Small current grounding system fault line selection method using power frequency component wavelet coefficients to carry out linear fitting detection
A technology of small current grounding and wavelet coefficients, applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., can solve the problems of unreliable capture of the head of the traveling wave, small high-frequency components, and large differences in electrical characteristics between cable lines and overhead lines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
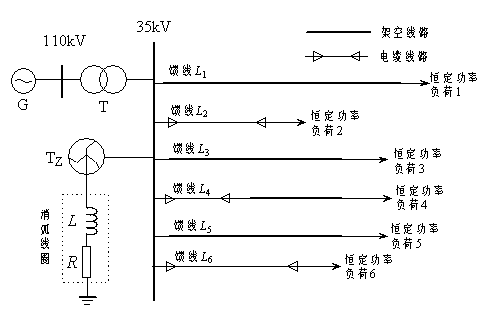
[0065] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 Shown: 110kV / 35kV small current grounding system single-phase ground fault simulation model, the power supply voltage in the figure is 110kV, which is changed to 35kV by the transformer and then sent to the load end. It has 6 feeders, and the neutral point of the Z-shaped transformer passes through the The arc coil series resistor is grounded. overhead feeder L 1 =15km, L 3 =18km, L 5 =30km, wire-cable hybrid feeder L 4 =17km, the overhead feeder is 12km, the cable is 5km, and the cable feeder L 2 =6km, L 6 =8km. Among them, the overhead feeder is JS1 pole type, LGJ-70 type conductor, the span is 80m, and the cable feeder is YJV23-35 / 95 type cable. G in the power grid is an infinite power supply; T is the main transformer with a transformation ratio of 110 kV / 35kV, and the connection group is Y N / d11;T Z Is a zigzag transformer; L is the arc suppression coil; R is the damping resistance of the arc suppression coil. The...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Embodiment 2: The single-phase ground fault simulation model of 110kV / 35kV small current grounding system is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the distance from the feeder L 1 A single-phase ground fault occurs at 5 km from the beginning, the ground resistance is 20Ω, the fault angle is 0°, and the sampling frequency is 10kHz.
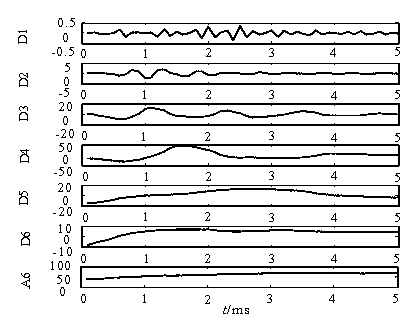
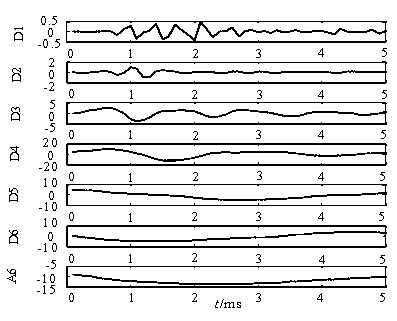
[0072] According to the same method as example 1, get the feeder L 1 and feeder L 2 The wavelet coefficients of the zero-sequence current in each frequency band are as attached Figure 5 And attached Figure 6 As shown, the straight line fitting for it is shown in the attached Figure 7 shown. The linear fitting of each feeder line containing the wavelet coefficients of the power frequency band is carried out to obtain the corresponding first-order coefficients:
[0073] =(0.6043 -0.0133 -0.0028 -0.0116 -0.0027 -0.0176), (9)
[0074] Take the calculation result of the selected line sign function, =(1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1), s...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap