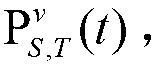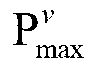Method for balancing load based on virtual cell breathing in long term evolution-advanced (LTE-A) system
A LTE-A, 1.LTE-A technology, applied in the field of load balancing based on virtual cell breathing, can solve problems such as increased network overhead and load imbalance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Embodiment one, such as Figure 4 A TD-LTE-A network is constructed as shown. There are 19 cells in total. Each cell uses omnidirectional antennas. The frequency reuse factor between cells is 1. Except for edge cells, each cell has six adjacent cells. , so the cell is virtually divided into six parts, each corresponding to a neighboring cell. The bandwidth of each physical resource block is 180kHz, each cell has one eNodeB, and the distance between every two eNodeBs is 500 meters, and each eNodeB manages six virtual transmission powers corresponding to different adjacent cells. Each virtual transmit power maintains 12 different values. In this example, cells 15, 17, and 19 each have 50 evenly distributed users, and the remaining cells each have 10 evenly distributed users. At this time, there are multiple non-adjacent cells (15, 17, 19) in the network that are overloaded, and the loads of other cells are light. The network in this case belongs to the above-mentioned ...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Embodiment two, such as Figure 4 A TD-LTE-A network is constructed as shown. There are 19 cells in total. Each cell uses omnidirectional antennas. The frequency reuse factor between cells is 1. Except for edge cells, each cell has six adjacent cells. , so the cell is virtually divided into six parts, each corresponding to a neighboring cell. The bandwidth of each physical resource block is 180kHz, each cell has one eNodeB, and the distance between every two eNodeBs is 500 meters, and each eNodeB manages six virtual transmission powers corresponding to different adjacent cells. Each virtual transmission power maintains 10 different values. In this embodiment, the central cell 13 has 50 uniformly distributed users, each of its six adjacent cells has 30 users, and the remaining cells in the network each have 10 users. At this time, the load of the central cell 13 is too heavy, and the load of its adjacent cells exceeds the acceptable load transfer threshold (AC_load is 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com