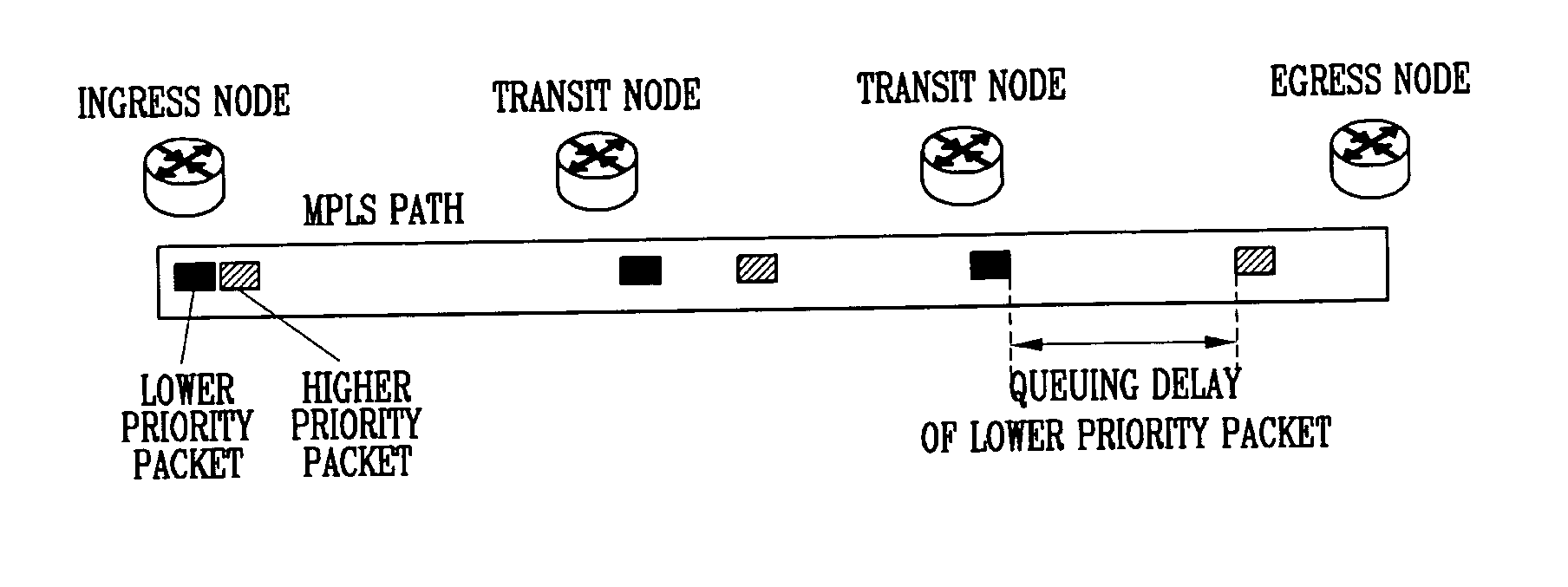
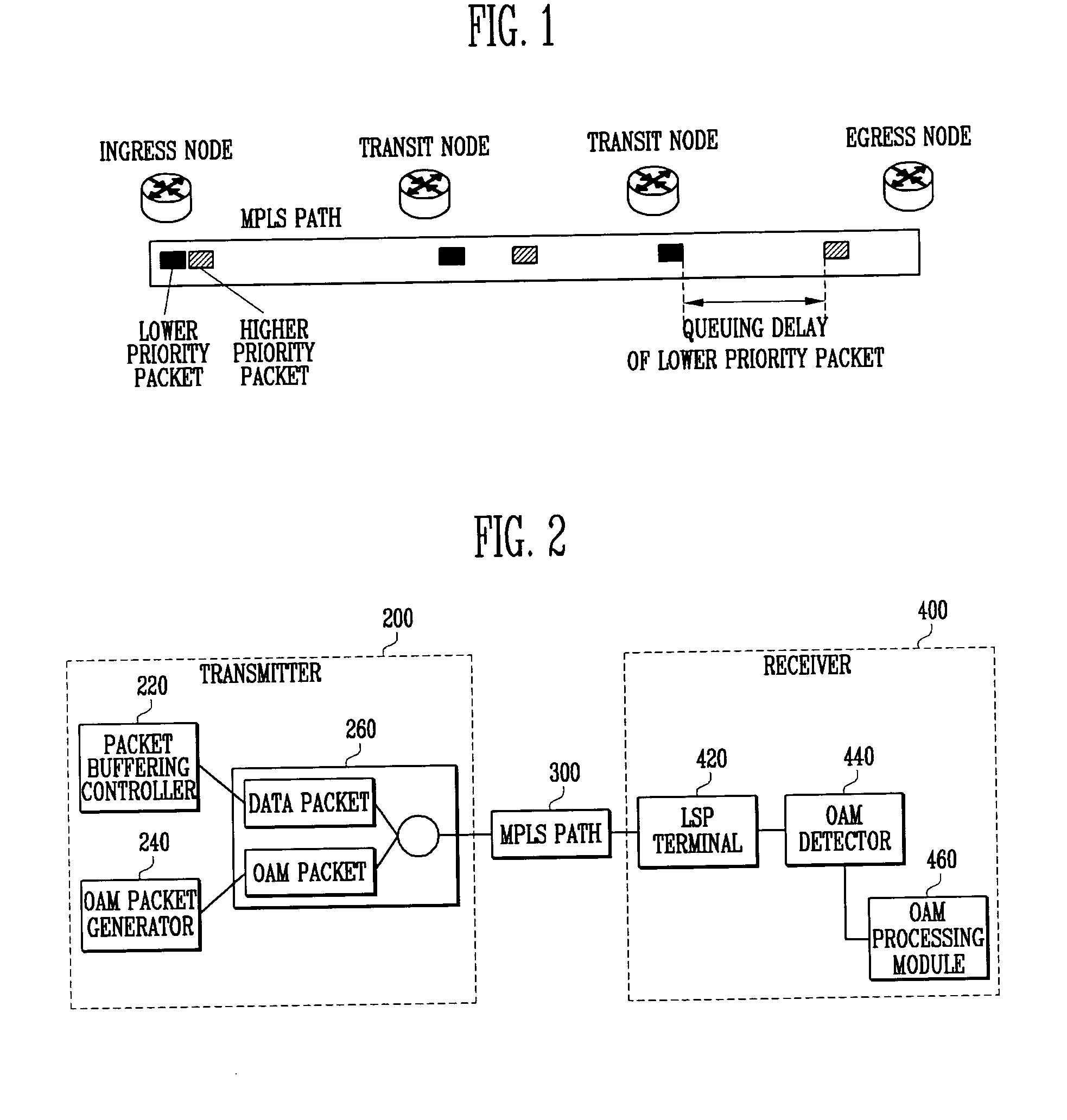
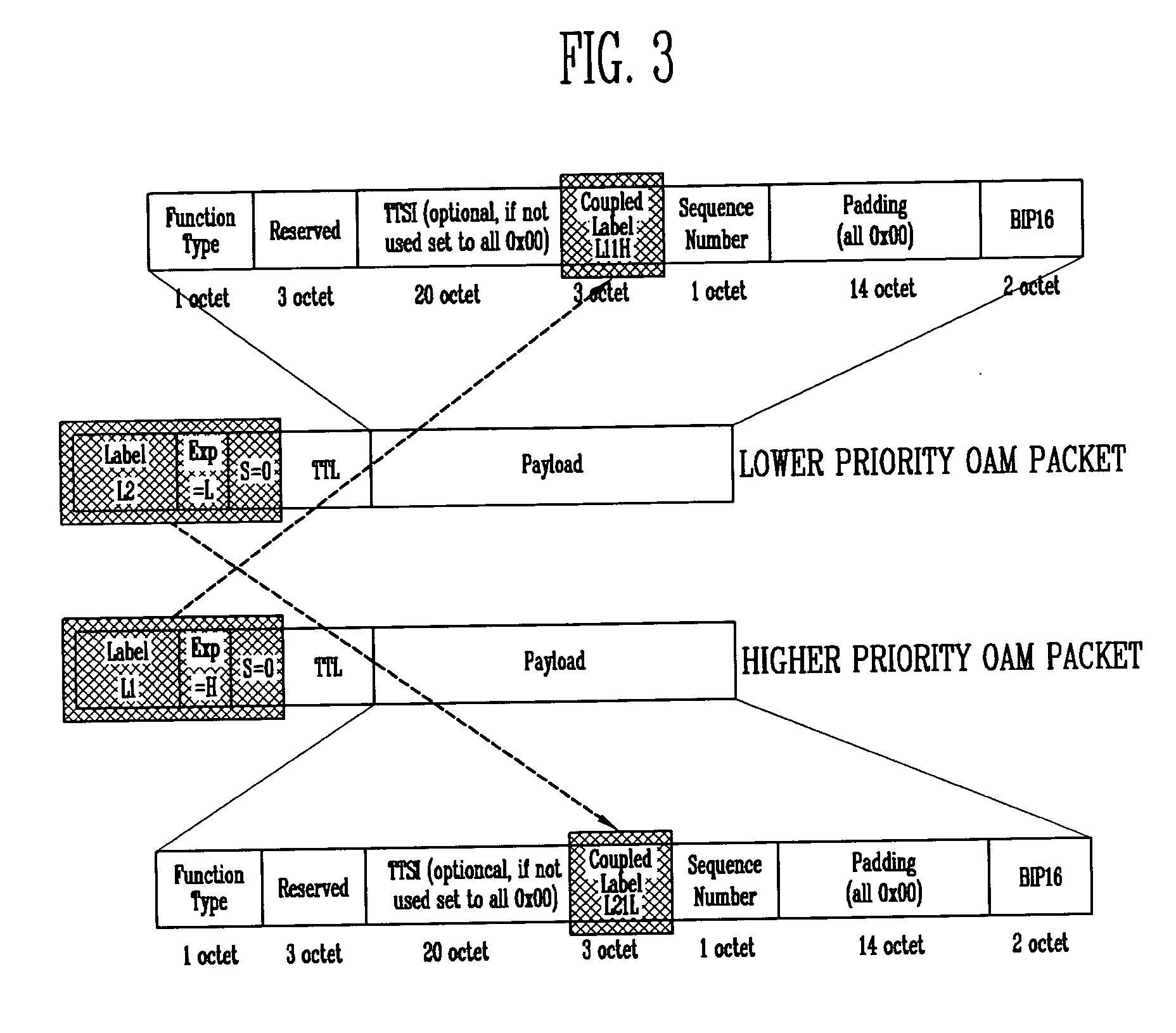
Method for measuring end-to-end delay in asynchronous packet transfer network, and asynchronous packet transmitter and receiver
InactiveUS20070097865A1Easily delay valueMeasured easily and convenientlyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetDelayed time
Provided are a method for measuring an end-to-end delay, and asynchronous packet transmitter / receiver, capable of conveniently and exactly measuring a packet delay in an asynchronous packet transfer network in which a transfer priority is determined as in MPLS. The method includes the steps of continuously transmitting a higher priority packet and a lower priority packet at an ingress node, measuring a time when the higher priority packet arrives at an egress node, measuring a time when the lower priority packet arrives at the egress node, and calculating a delay time from the arrival time of the higher and lower priority packets. The higher and lower priority packets each include Coupled Label and Sequence Number fields for discriminating one of the packets that are repeatedly transmitted, the Coupled Label field of the higher priority packet is recorded with a label value of the lower priority packet, and the Coupled Label field of the lower priority packet is recorded with a label value of the higher priority packet.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
