MUC1 (Mucins 1) and GM-CSF (Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor) dual-gene co-expression recombinant vector and preparation method and application thereof
A GM-CSF, recombinant vector technology, applied in the field of recombinant vector and its preparation, can solve the problems of immune regulation, low anti-tumor ability, lack of immunotherapy targeting, etc., to promote T cell immune response, improve tumor immunity Therapeutic effect, the effect of enhancing the antibody response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1: Obtaining MUC1 gene fragments containing specific enzyme cleavage sites
[0051] 1. Primer design
[0052] According to the nucleotide sequence of the MUC1 gene (as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence listing) and the expected insertion multiple cloning site on the pIRES2-EGFP plasmid vector, design specific primers as follows:
[0053] MUC1 upstream primer (as shown in SEQ ID NO:4 in the sequence listing):
[0054] 5'-GA AGATCT ATGACACCGGGCACCC-3' (the underlined part is the sequence of the Bgl II restriction site),
[0055] MUC1 downstream primer (as shown in SEQ ID NO:5 in the sequence listing):
[0056] 5'-TT GAATTC CTACAAGTTGGCAGAAGTGG-3' (the underlined part is the sequence of EcoR I restriction site).
[0057] 2. Obtain cDNA template
[0058] RNA was extracted from human breast cancer cell MCF-7 by TRIzon method (TRIzon total RNA extraction kit was purchased from Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology Co., Ltd., product number is CW0580), and r...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2: Construction of pIRES2-MUC1-EGFP recombinant vector
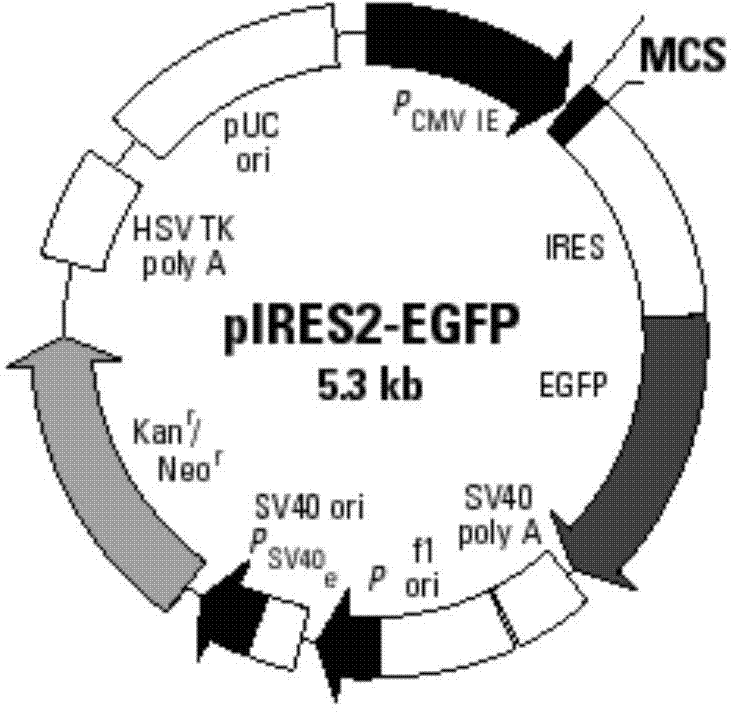
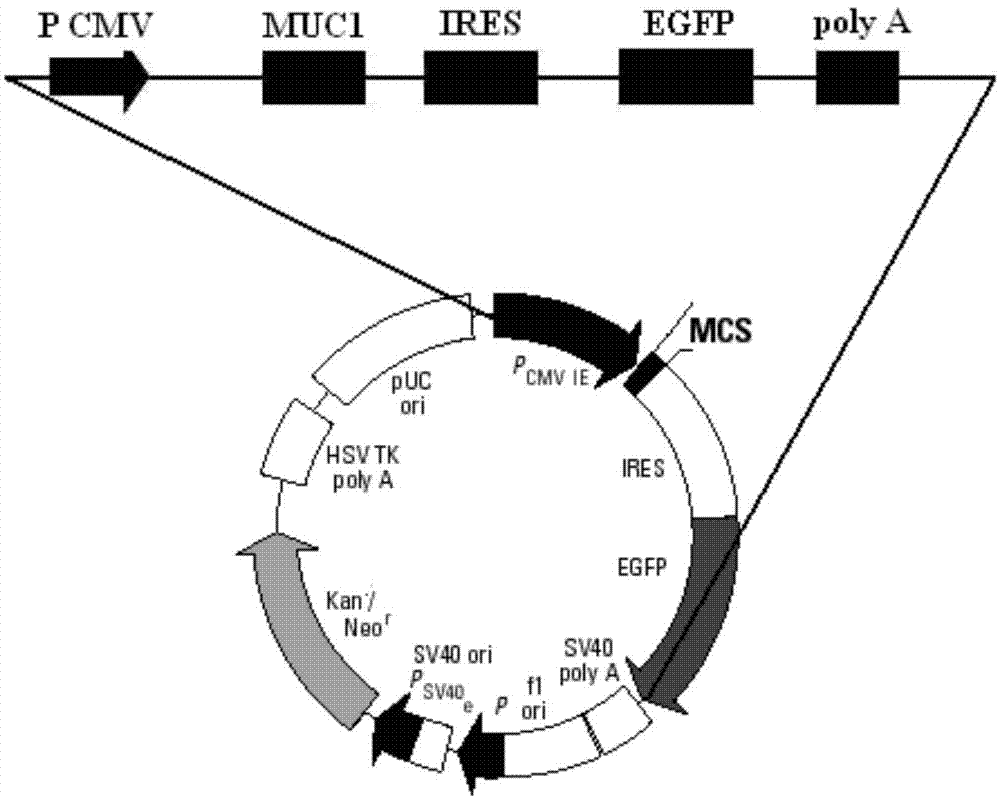
