Redundant drive symmetric three degree-of-freedom mobile parallel mechanism
A degree of freedom, symmetrical technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problem of redundant drive three-degree-of-freedom mobile parallel mechanism report and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
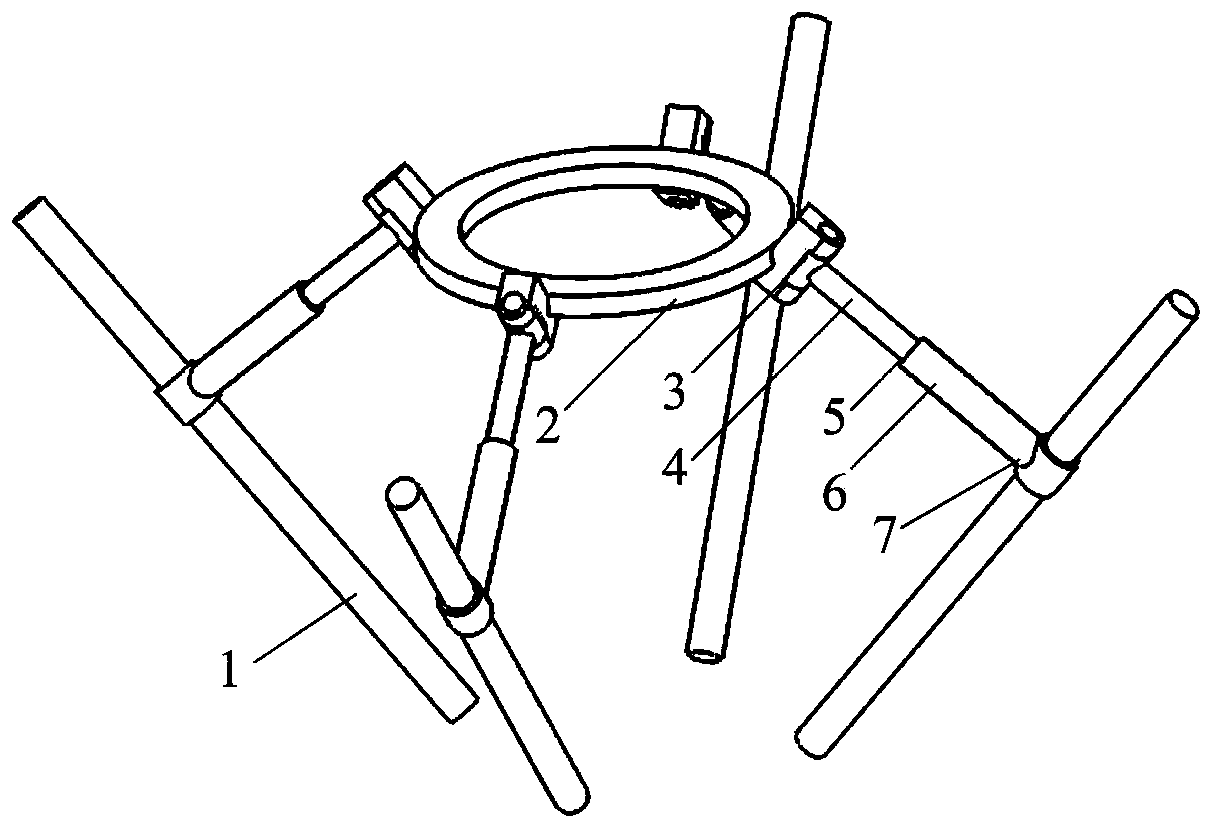
[0012] exist figure 1 In the schematic diagram of the redundant drive symmetrical three-degree-of-freedom mobile parallel mechanism shown, four branch chains with the same structure connect the moving platform 2 and the four fixed guide rails 1, and the four fixed guide rails are evenly distributed on the same conical surface. One end of the upper connecting rod 4 is connected with the moving platform through the rotating pair 3, the other end of the upper connecting rod is connected with one end of the lower connecting rod 6 through the moving pair, and the other end of the lower connecting rod is connected with the fixed guide rail through the cylindrical pair 7 , the moving part of the cylindrical pair is the input kinematic pair, the axis of the cylindrical pair coincides with the axial direction of the fixed guide rail, and the four rotating pairs on the four branch chains are evenly distributed on the moving platform. The axis of the cylinder pair is parallel, and the ax...