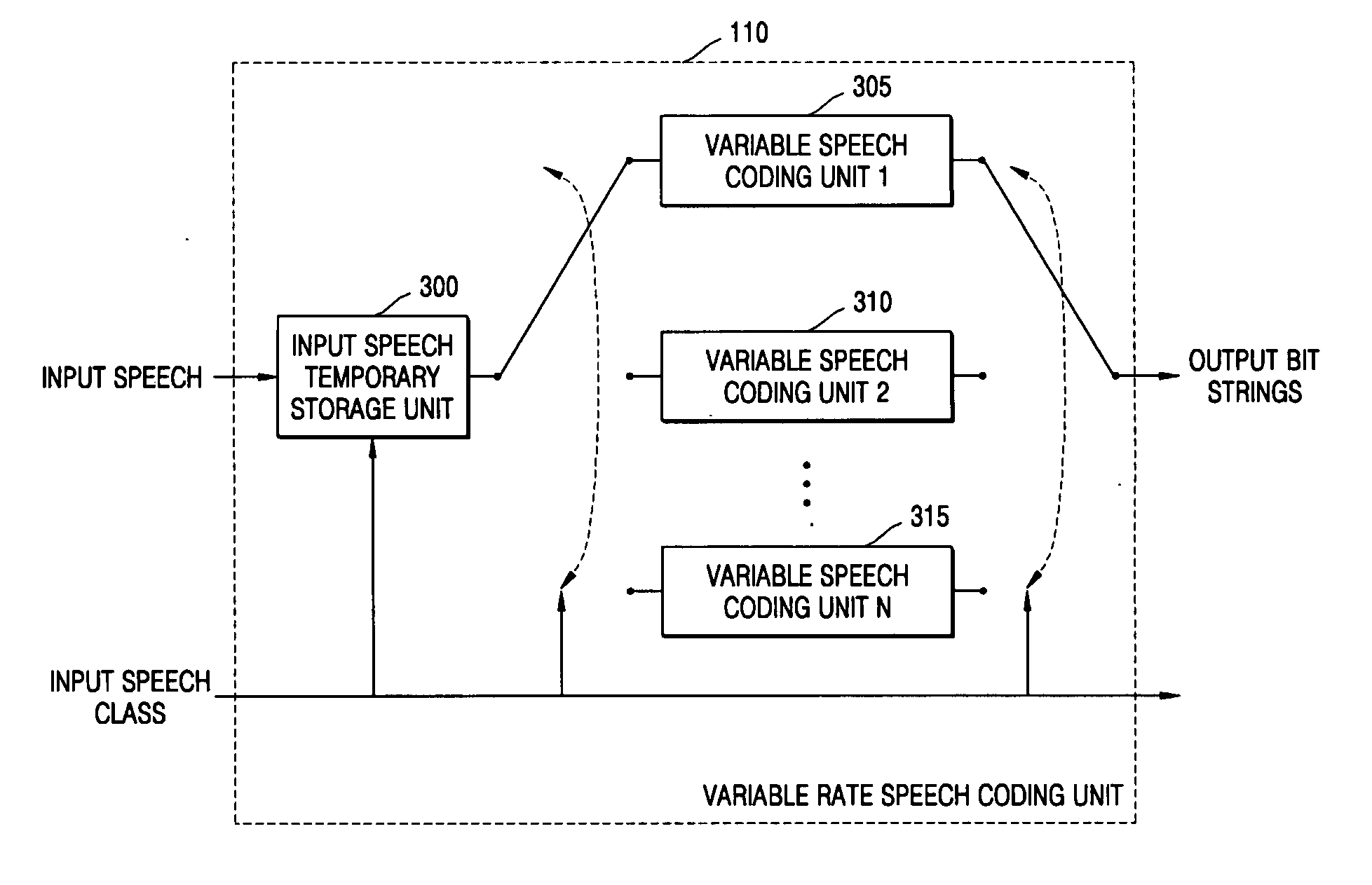
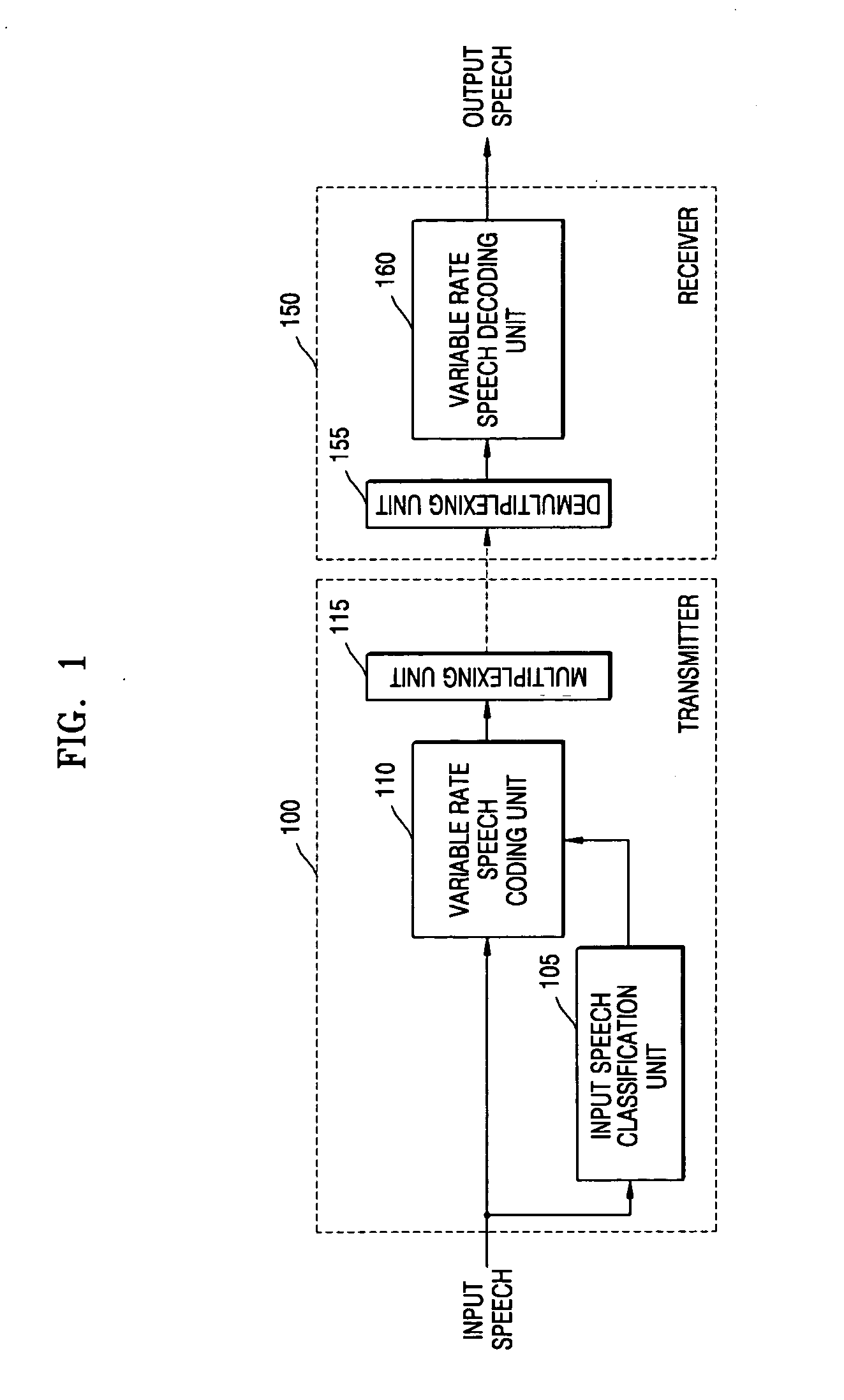
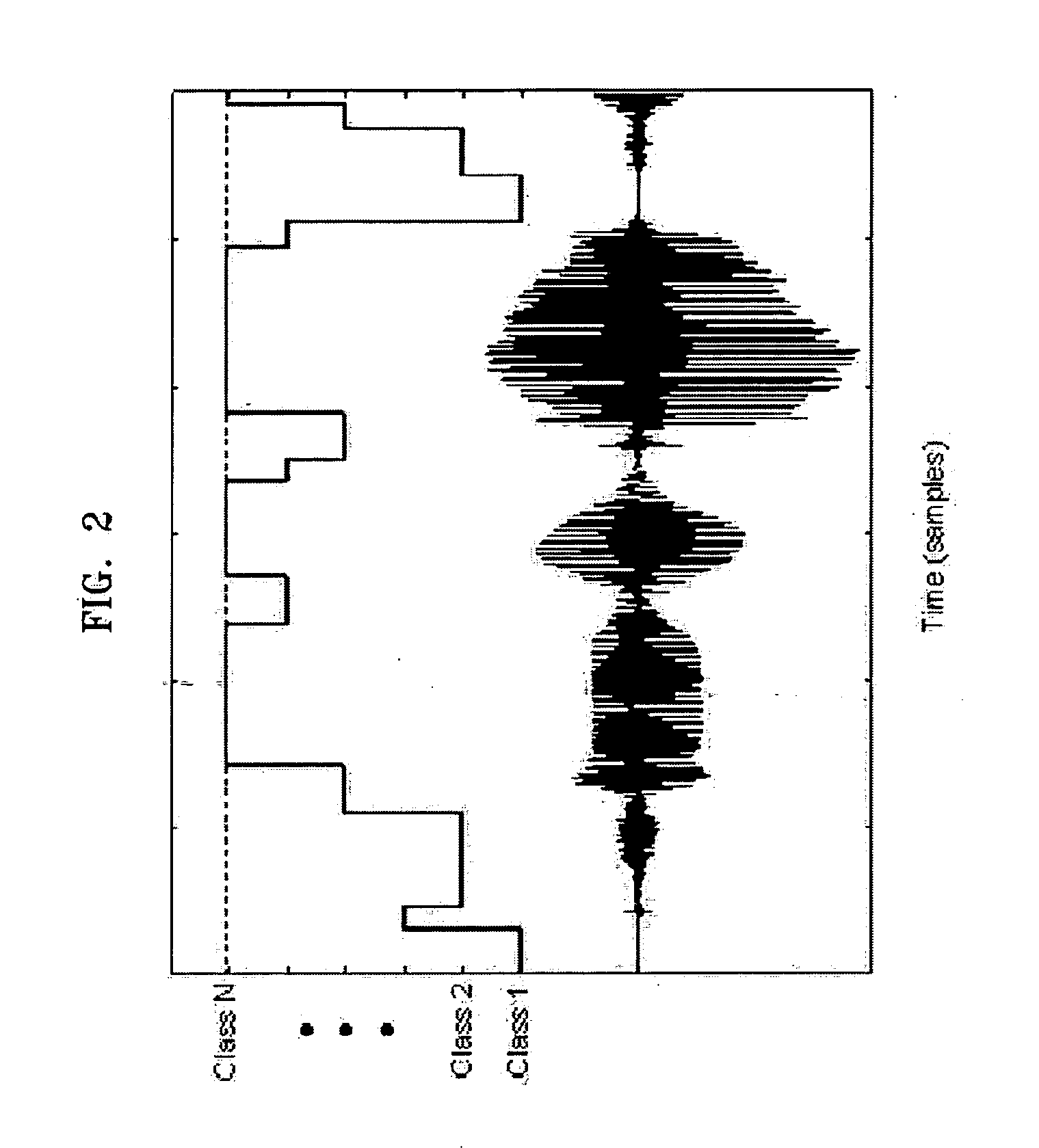
Variable-frame speech coding/decoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050143979A1Improve performanceImprove service qualitySpeech analysisSpeech codeNetwork conditions
There is provided a speech coding / decoding apparatus and method, in which the input speech signals are classified into several classes in accordance with characteristics of the input speech signals and the input speech signals are coded using frame sizes, quantizer structures, and bit assignment methods corresponding to the determined classes, or in which the frame sizes can be adjusted in accordance with network conditions or codec type of a counter part. Therefore, by optimally adjusting the frame size, the quantizer structure, and the bit assignment method in accordance with the characteristics of input speech, it is possible to improve the performance of the speech coding apparatus, and by adjusting the frame size in accordance with the speech codec type of a counter part, it is also possible to reduce the total end-to-end delay.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
