Rabies virus like particle production in plants
A technology of rabies virus and rabies, which is applied in the direction of plant products, viruses, and viral peptides, and can solve the problems of reduced yields and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0133] Example 1: Assembly of expression cassettes with rabies protein
[0134] A-X35S / CPMV-HT / Rabies M / NOS (Construct No. 1066)
[0135]The sequence encoding the M protein from the ERA strain of rabies virus was cloned into the 2X35S / CPMV-HT / NOS expression system of the plasmid containing the Plasto_pro / P19 / Plasto_ter expression cassette using a PCR-based approach as follows. Using a synthetic M gene (corresponding to nt2496-3104 from Genbank accession number FJ913470) ( Figure 4C , SEQ ID NO: 3) as template, using primer IF-RabM-S3.c ( Figure 4A , SEQ ID NO: 1) and IF-RabM-S1-4.r ( Figure 4B , SEQ ID NO: 2) amplifies a fragment comprising the entire M protein coding sequence. PCR products were cloned into the 2X35S / CPMV-HT / NOS expression system using the In-Fusion cloning system (Clontech, Mountain View, CA). Construct No. 1191 was digested with SacII and StuI restriction enzymes ( Figure 4D ) and use the linearized plasmid in an In-Fusion assembly reaction. Cons...
Embodiment 2
[0142] Example 2: Preparation of Plant Biomass, Inoculum and Agrobacterium Infiltration
[0143] As used herein, the terms "biomass" and "plant matter" are meant to reflect any matter derived from plants. Biomass or plant matter may include whole plants, tissues, cells, or any fraction thereof. Additionally, biomass or plant matter can include intracellular plant components, extracellular plant components, bodily fluid or solid extracts of plants, or combinations thereof. Additionally, biomass or plant matter can include plants, plant cells from plant leaves, stems, fruits, roots, or combinations thereof, tissues, liquid extracts, or combinations thereof. A part of a plant may comprise plant matter or biomass.
[0144] N. benthamiana was grown from seed in flats filled with a commercially available peat moss substrate. Plants were grown in a greenhouse with a 16 / 8 photoperiod and a temperature regime of 25°C day / 20°C night. Three weeks after sowing, individual plantlets we...
Embodiment 3
[0155] Example 3: Evaluation of rabies G protein expression and co-expression strategies
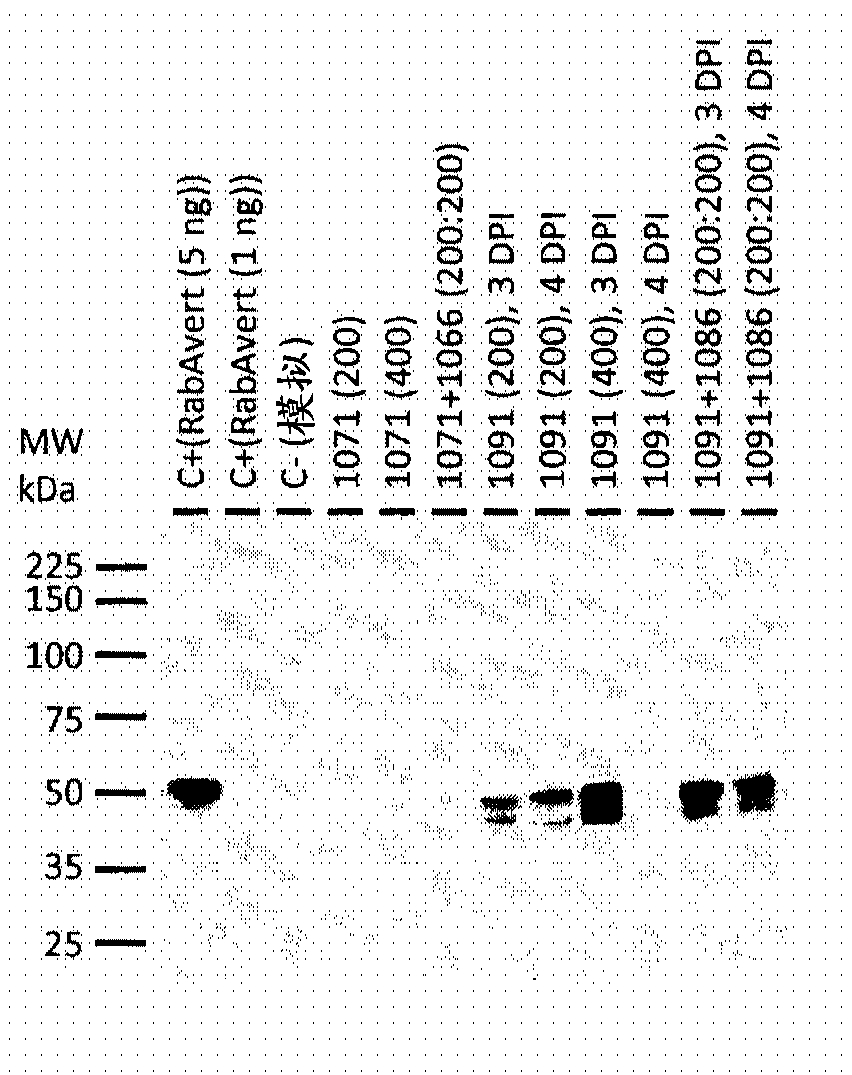
[0156] N. benthamiana plants were agro-infiltrated with AGL1 / 1071 (with or without AGL1 / 1066) or AGL1 / 1091 (with or without AGL1 / 1086) inoculum at different concentrations, for 1071-infiltrated plants and 1071-infiltrated plants Leaves were harvested after 5 days post infiltration (DPI) for +1066 infiltrated plants or after 3 to 4 DPI for 1091 infiltrated plants and 1091+1086 infiltrated plants. Western blot analysis of leaf protein extracts from transformed plants showed that the BeYDV element was required to achieve detectable levels of G protein accumulation ( figure 1 Comparison of 1071-infiltrated plants with 1091-infiltrated plants). For plants infiltrated with AGL1 / 1091 co-expressed with or without the M protein (AGL1 / 1086), the maximum level of accumulation was reached at 3 DPI ( figure 1 ).
