Next hop computation functions for equal cost multi-path packet switching networks
A technology of packet switching network and packet network, applied in the field of next hop calculation function, which can solve problems such as poor traffic distribution and insufficient traffic propagation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
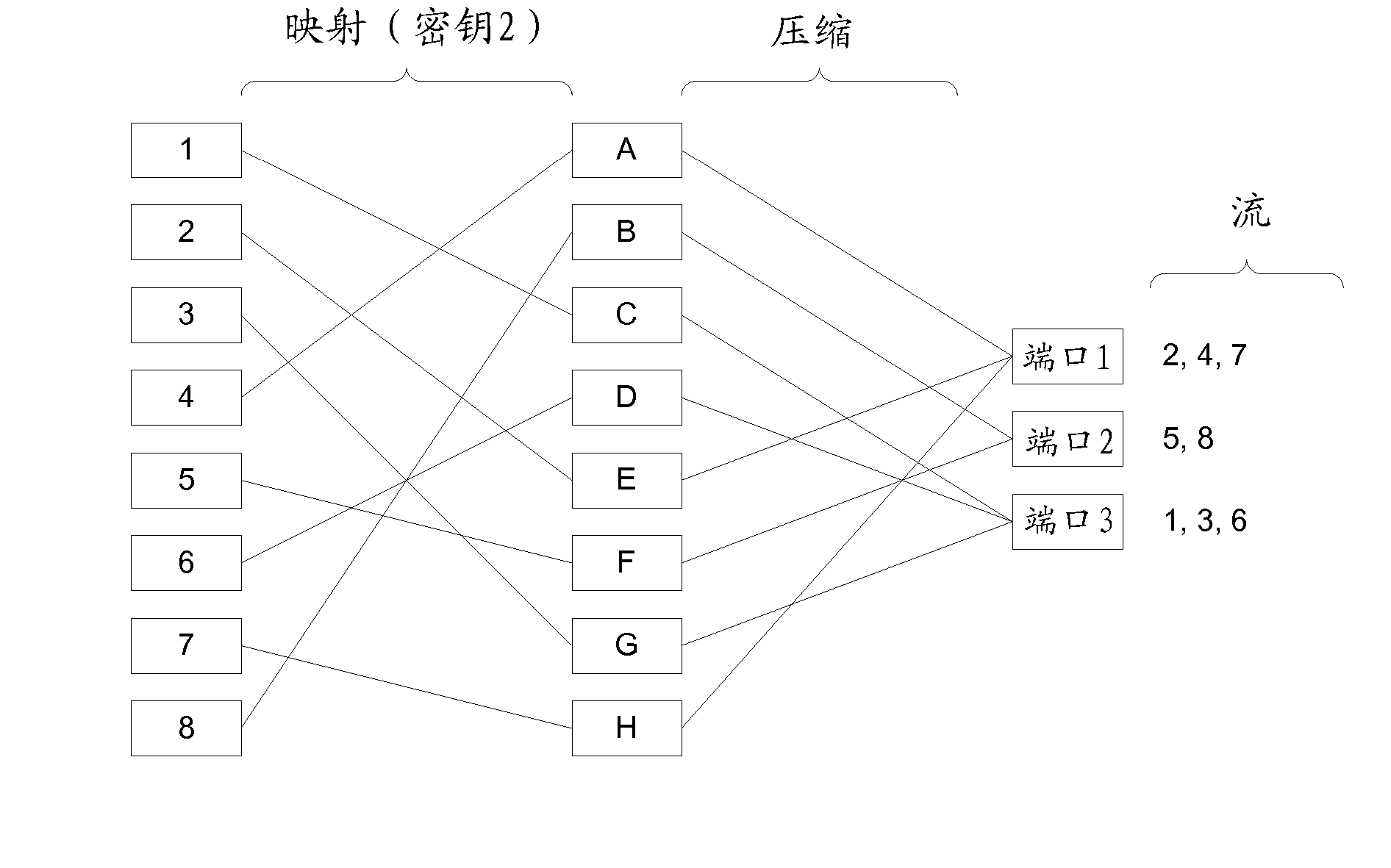
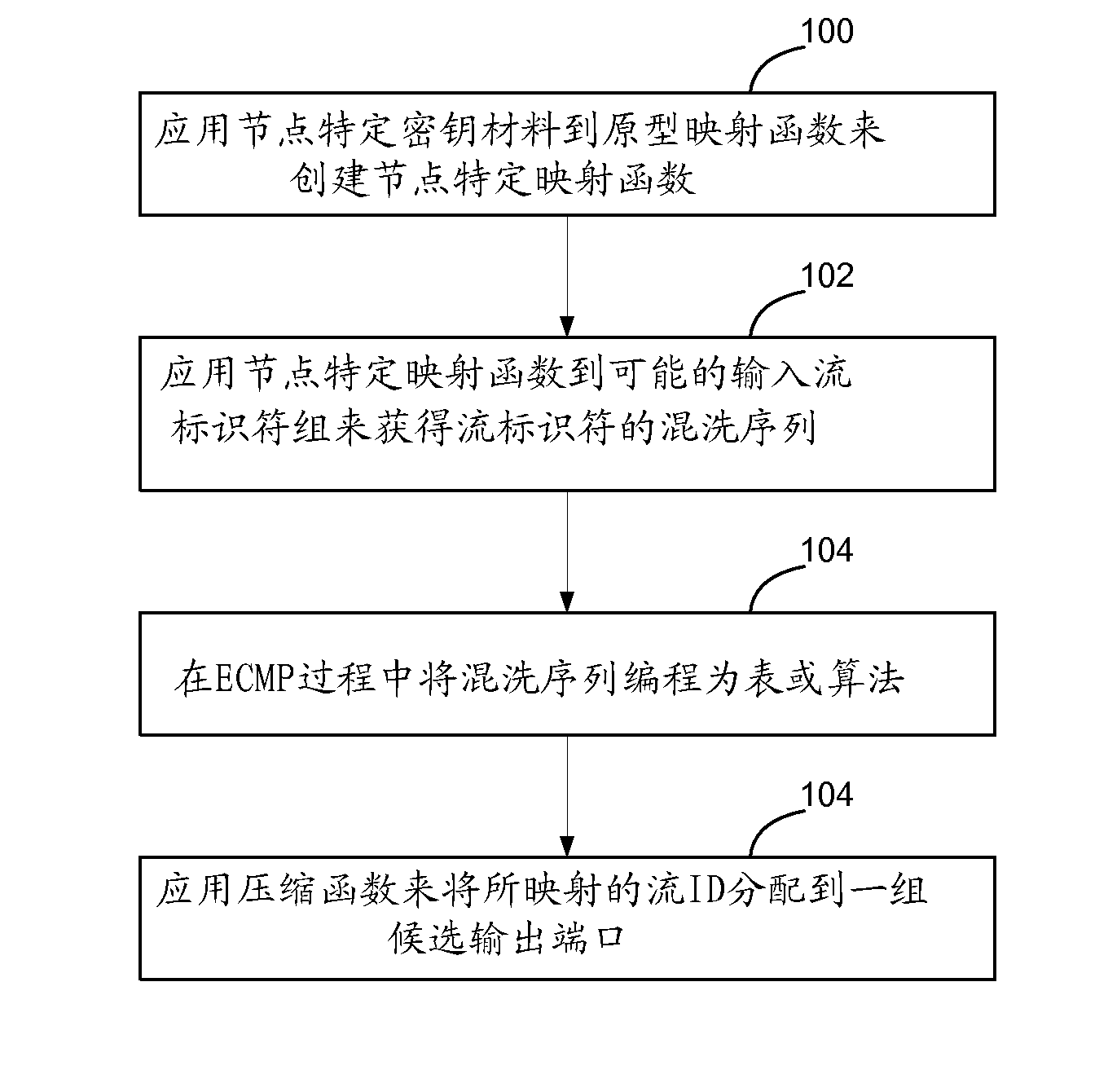
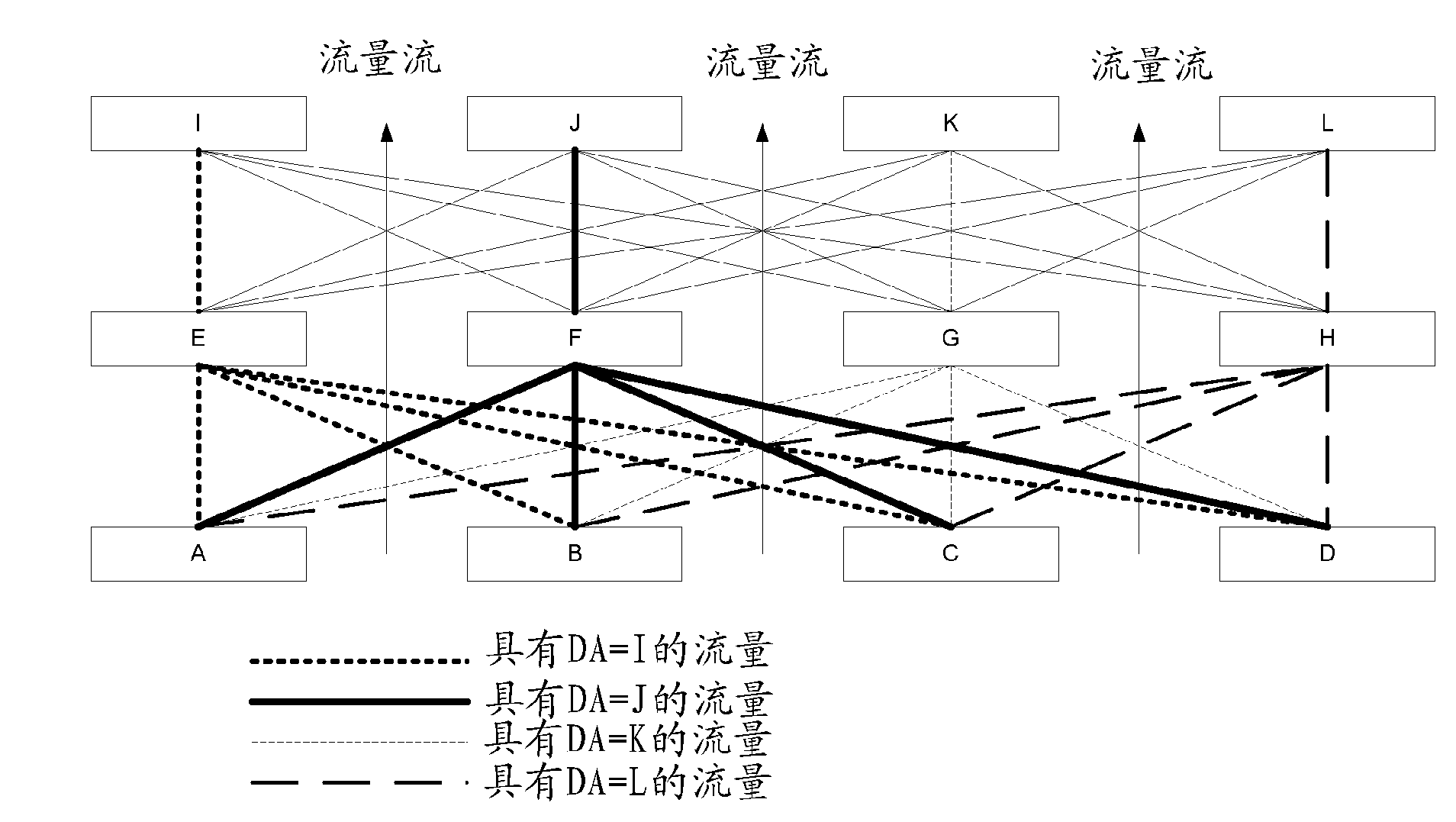
[0018] figure 1 A sample network is shown where the same next-hop calculation function is used at each hop in the network. flow from figure 1 The bottom of the flow to the top, and at each node, the flow is mapped locally by the node to one of 4 possible output ports. Traffic is evenly distributed between the bottom and middle rows of switches, where each link of the mesh connects the two rows being utilized. However, the middle row of switches cannot utilize all the links connecting it to the top row. The leftmost switch in the middle row receives only traffic that is mapped to the leftmost egress port. Similarly, the ith switch in the row only receives traffic that is mapped to the ith port in the previous stage. This irrational behavior is caused by the use of the same mapping function at each node and the regular nature of the mesh used in this example. However, very regular network structures of this type are not uncommon at all. In particular, data centers tend t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com