A Label Anti-collision Method Based on Binary Split Tree
A binary splitting and anti-collision technology, which is applied in the field of label anti-collision, can solve the problems of complex method of estimating the number of labels, low label recognition efficiency and inaccuracy, and achieve the effect of eliminating label starvation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
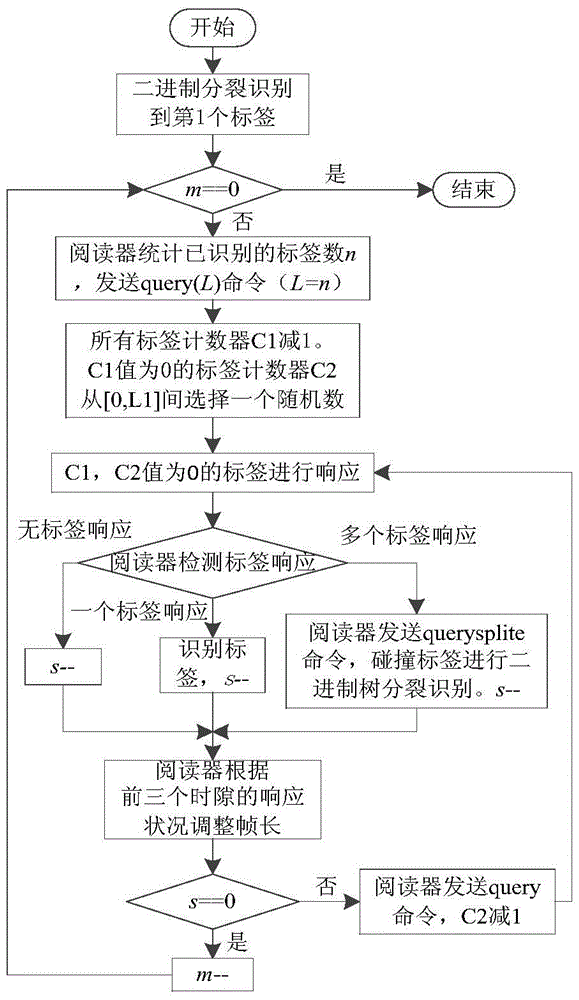
[0021] figure 1 For the implementation flow of the present invention, mainly comprise:
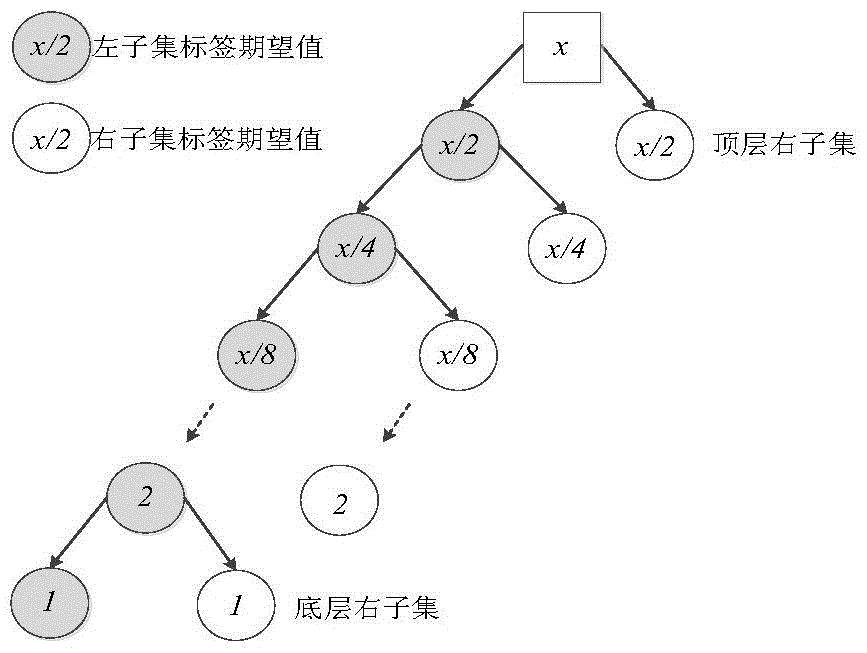
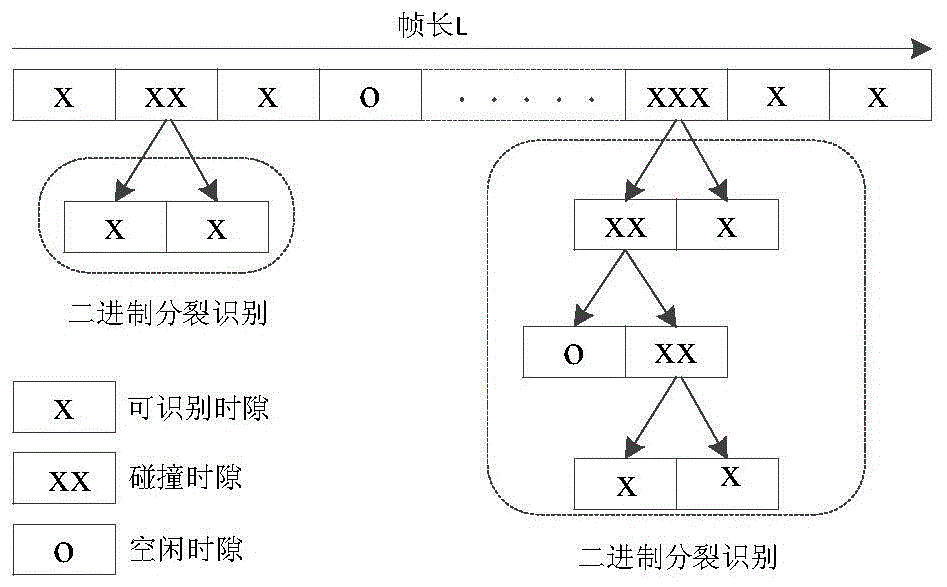
[0022] Set the counter C1 to record the layer where the label is located, and the counter C2 to record the frame time slot. The reader sends a start command to enter the layering stage, and after the first tag is recognized, the layering ends. Then, the labels of each layer are identified layer by layer starting from the bottom layer until the highest layer subset labels are identified. The reader first adopts the binary splitting tree algorithm to carry out tag layering, and splits the tags into subsets of different layers. At the same time, the tag counter records the layer to which the tag belongs. Then, starting from the right subset of the bottom layer, the labels of each layer are recognized layer by layer. After the recognition of each l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com