A scanning method for laser ablation processing based on spatio-temporal optimization
A technology of laser ablation and scanning method, applied in laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as overheating, reducing ablation unevenness, reducing laser energy on the surface of the object to be ablated, and extending the interval time , Increase the coordinate spacing of selected points and reduce the effect of overlapping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0025] Embodiment: a kind of scanning method of ablation corneal tissue comprises the following steps:
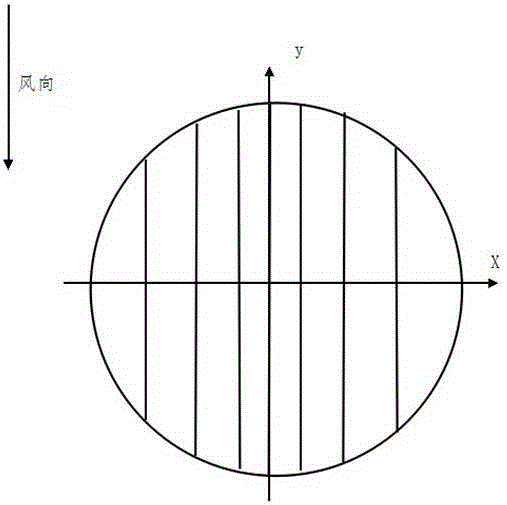
[0026] The first stage: the computer calculates the total number of points to be ablated to be ablated through the scanner, obtains the coordinates of each point to be ablated, and then divides the coordinate points into scanning areas, and the number of scanning points in each scanning area is the same.
[0027] The division of the scanning area: firstly, the computer divides all the calculated points a into n parts according to the spot parameters, and marks them as Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ...the remaining parts are assigned to the first few scans in order area, so that the number of scan points for each scan area is obtained. According to the abscissa x of the scanning points (perpendicular to the wind direction), they are arranged in ascending order, and the corresponding number of scanning points are counted in order as the first area, and the abscissa of the boundary line of the sc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com