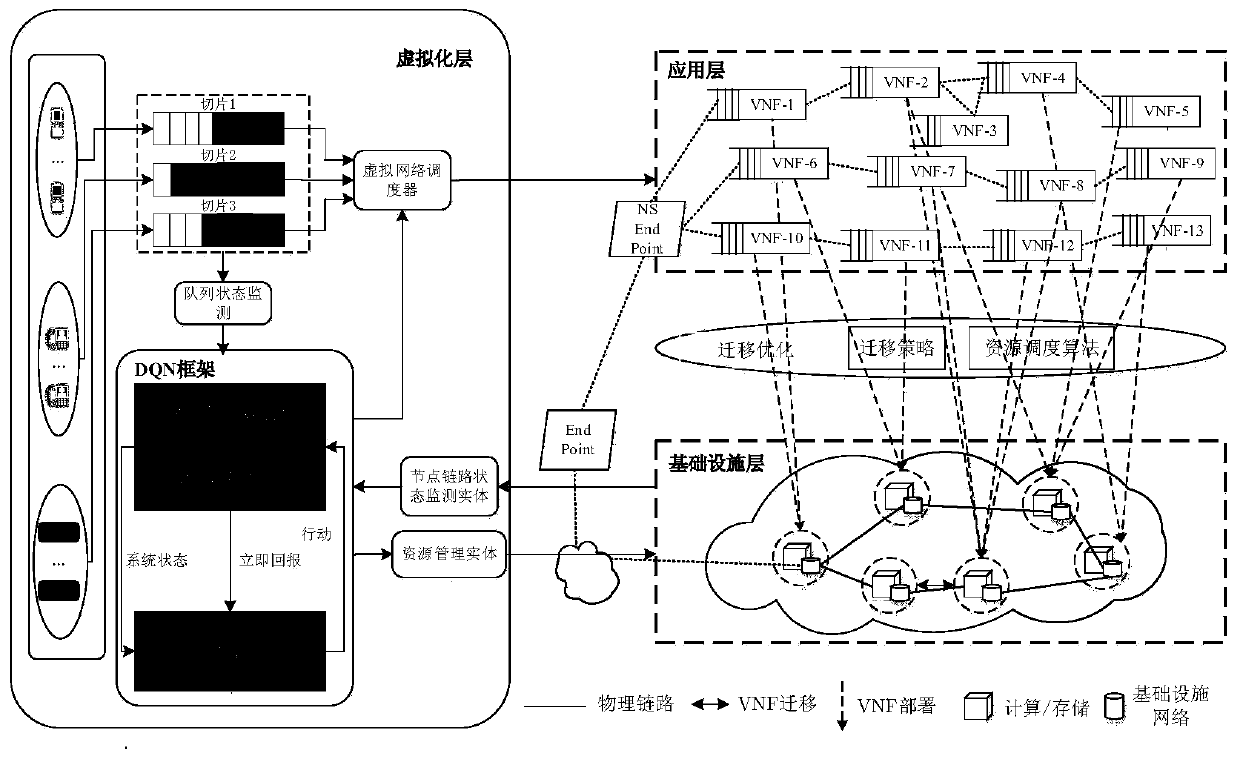
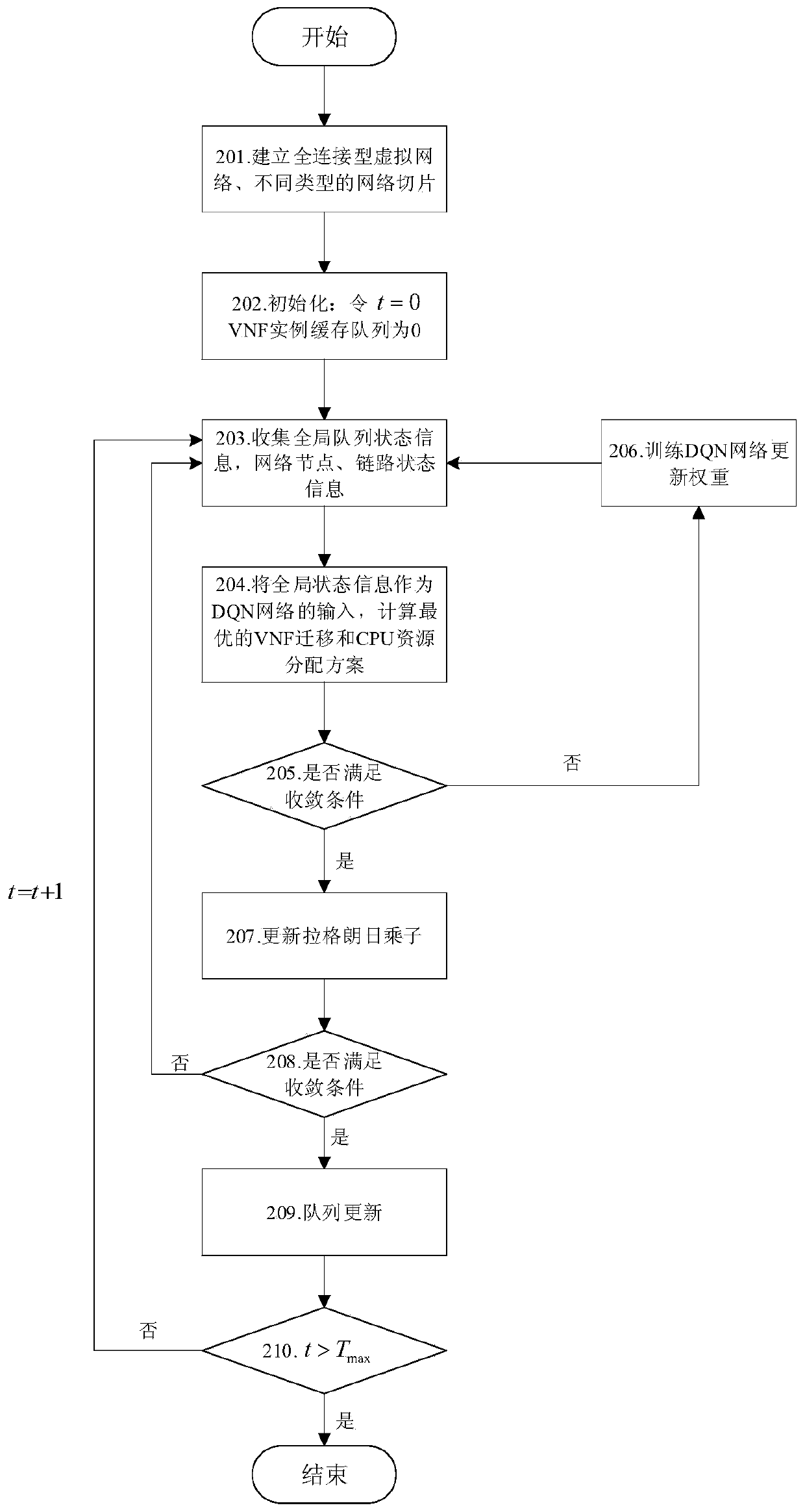
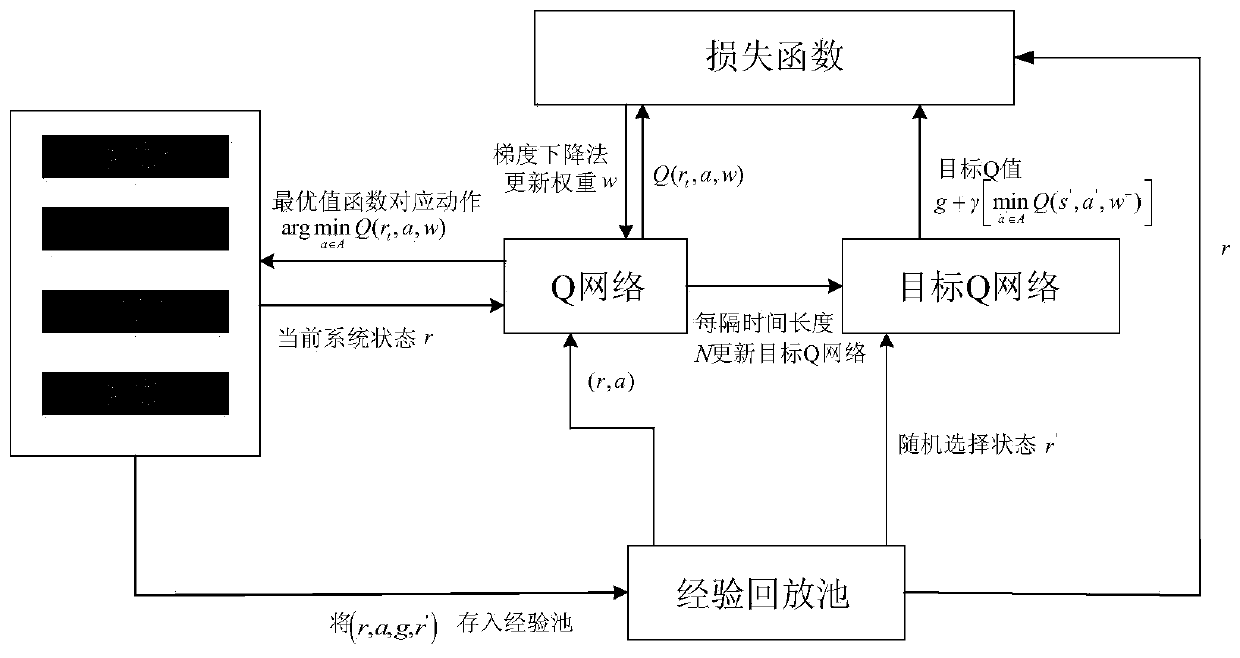
Virtual network function intelligent migration method
ActiveCN110275758ATake advantage ofAchieve sharingResource allocationEnergy efficient computingResource consumptionTime delays
The invention relates to a virtual network function intelligent migration method, and belongs to the technical field of mobile communication. In the virtual network function intelligent migration method, on each discrete time slot, on the premise that the highest average time delay constraint, the node cache resource consumption limitation and the link bandwidth capacity limitation of each slice are ensured, according to the queue state information, the node state information and the link state information of each Virtualized Network Function (VNF) instance, an optimal VNF migration strategy is formulated for slices, and an allocation strategy of node CPU resources in the network is dynamically adjusted by aiming at minimizing the average operation energy consumption of the general server. According to the virtual network function intelligent migration method, CPU resources can be fully utilized, and the requirement for average end-to-end time delay of slices can be met; and the sharing of the VNF instances is realized, and the