Power distribution fault studying and judging method based on multisystem collaboration
A multi-system, fault technology, applied in the direction of the fault location, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings: It should be emphasized that the embodiments of the present invention are illustrative rather than restrictive, and should not limit the protection scope of the present invention.
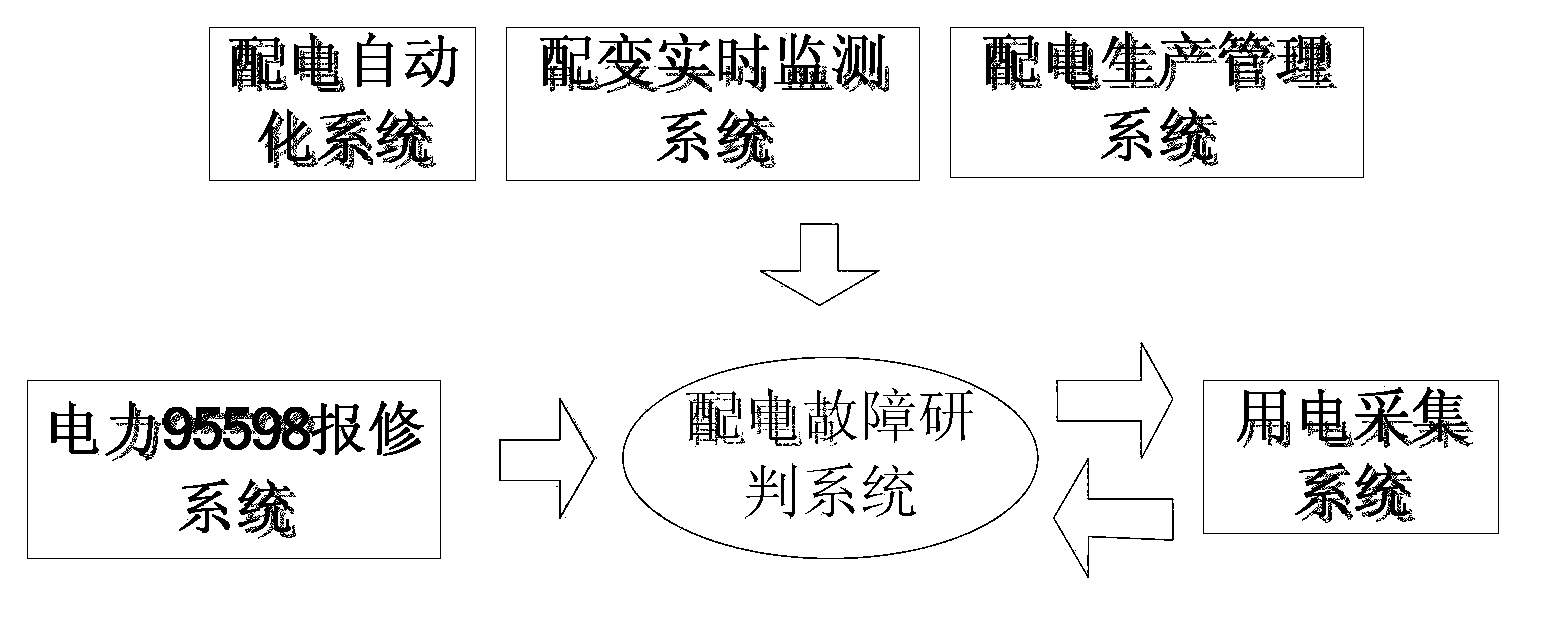
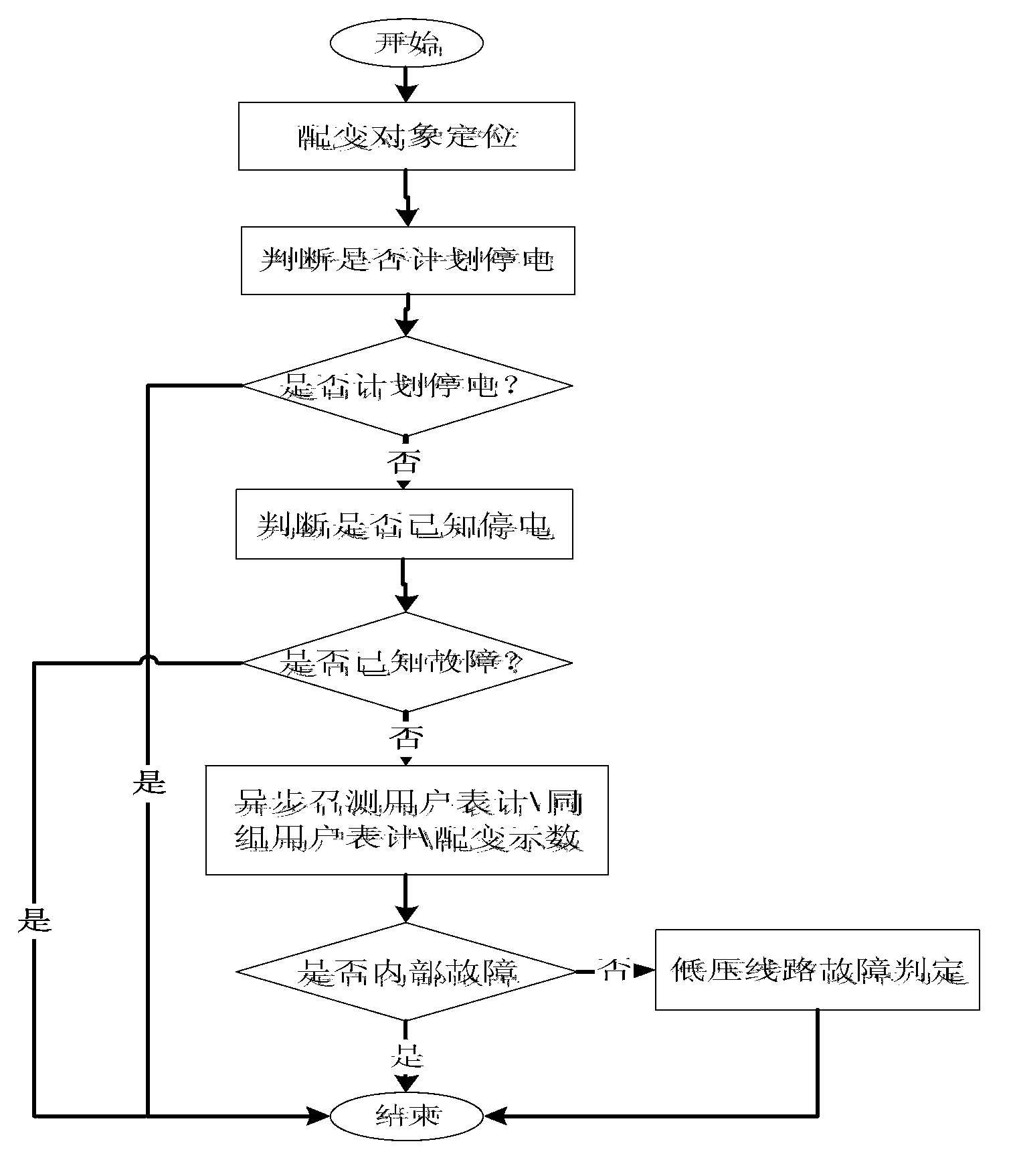
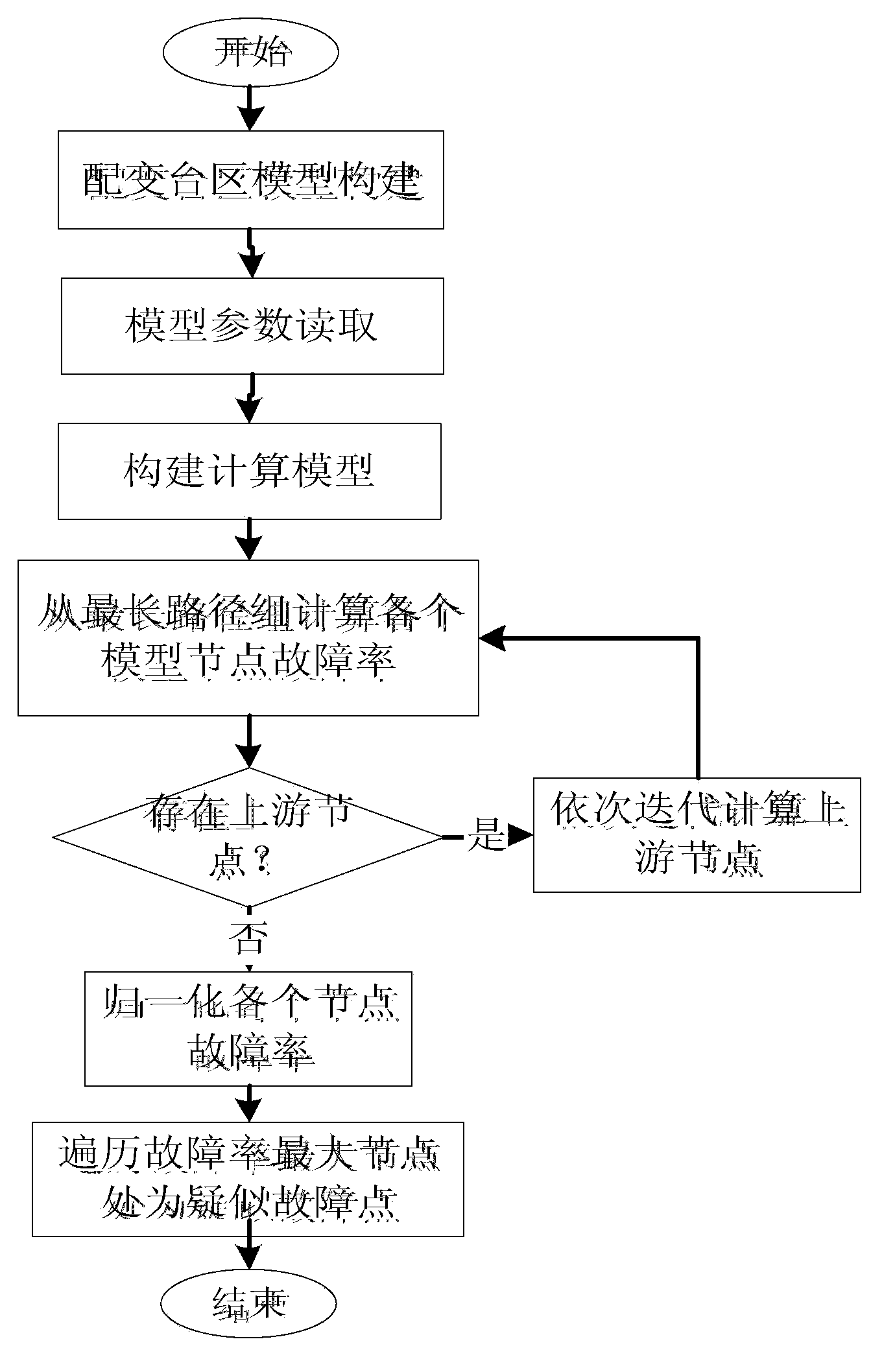
[0035] A power distribution fault research and judgment method based on multi-system cooperation, such as figure 1 As shown, the research and judgment method is based on the established distribution automation system (DMS), comprehensive power acquisition system, distribution transformer real-time monitoring system, distribution production management system and electric power 95598 repair based on the 95598 fault The repair report is realized as the initial trigger condition. The innovation of the present invention is that it realizes the automatic judgment of the failure of the medium-voltage equipment and the automatic judgment of the failure of the low-voltage e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com