Master-slave type cooperative control method for autonomous underwater vehicles
A collaborative control and underwater navigation technology, applied in the field of control, can solve problems such as limiting engineering applications and not considering the influence of underwater ocean currents on system disturbances, and achieve the effect of collaborative control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example
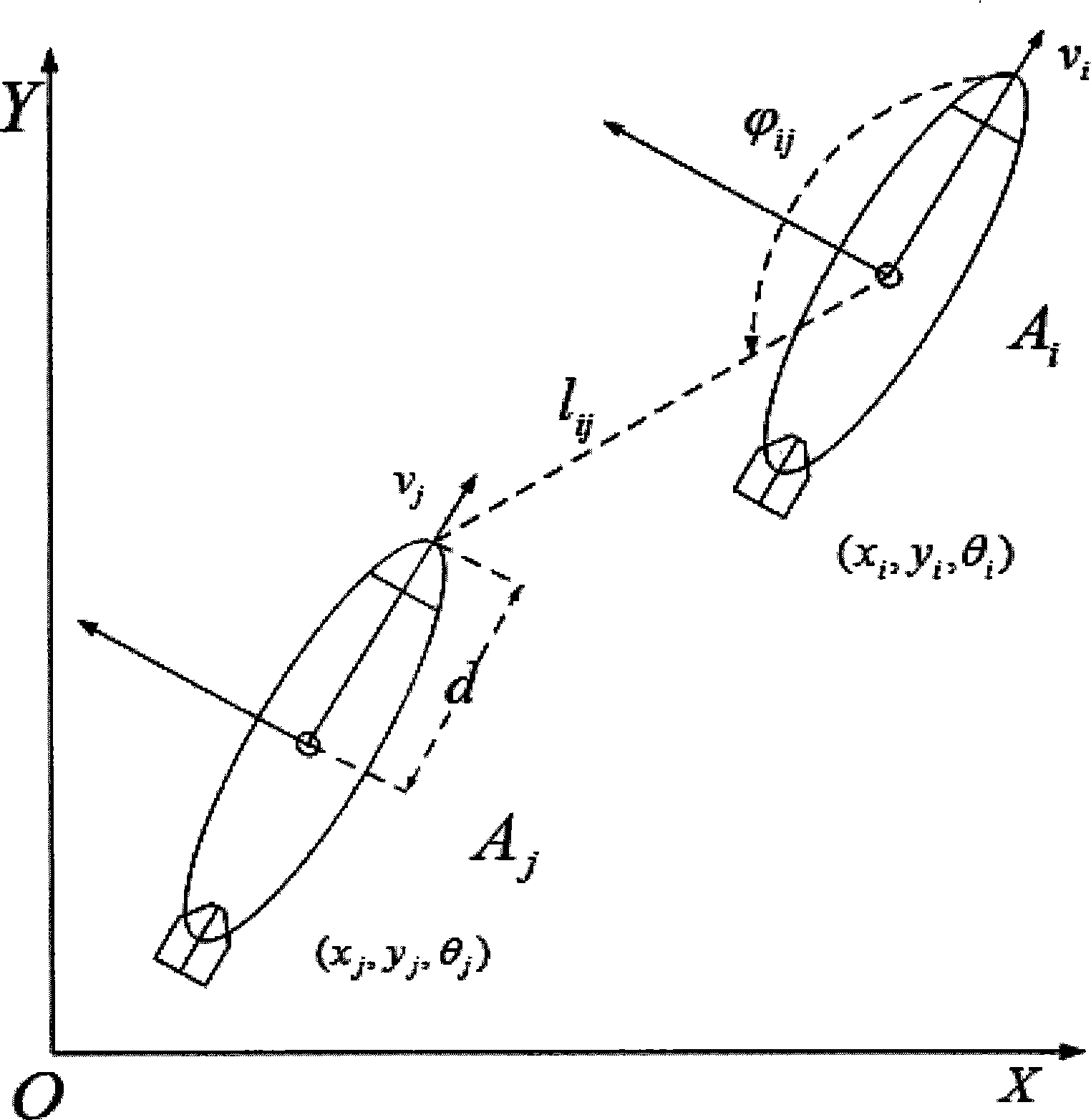
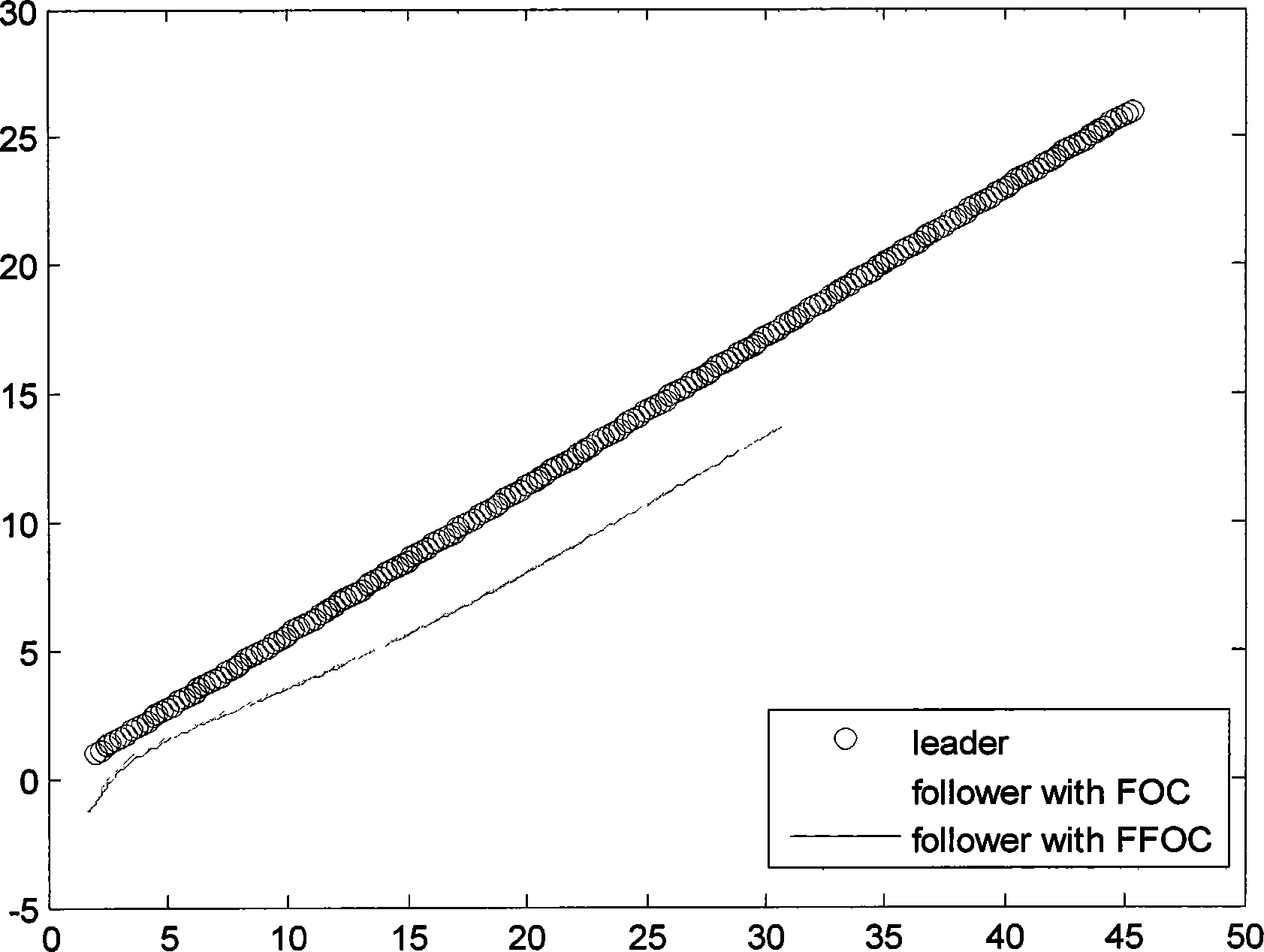
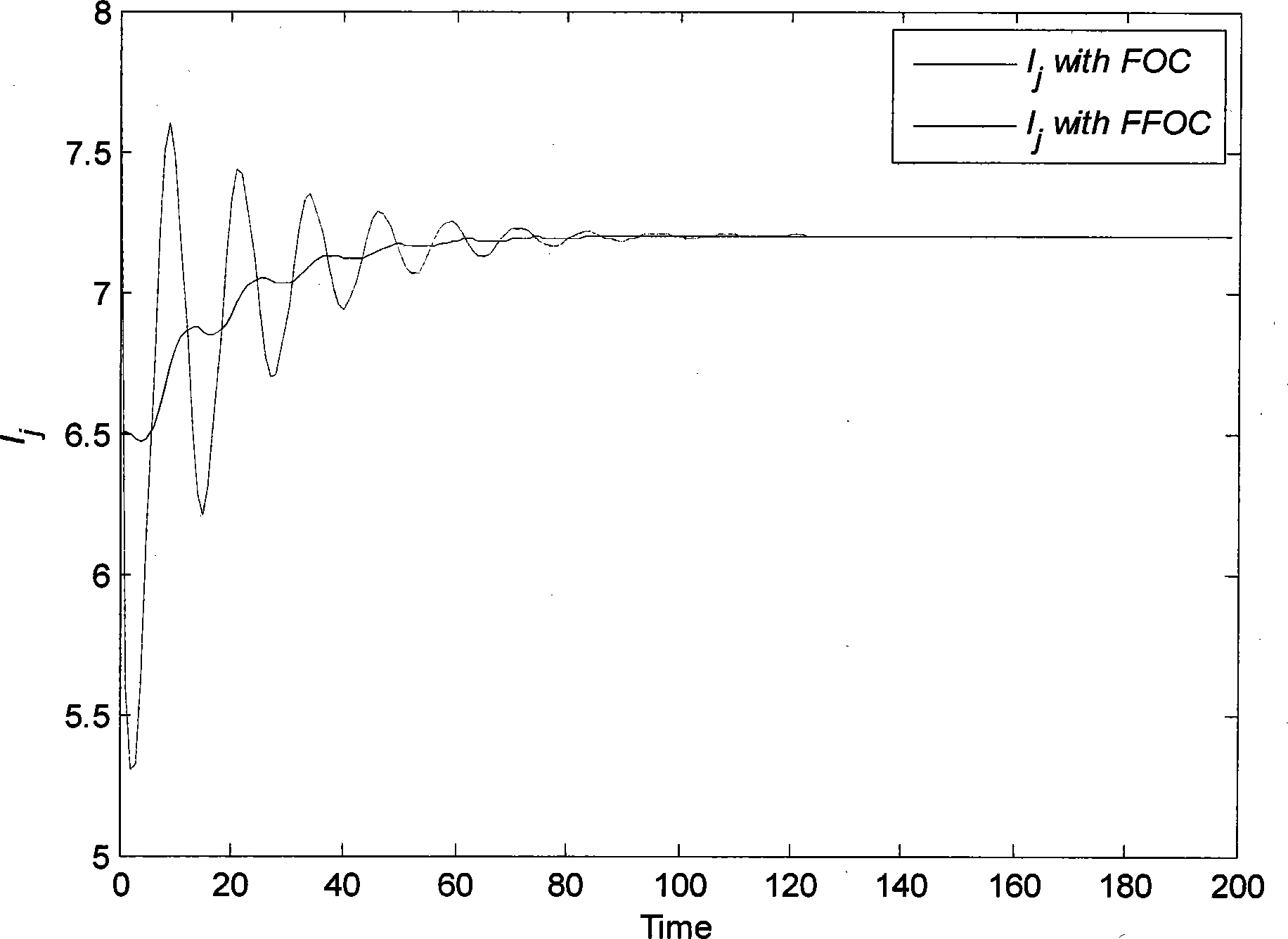
[0035] Under the inertial coordinate system, the main aircraft measures its initial position and attitude state through various sensors of its own. The initial state is p i (0)=[x i (0)y i (0) θ i (0)] T =[2m 1m π / 6rad] T , the velocity and angular velocity measured by acceleration and gyroscope are respectively v=3.5m / s, ω=0rad / s and remain unchanged. Measure the initial position and attitude state of the aircraft through its various sensors, and its initial state is p j (0)=[x j (0)y j (0) θ j (0)] T =[1.8m -1.2m 0rad] T , the desired spacing desired tracking angle but The underwater disturbance correlation matrix is the following formula (5):
[0036] D = - 0.5 0 1 1 , G = ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com