Embodiment 2
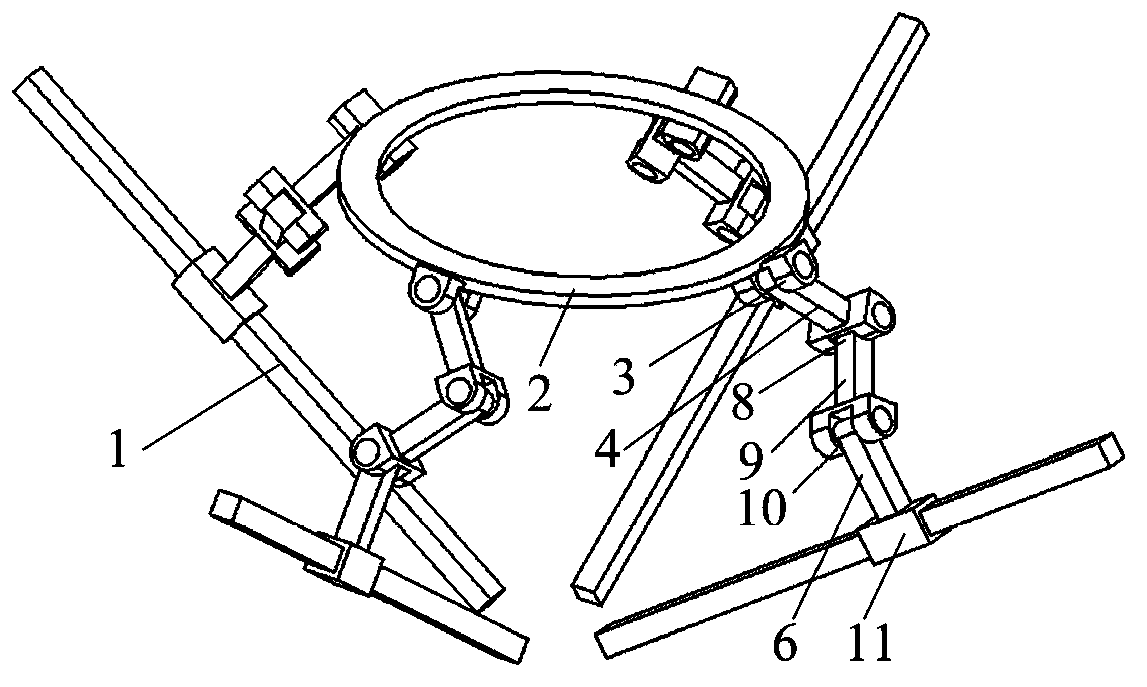
[0014] exist figure 2 In the schematic diagram of the redundant drive symmetrical three-degree-of-freedom mobile parallel mechanism shown, four branch chains with the same structure connect the moving platform 2 and the four fixed guide rails 1, and the four fixed guide rails are evenly distributed on the same conical surface. One end of the upper connecting rod 4 is connected with the moving platform through the rotating pair 3, the other end of the upper connecting rod is connected with one end of the middle connecting rod 9 through the rotating pair 8, and the other end of the middle connecting rod is connected with the lower connecting rod through the rotating pair 10. One end of the rod 6 is connected, and the other end of the lower connecting rod is connected with the fixed guide rail through the moving pair 11. The moving pair is an input kinematic pair, and its axis coincides with the axial direction of the fixed guide rail. The axes of the moving pairs are parallel, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com