Identification method of complex power grid self-organization critical state
A technology of self-organized criticality and identification method, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
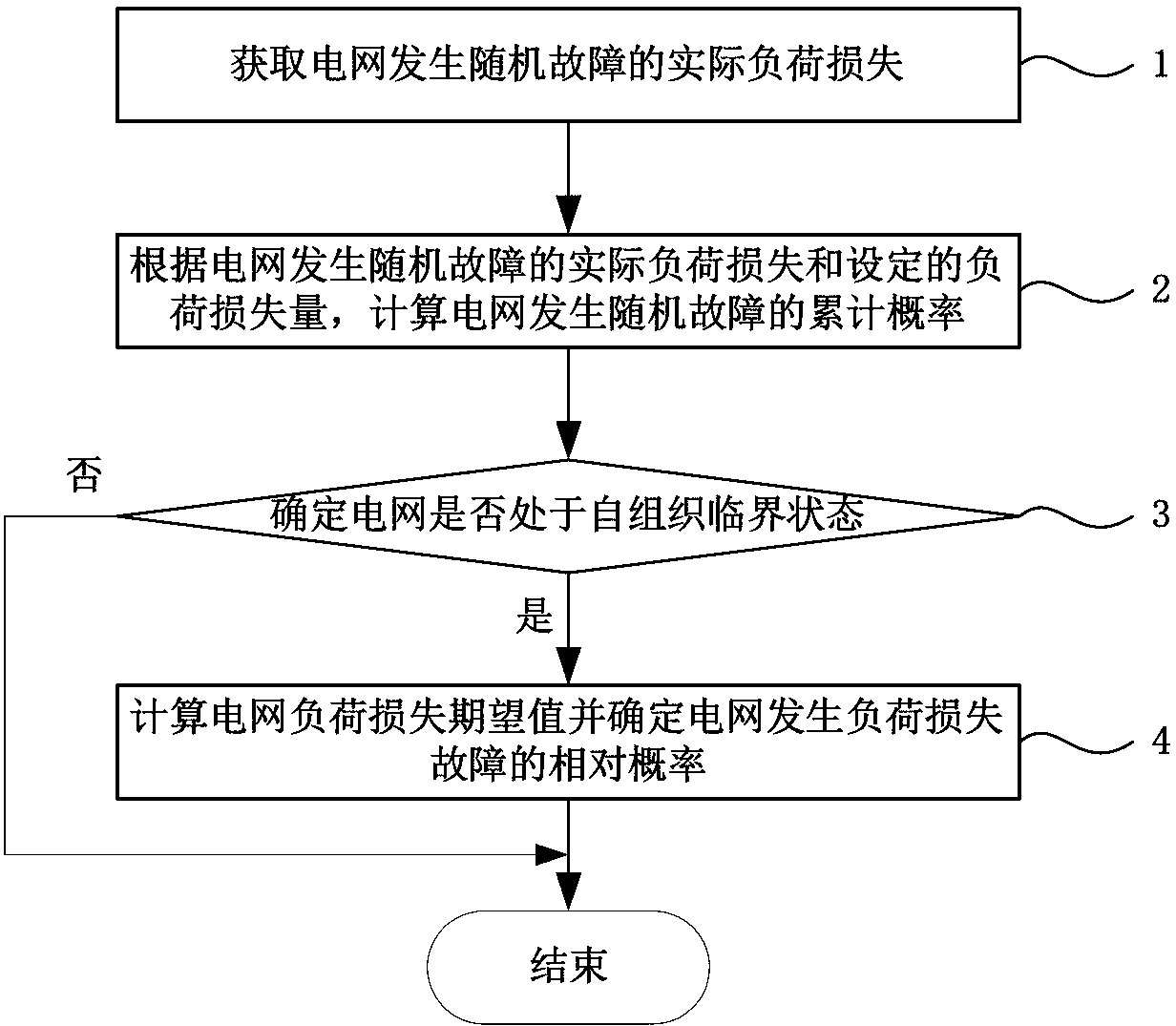
[0041] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the identification method for the self-organized critical state of the complex power grid provided by the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the process of identification method for self-organized critical state of complex power grid includes:
[0042] Step 1: Obtain the actual load loss of random faults in the power grid.
[0043] The present invention adopts the OPA model based on removing slow dynamic process, obtains the load loss of the current power grid under random faults through DC power flow calculation and network topology analysis, and provides data support for the self-organized critical state judgment and quantitative description of the power grid.