stability of the system is effectively maintained while the average energy consumption of the system is saved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for flexible packet selection in a wireless communication system
Adaptive De-Jitter Buffer for Voice over IP (VoIP) for packet switch communications. The de-jitter buffer methods and apparatus presented avoid playback of underflows while balancing end-to-end delay. In one example, the de-jitter buffer is recalculated at the beginning of each talkspurt. In another example, talkspurt packets are compressed upon receipt of all remaining packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
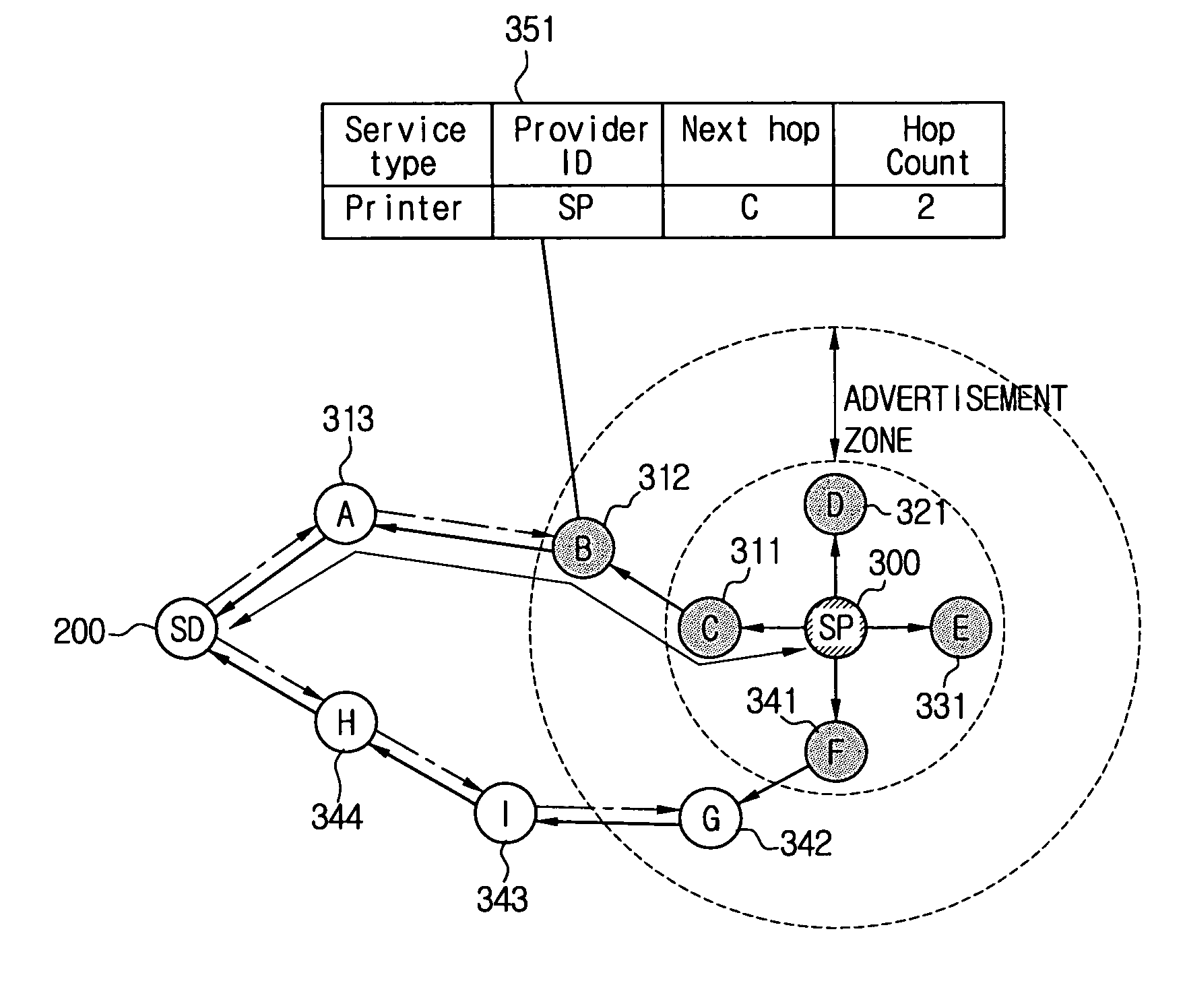
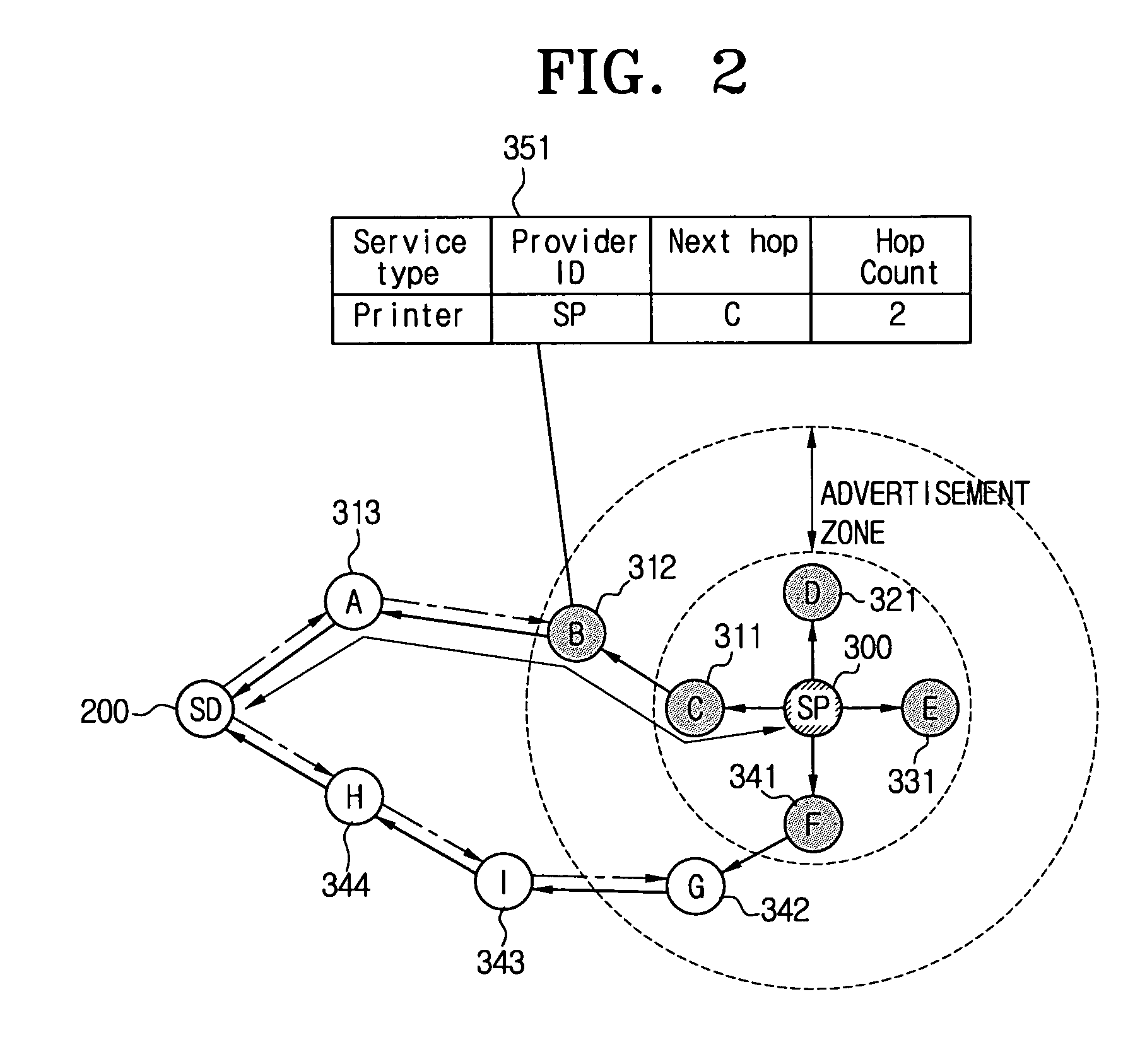
Method for service discovery in mobile ad-hoc network
ActiveUS7457304B2Lower end-to-end latencySimple methodVehicle seatsFrequency-division multiplex detailsService provisionService information
A method for a hybrid service discovery adapting between push-based and pull-based schemes in a mobile ad-hoc network and a system thereof. The method includes periodically transmitting a first control packet for providing service information from a service provider that is capable of providing a service to nodes located in a specified advertisement zone, transmitting a second control packet requesting the service from a service demander to one or more nodes in a network, and transmitting a third control packet including path information of the service provider if at least one of the nodes located within the advertisement zone and the service provider receives the second control packet. The method and the system can reduce the amount of control packet transmission and minimize an end-to-end delay.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
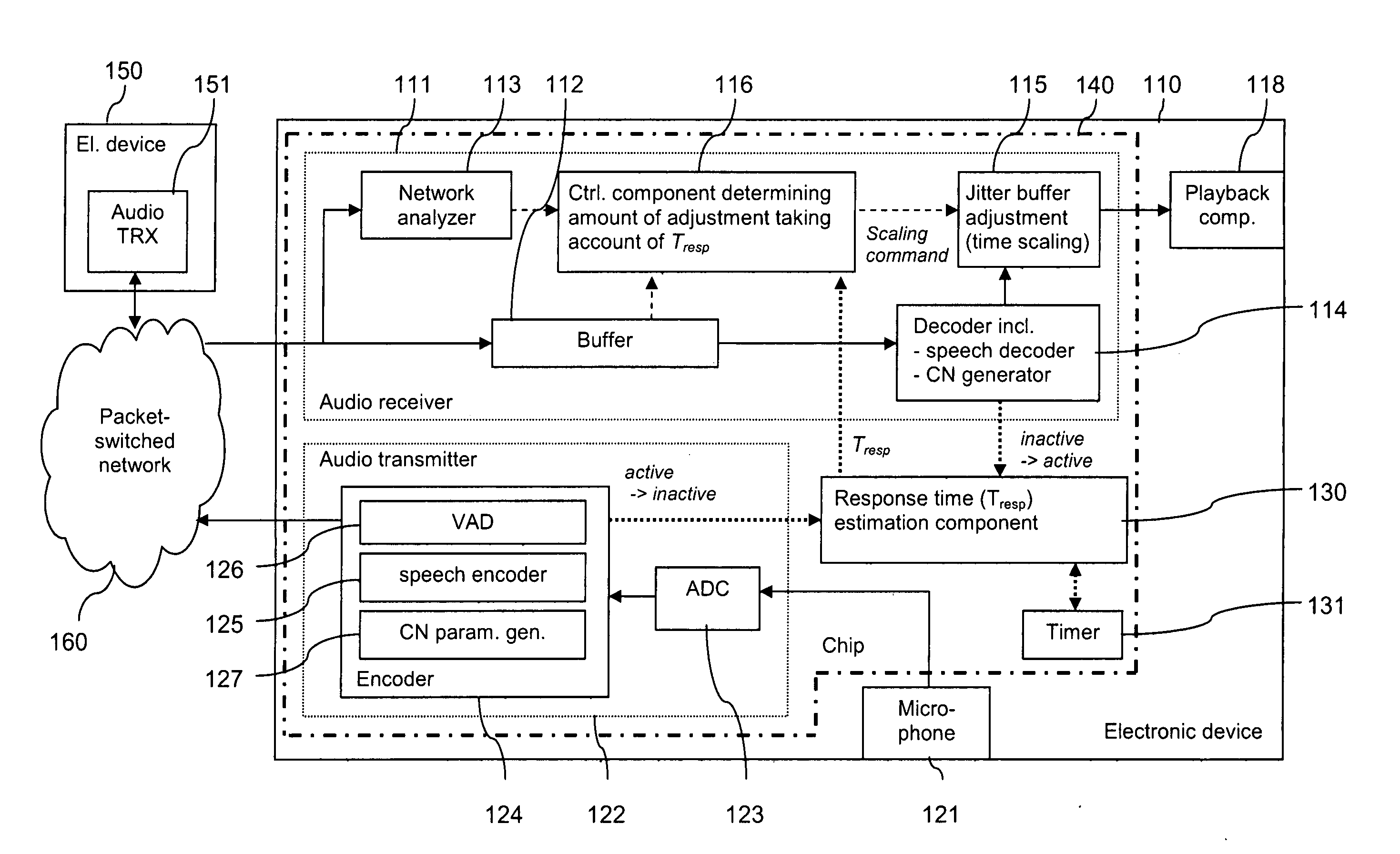
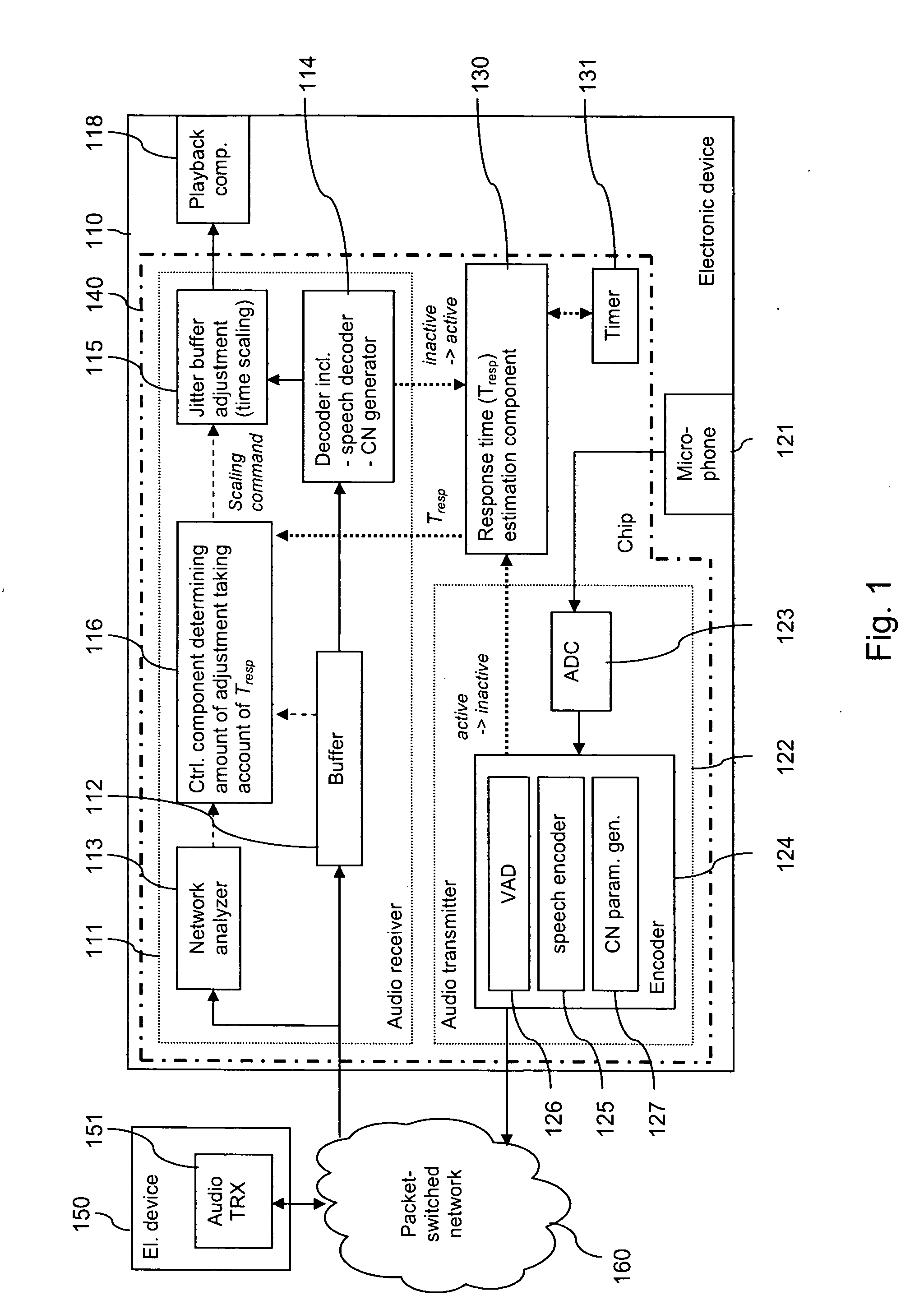
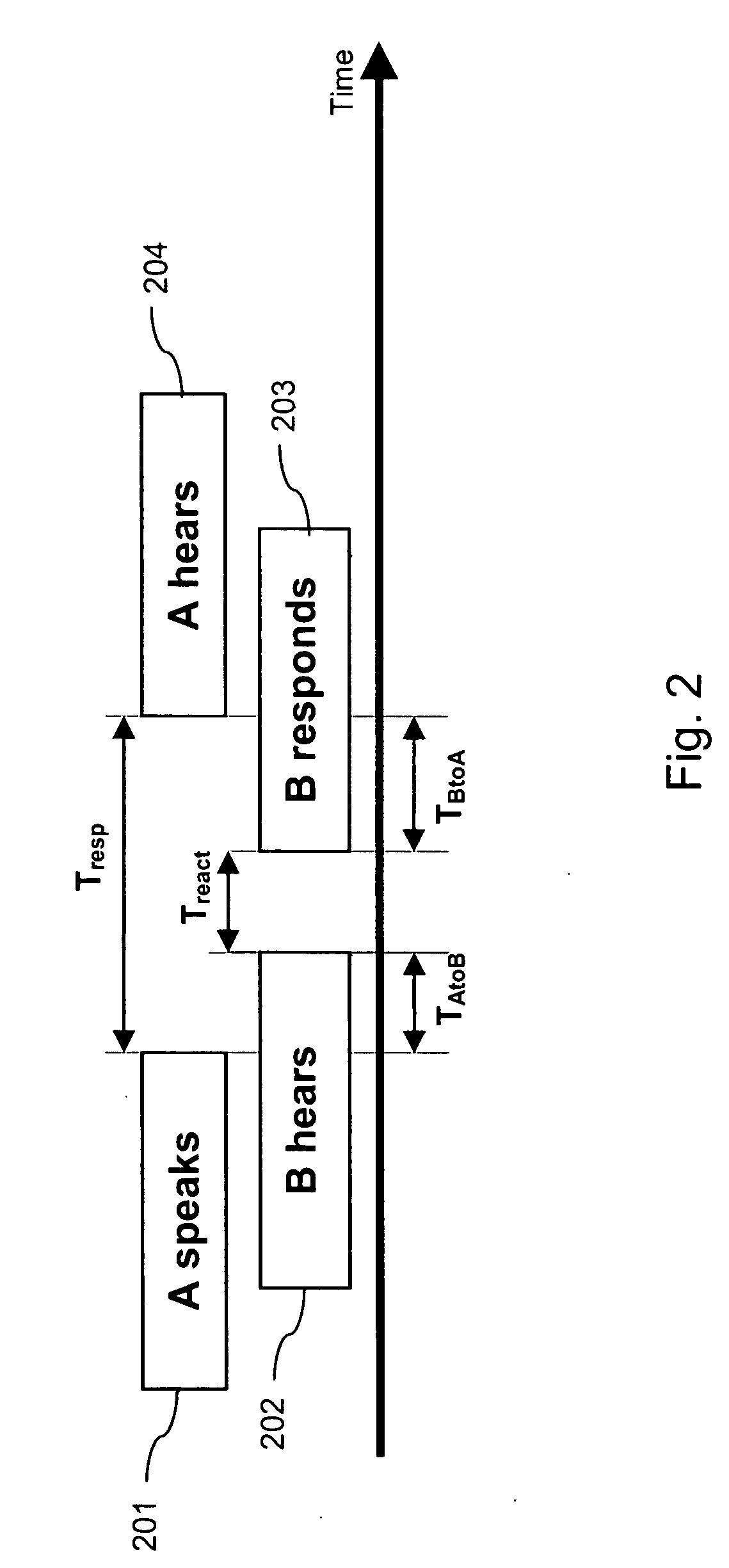
Jitter buffer adjustment
ActiveUS20080049795A1Faster and accurate informationImprove buffering effectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWrite bufferPacket switched
For enhancing the performance of an adaptive jitter buffer, a desired amount of adjustment of a jitter buffer is determined at a first device using as a parameter an estimated delay. The delay comprises at least an end-to-end delay in at least one direction in a conversation. For this conversation, speech signals are transmitted in packets between the first device and a second device via a packet switched network. An adjustment of the jitter buffer is then performed based on the determined amount of adjustment.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System and method for thinning of scalable video coding bit-streams
ActiveUS20120014434A1Flexibility in processingImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer architectureThe Internet
A system for videoconferencing that offers, among other features, extremely low end-to-end delay as well as very high scalability. The system accommodates heterogeneous receivers and networks, as well as the best-effort nature of networks such as those based on the Internet Protocol. The system relies on scalable video coding to provide a coded representation of a source video signal at multiple temporal, quality, and spatial resolutions. These resolutions are represented by distinct bitstream components that are created at each end-user encoder. System architecture and processes called SVC Thinning allow the separation of data into data used for prediction in other pictures and data not used for prediction in other pictures. SVC Thinning processes, which can be performed at video conferencing endpoints or at MCUs, can selectively remove or replace with fewer bits the data not used for prediction in other pictures from transmitted bit streams. This separation and selective removal or replacement of data for transmission allows a trade-off between scalability support (i.e. number of decodable video resolutions), error resiliency and coding efficiency.