[0066] Using restriction endonucleases Bgl II and EcoR I, digest the pIRES2-EGFP plasmid (the multiple cloning site of the plasmid contains Bgl II, EcoR I restriction sites) and the MUC1 gene fragment obtained in Example 1, respectively, to obtain Linearized pIRES2-EGFP vector after digestion and MUC1 gene sequence after digestion; use T4 DNA ligase system for ligation reaction, incubate at 22°C for 30 minutes, and then inactivate at 70°C for 5 minutes to construct pIRES2-MUC1 -EGFP recombinant vector (such as image 3 shown).
[0067] Structural features of the pIRES2-EGFP plasmid (eg figure 2 Shown) It can be seen that after the MUC1 gene is inserted into the multiple cloning site of the pIRES2-EGFP plasmid, it is located upstream of the self-sequence IRES of the plasmid vector (such as image 3 shown), that is, MUC1 and EGFP sequences were expressed separately under the same promoter.
[0068] 1. D...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3: Double PCR method to obtain GM-CSF gene fragments with restriction endonuclease cohesive ends
[0096] According to the GM-CSF gene sequence and the expected insertion multiple cloning site on the pIRES2-EGFP plasmid vector, design two pairs of primers with different lengths and sticky ends with restriction endonucleases; reverse transcribe with RNA extracted from CIK cells The cDNA of cDNA was used as a template, and the above two pairs of primers were used for PCR amplification to obtain two PCR amplification products; the two PCR amplification products were mixed and then denatured and annealed sequentially to obtain four GM-CSF gene fragments, wherein Both GM-CSF gene fragments have restriction endonuclease cohesive ends, which allow directional ligation of the GM-CSF gene fragments into the desired polyclonal of the plasmid vector without the need for restriction endonuclease digestion site.
[0097] Compared with the traditional PCR product cloning met...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com