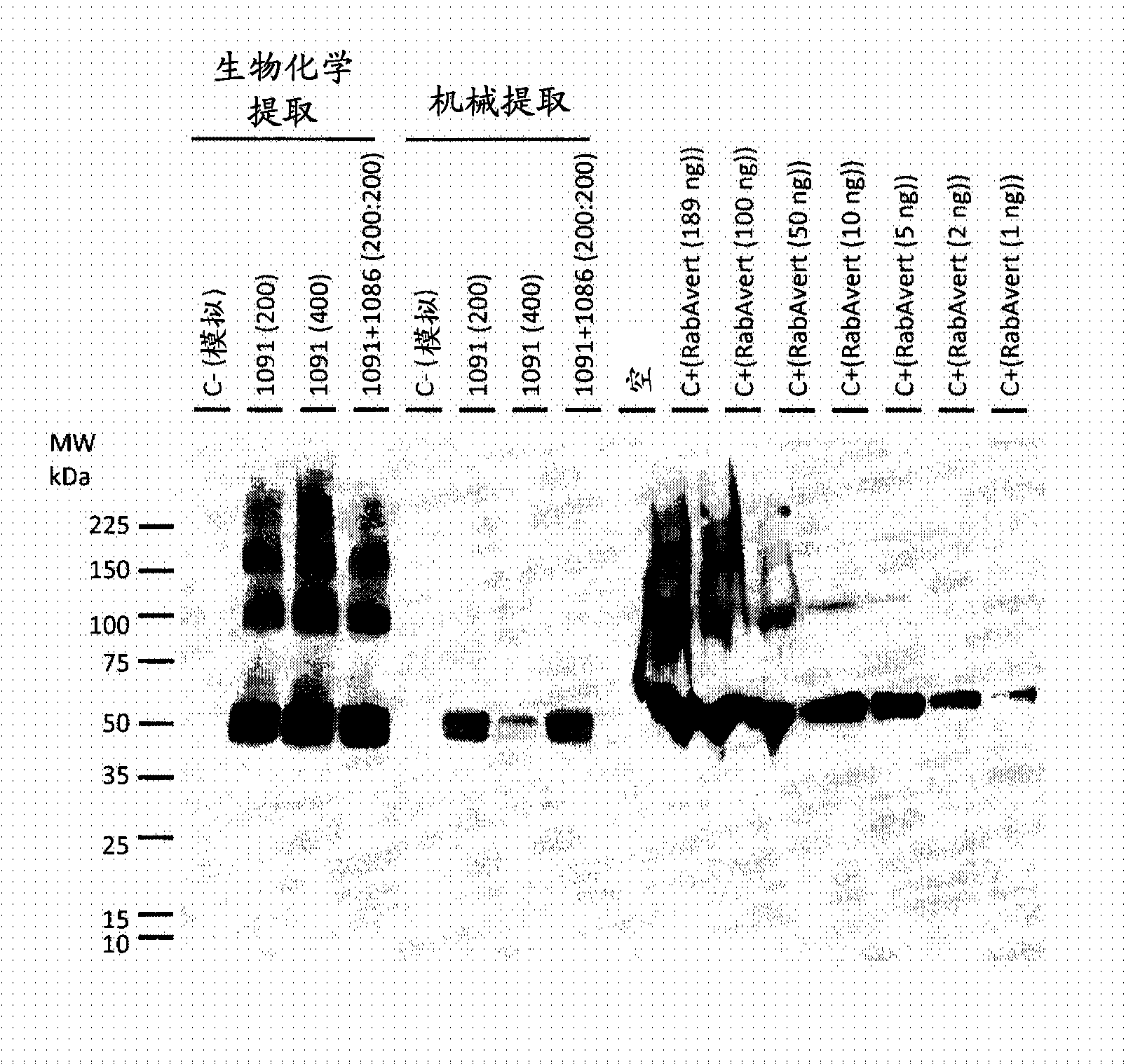
[0157] Biochemical extraction methods were able to release the rabies G protein from...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com