Owner:VIDYO
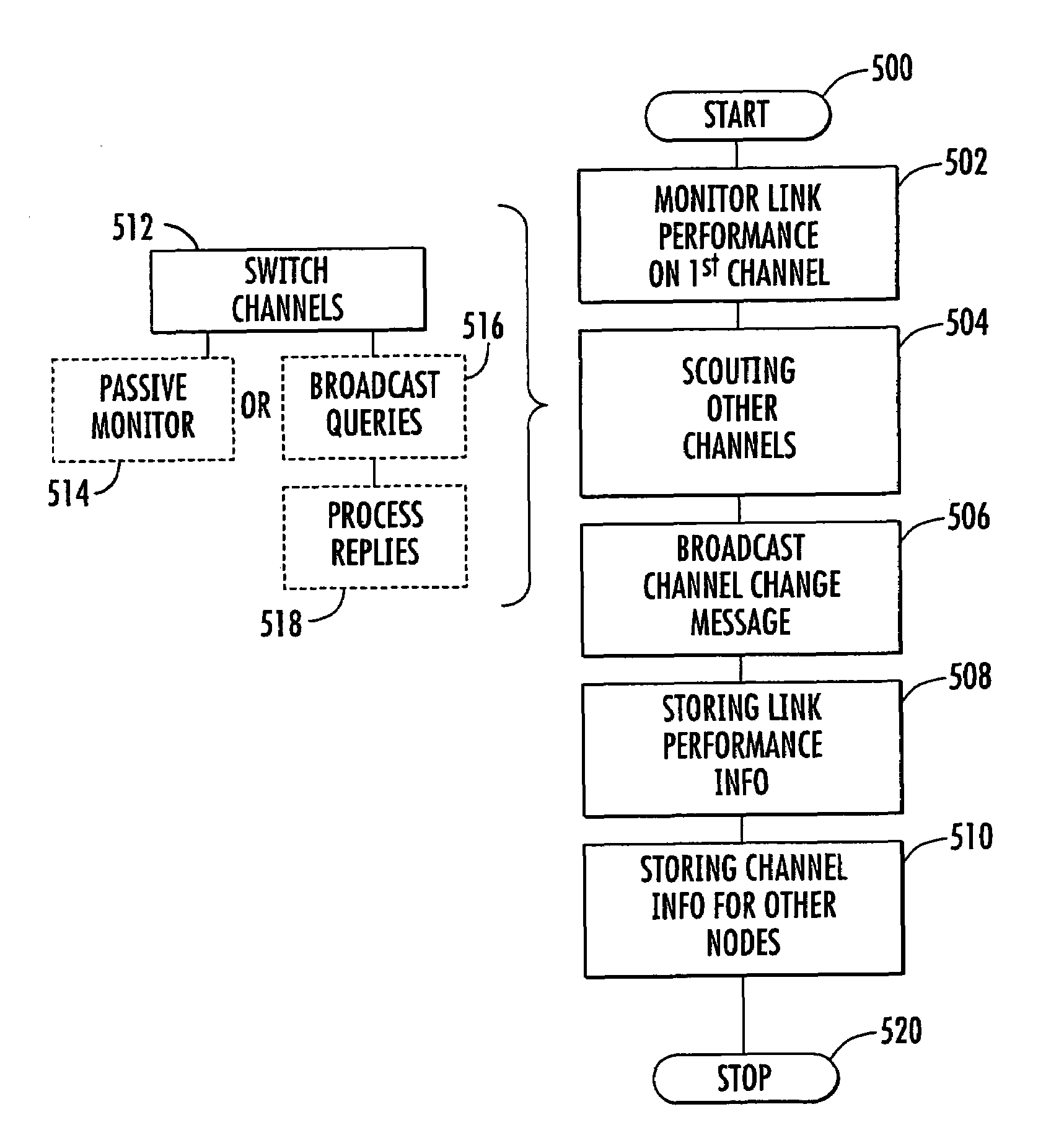
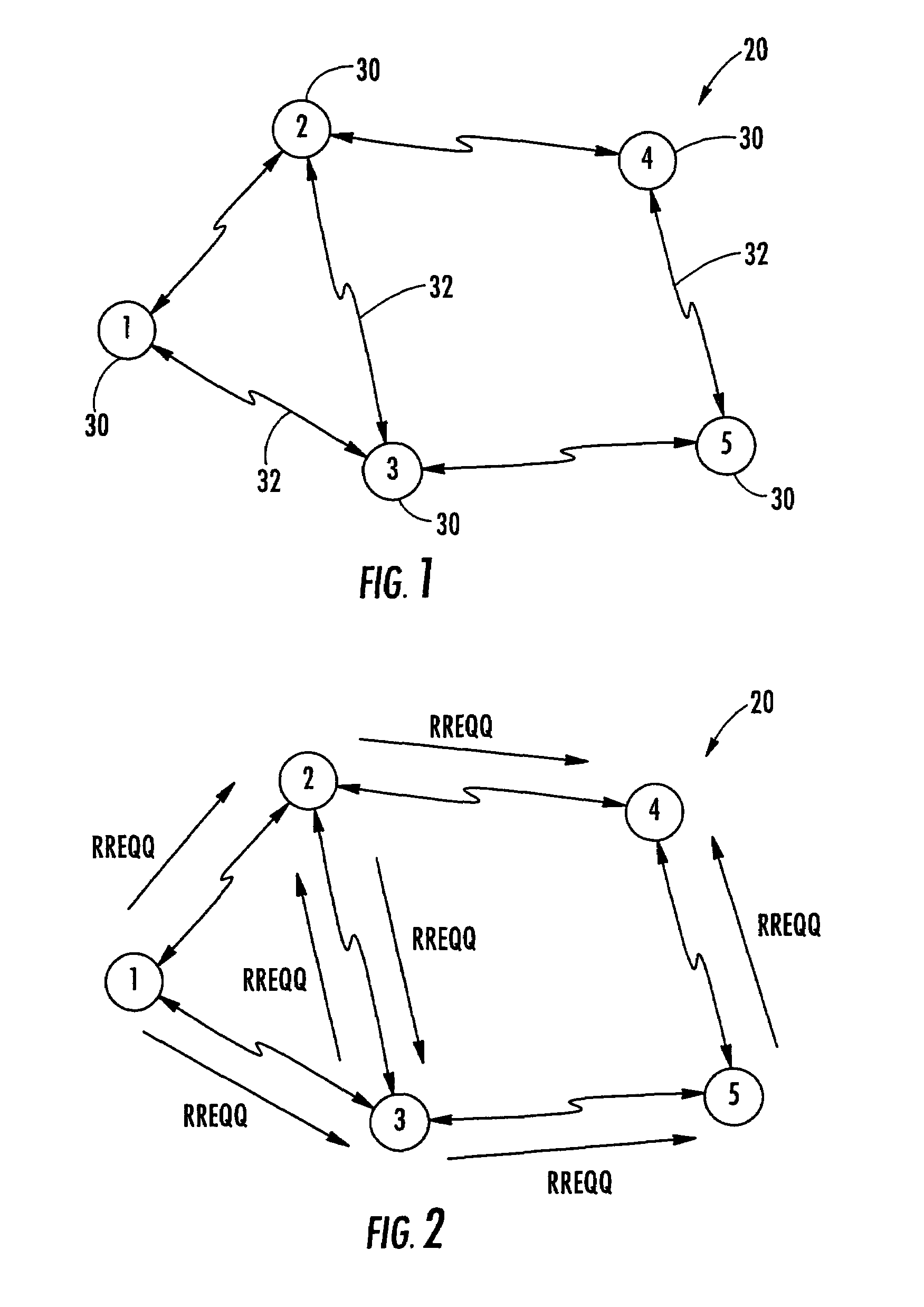
Allocating channels in a mobile ad hoc network
ActiveUS7616961B2Easy to useError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
A mobile ad hoc network includes a plurality of wireless mobile nodes and a plurality of wireless communication links connecting the plurality of nodes together over a plurality of channels. The method includes each node monitoring link performance on a first channel, link performance being based upon at least one quality of service (QoS) threshold, and each node scouting one or more other available channels when the monitored link performance on the first channel falls below the QoS threshold. The QoS threshold is preferably based upon at least one of available bandwidth, error rate, end-to-end delay, end-to-end delay variation, hop count, expected path durability, and priority.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Bandwidth optimization of video program bearing transport streams
InactiveUS20050105486A1Flexible processIncrease flexibilityTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexProgram clock referenceComputer science
A method and system are provided for remultiplexing program bearing data. The remultiplexing method and system are applicable to MPEG-2 compliant transport streams carrying video programs. A descriptor based system is used for scheduling the timely output of transport packets wherein each descriptor records a dispatch time as well as a receipt time for each transport packet. The receipt time is used for estimating program clock reference adjustments, but final program clock reference adjustment is performed in hardware in relation to the precise output timing of each transport packets. A descriptor and transport packet caching technique is used for decoupling the synchronous receipt and transmission of transport packets from any asynchronous processing performed thereon. The descriptors can also be used for managing scrambling and descrambling control words (encryption and decryption keys). Remultiplexing functions may be distributed across a network. The remultiplexer can furthermore optimize the bandwidth of transport streams by replacing null transport packets with transport packet data to be inserted into the output transport stream. Program data transmitted via asynchronous communication links is re-timed and assistance is provided for outputting program data on such asynchronous communication links to reduce a variation in end-to-end delay incurred by the program data. Remultiplexing and program specific information can be seamlessly dynamically varied without stopping, or introducing a discontinuity in, the flow of outputted transport packets. A technique is also provided for locking multiple internal reference clock generators.
Owner:TANDBERG TELEVISION
Routing method and node device of delay tolerant network
