Method and device for creating tables, saving records and deleting records for embedded system database
An embedded system and database technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of invariable length and low utilization of storage space, and achieve the effect of solving complex algorithms and improving data processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
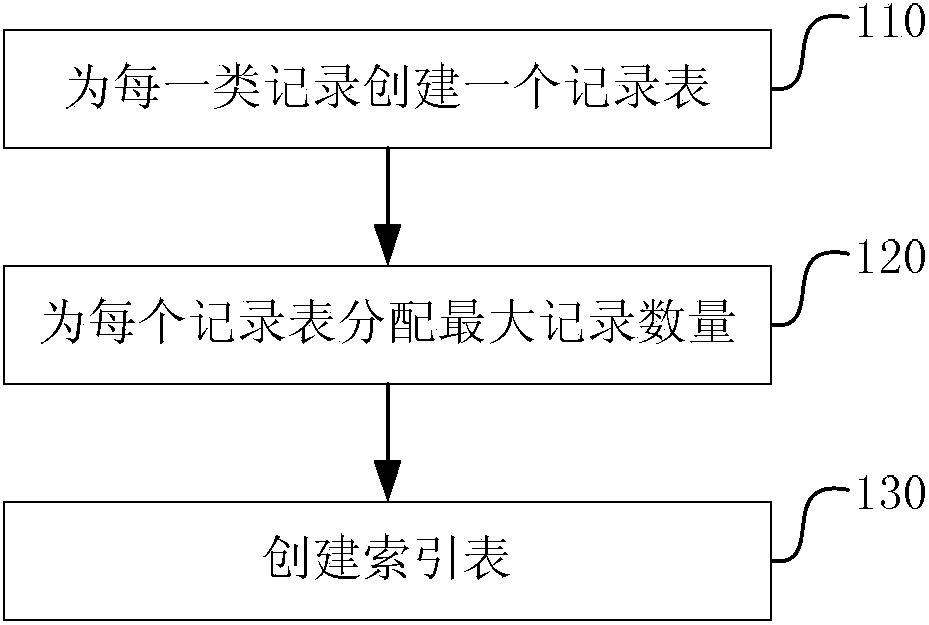
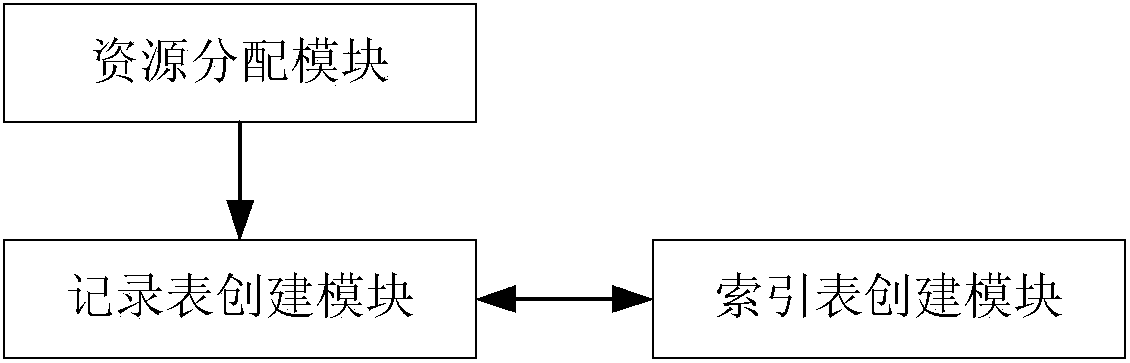
[0061] This embodiment introduces the method for creating table in the embedded system database, as figure 1 shown, including the following steps 110-130:
[0062] Step 110, create a record table for each type of record, each record table includes a newness identification field, and the newness identification is used to identify the newness of each record;
[0063] The class of records is distinguished by the types of records that the system needs to save;
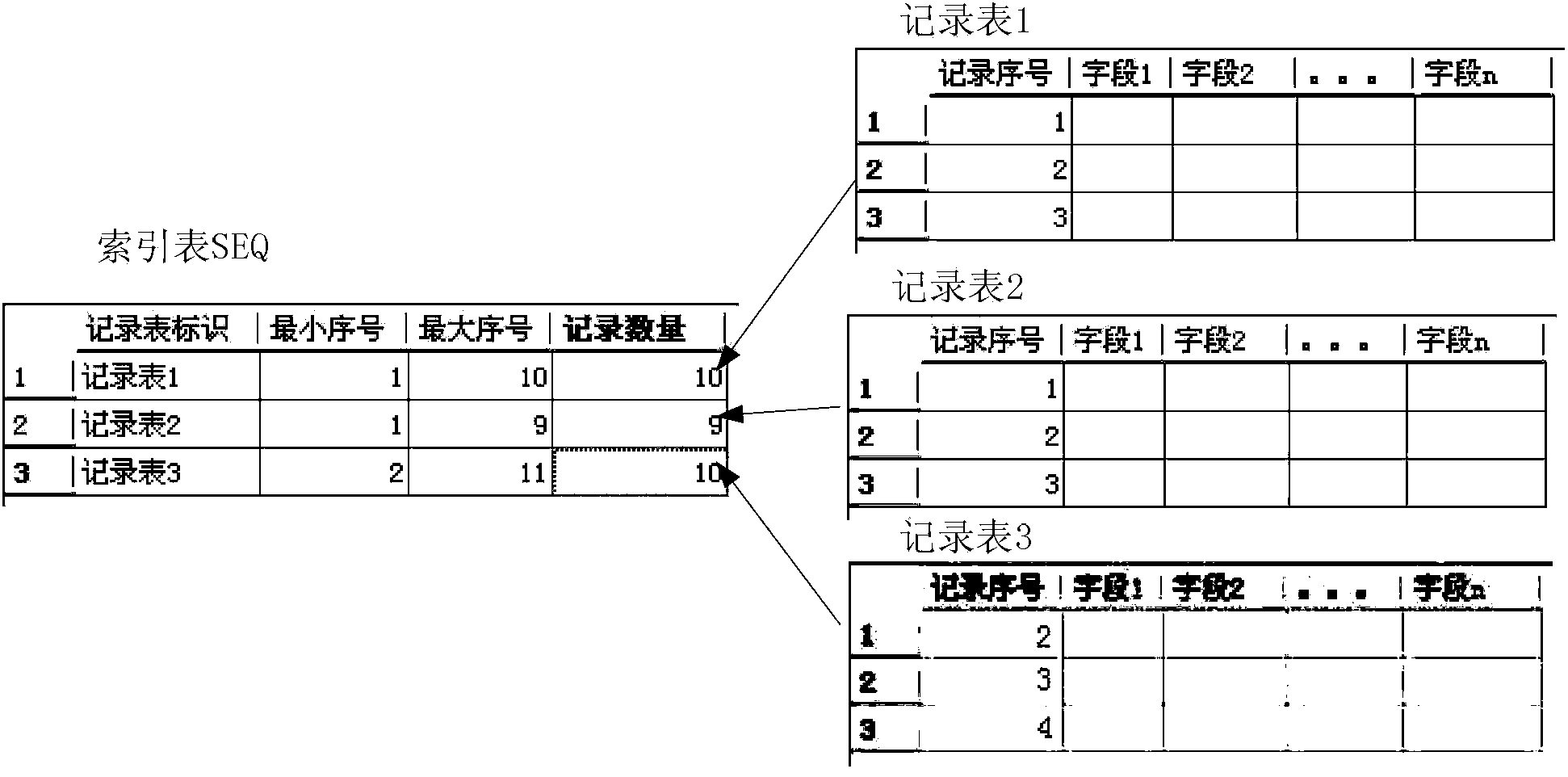
[0064] The newness and oldness identification field is, for example, the record serial number field. It can be set that the smaller the record serial number is, the earlier the record is, and the older the record is. The larger the record serial number is, the newer the record is. The record with the smallest serial number in the record table is the oldest record. The largest record is the newest record;
[0065] Step 120, assigning the maximum number of records for each record table;
[0066] Specifically, allocate the...
Embodiment 2
[0075] This embodiment introduces the method for storing records in the embedded system database table created above, such as Figure 4 As shown, including the following steps 210-240:
[0076] Step 210, when storing the record to be stored into the record table, read the current record quantity of the record table from the index table corresponding to the record table;
[0077] Step 220, judging whether the record table is full according to the current record quantity, if it is not full, execute step 230, if it is full, execute step 240;
[0078] Specifically, it is judged whether the current record quantity is greater than or equal to the maximum record quantity of the record table, if yes, it means that it is full, if not, it means it is not full.
[0079] Step 230, write the record to be stored into the record table as a new record, and update the old and new record information and the current record quantity of the record table in the index table;
[0080] The new and o...
Embodiment 3
[0097] This embodiment introduces the method for deleting records in the embedded system database table created above, such as Figure 8 As shown, including the following steps 310-320:
[0098] Step 310, delete records in the record table;
[0099] The recording table described here is the recording table created in Embodiment 1.
[0100] Step 320, updating the current number of records in the index table.
[0101] The index table described here is the index table created in Embodiment 1.
[0102]Preferably, in step 310, if the non-oldest and non-latest records in the record table are deleted, only the current number of records in the index table needs to be updated. If the deleted record includes the oldest record and / or the newest record in the record table, then update the old and new record information in the index table, for example, correspondingly update the oldest record identifier and / or the latest record identifier in the index table.
[0103] In short, when del...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com