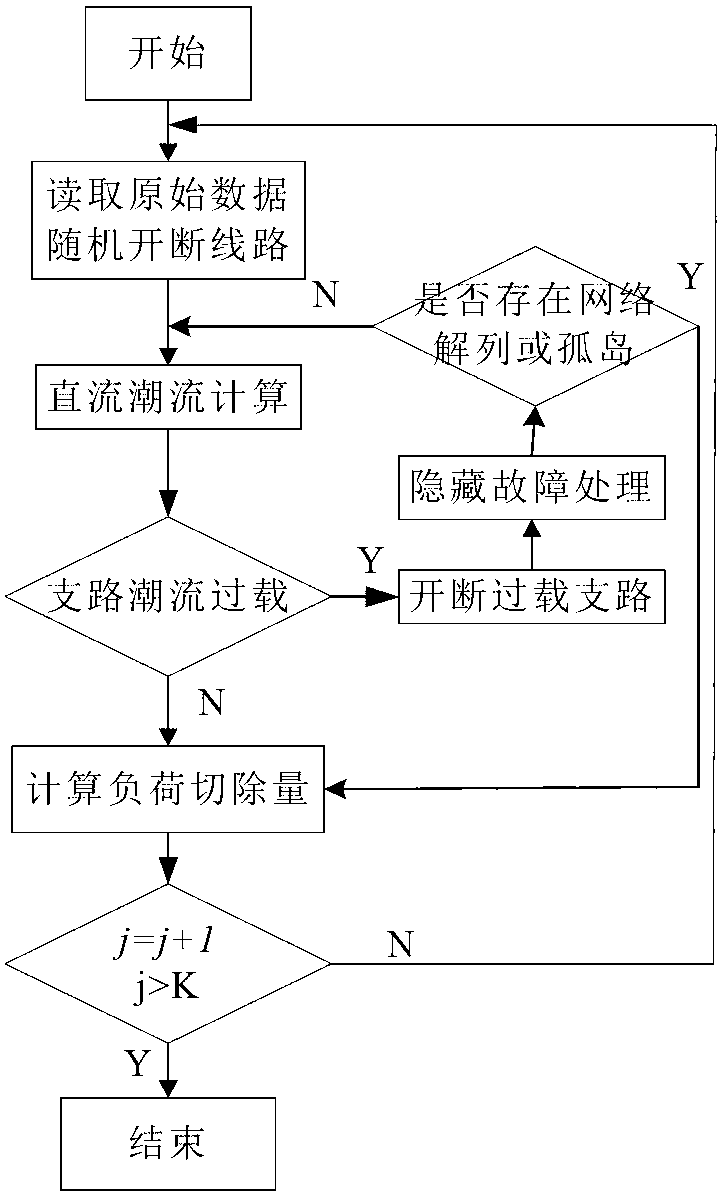
[0044] Such as figure 2 As shown, the simulation method is used to obtain the actual load loss of random faults in the power grid, including:
[0045] Sub-step 101: set the number K of random faults in the power grid during simulation, and set j=1.
[0046] Since...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Step 1: First, read in the parameters of regional power grids A and B and the power flow limit of each line component, determine the maximum output and load demand of the generator, and obtain the actual load loss of random faults in the power grid. The generation and load power of power grids A and B are counted, as shown in Table 3.
[0097]
[0098] Table 3. Generation and load power of regional power grids A and B (MW)
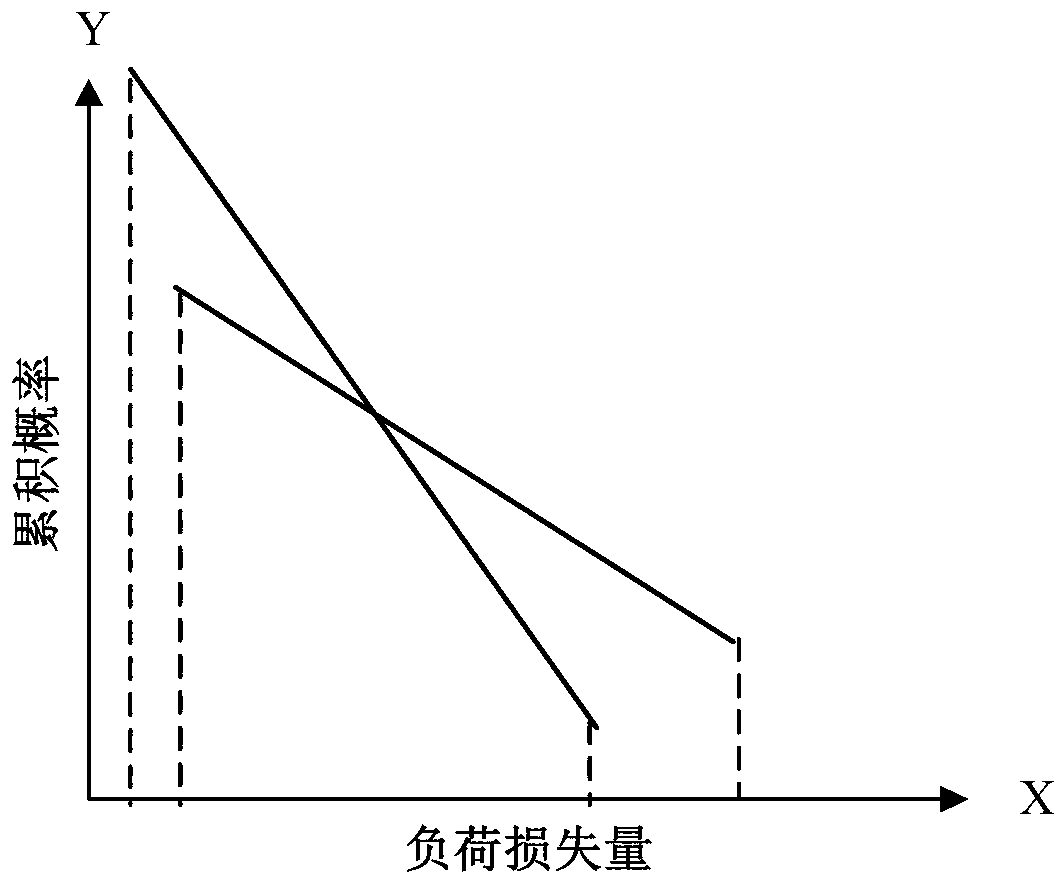
[0099] Step 2: Set the number of power outage simulations to 20, and calculate the load loss and cumulative probability of power grids A and B after random failures in the current state. As shown in Table 4 and Table 5. Only the cases with load loss are counted in the table.
[0100] Load loss (MW)
25
41
100
120
cumulative probability
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
[0101] Table 4. Load loss and cumulative probability after random failure of power grid A
[0102] Load loss (MW)
50
60...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com