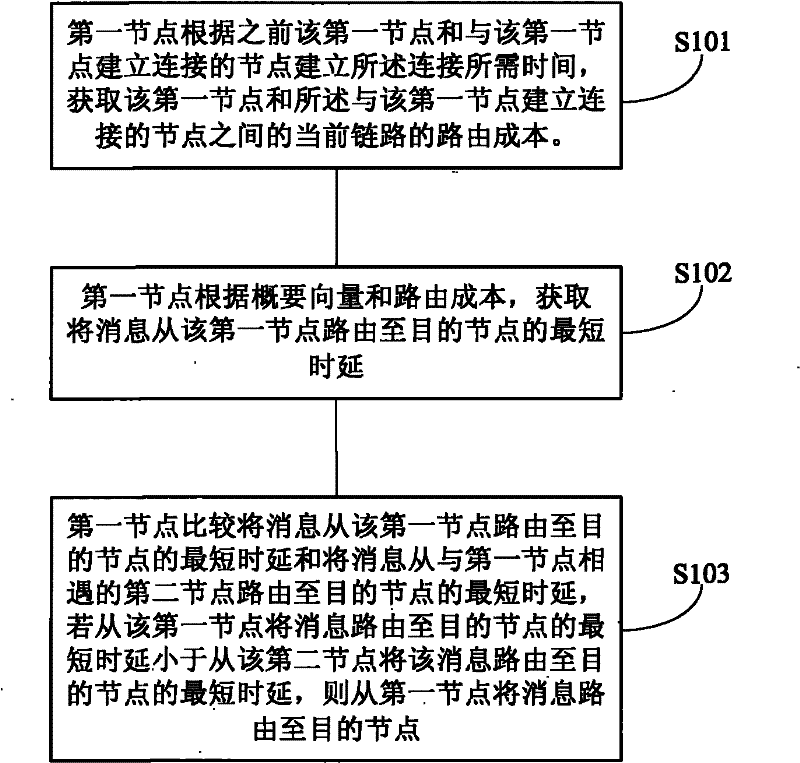
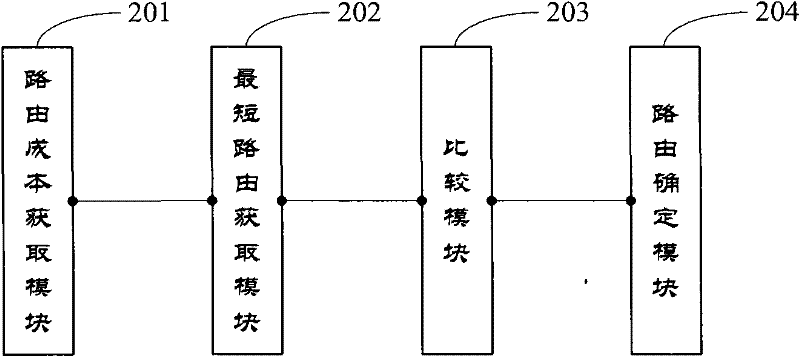
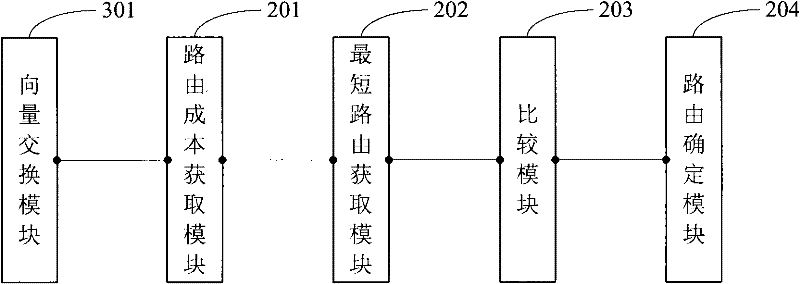
InactiveCN102348250AReduce loss rateImprove sending success rateWireless communicationTime delaysEnd-to-end delay
The embodiment of the invention provides a routing method and a node device of a delay tolerance network in order to reduce the network load, reduce the end-to-end delay and improve the success rate of data sending. The method comprises the following steps: the routing cost of a current link between a first node and a node connected with the first node is obtained by the first node according to the time needed for the connection between the first node and the node connected with the first node; the shortest time delay for routing messages from the first node to a target node is obtained by the first node according to a summary vector and the routing cost; and the shortest time delay for routing the messages from the first node to the target node is compared with the shortest time delay for routing the messages from a second node encountered with the first node to the target node by the first node, and if the former time delay is smaller than the later time delay, the messages are routed from the first node to the target node. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the waiting time for the connection establishment is reduced, the network load is reduced, and the success rate of message sending in the network is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Multi-path delay sensing optimal route selecting method for cognitive network
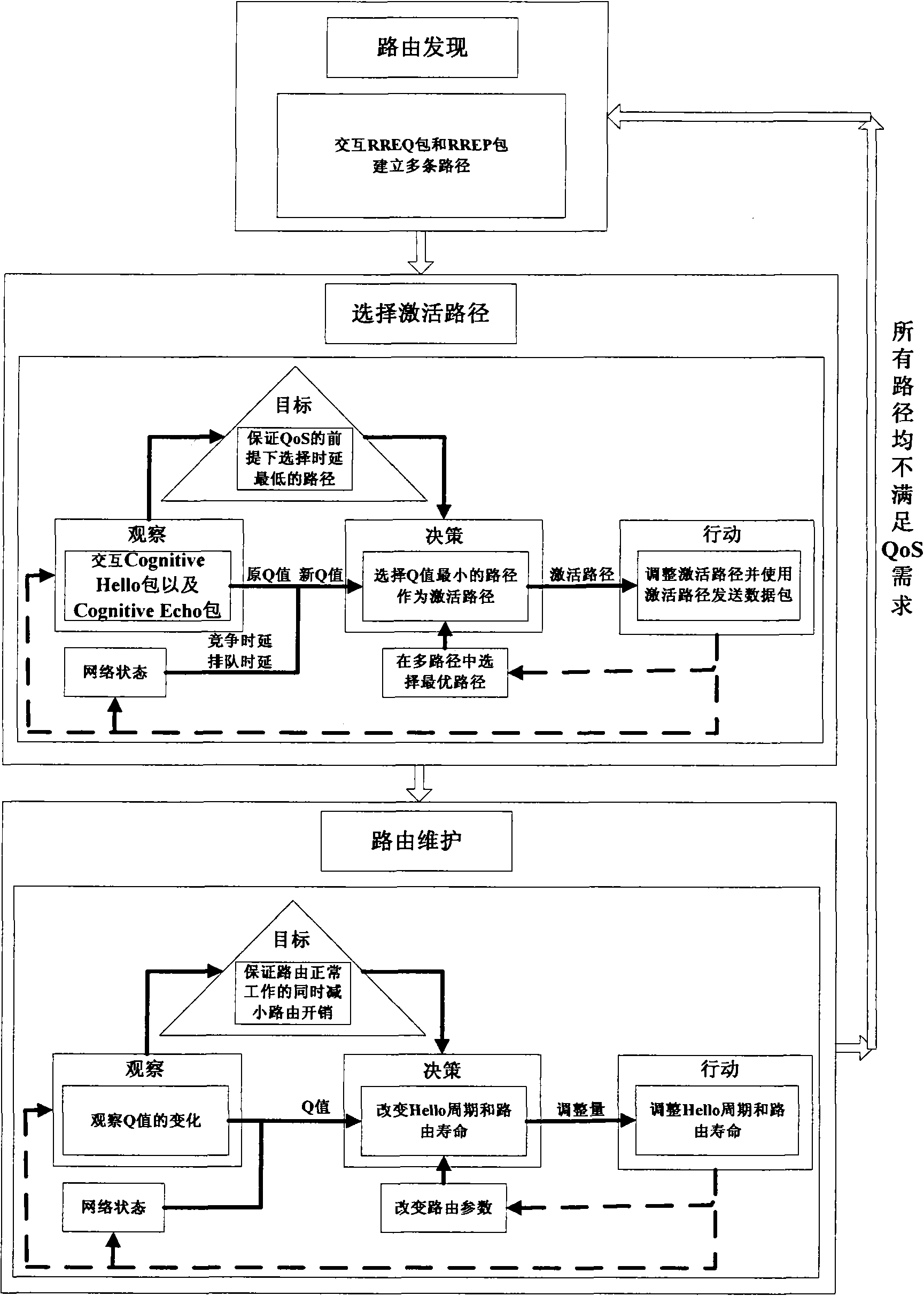
InactiveCN101835239AReduce latencyLoad balancingHigh level techniquesWireless communicationMulti pathEnd-to-end delay
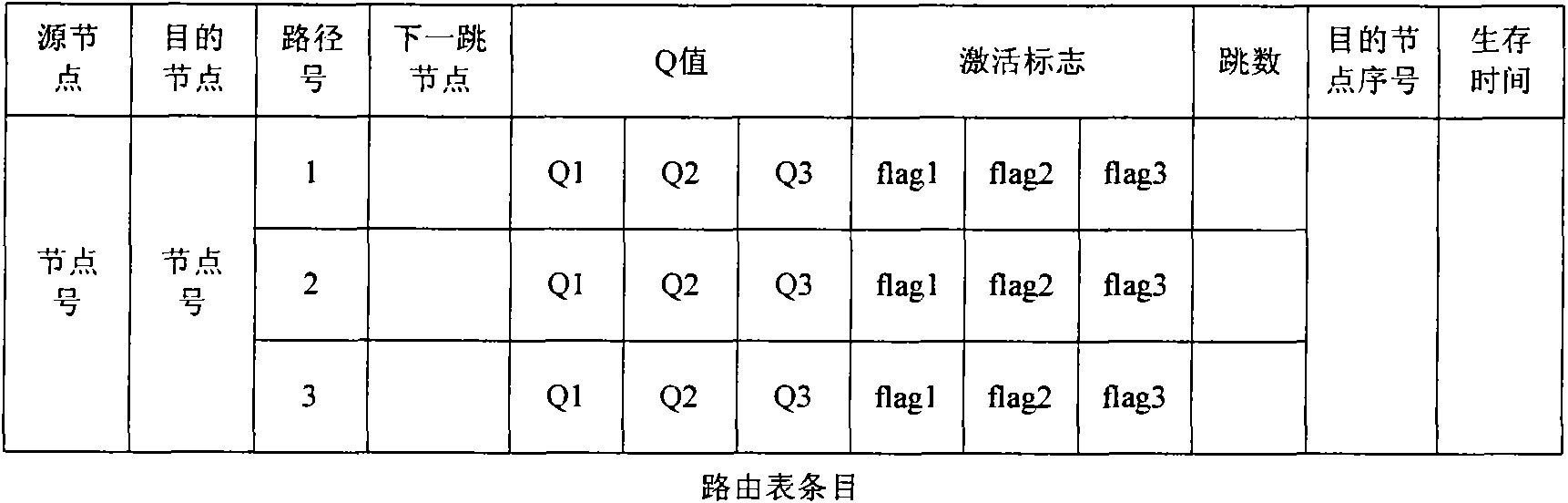
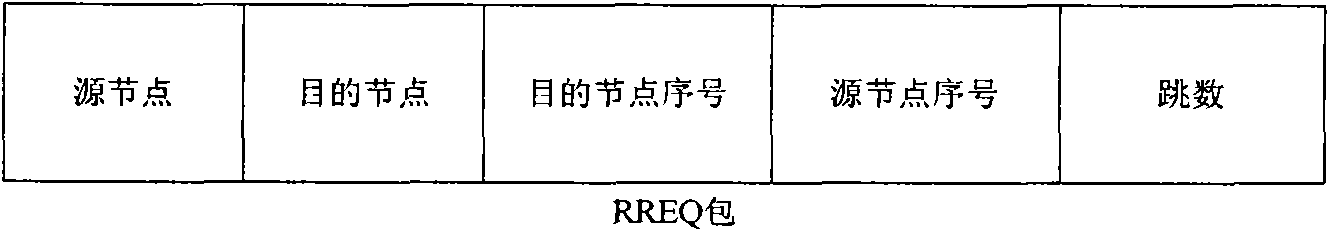
The invention discloses a multi-path delay sensing optimal route selecting method for a cognitive network, which comprises the following steps of: dividing service into different classes; establishing a plurality of paths through route discovery; adopting an end-to-end delay recorded in the route discovery process as an initial value of a Q value; updating the Q value of the path by utilizing a Q learning algorithm, and introducing the estimation of node queue delay and the estimation of channel contending delay during updating; selecting an activating path according to the Q value to send a data package; reducing route control packet overhead by utilizing the Q learning algorithm; and when the plurality of paths cannot meet the requirement of QoS of the service, beginning the process again. The method has the advantages of quick transmission of advanced service, short path delay, high routing efficiency and high network load bearing capacity, and can be used for a cognitive wireless network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com