Layering storage and inquiring method based on key value database
A query method and data storage technology, applied in the field of key-value databases, can solve the problems of low overall efficiency, difficulty in querying key-value databases, and long time consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
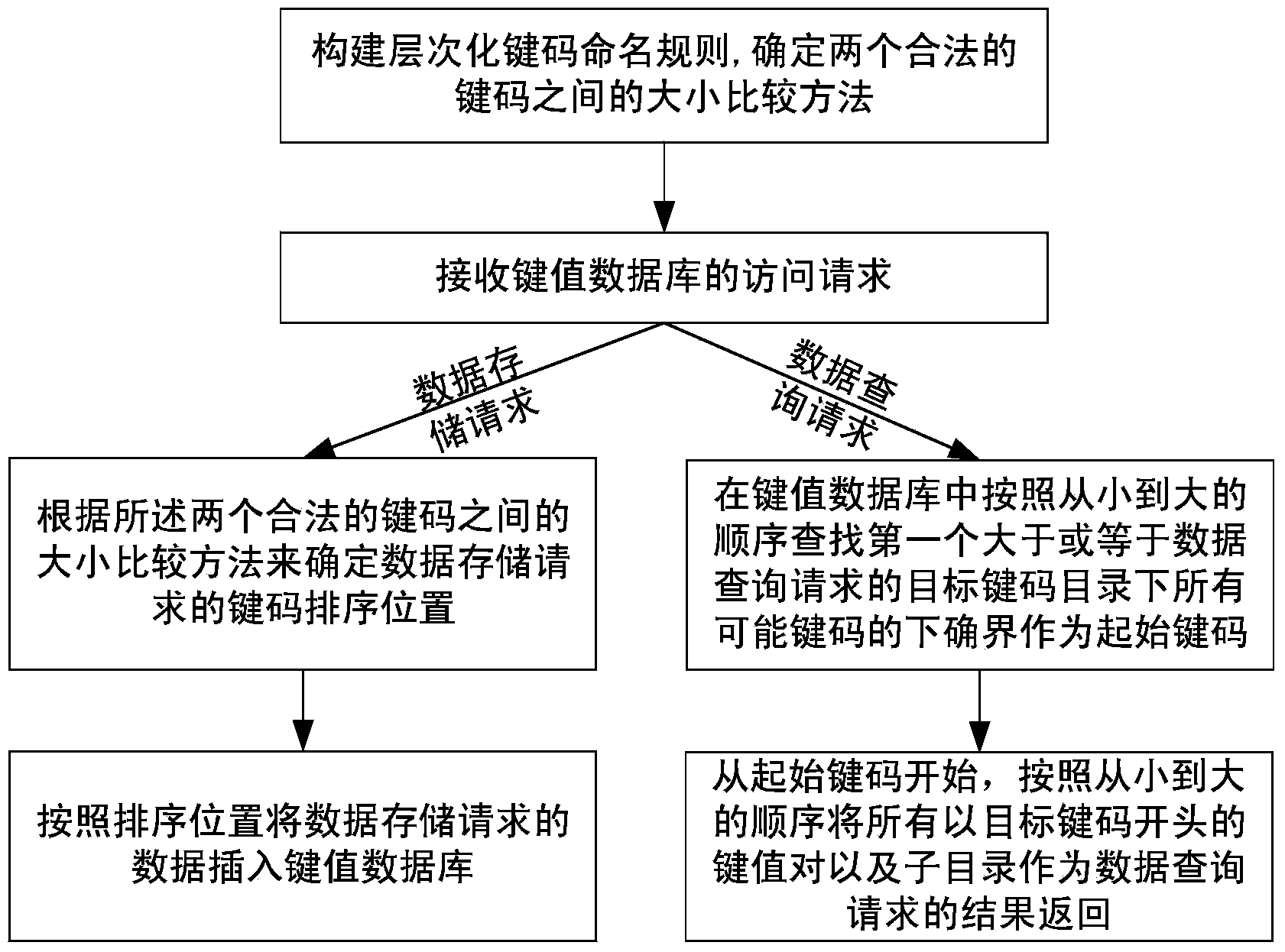
[0068] Such as figure 2 As shown, the implementation steps of the hierarchical storage and query method based on the key-value database in this embodiment are as follows:
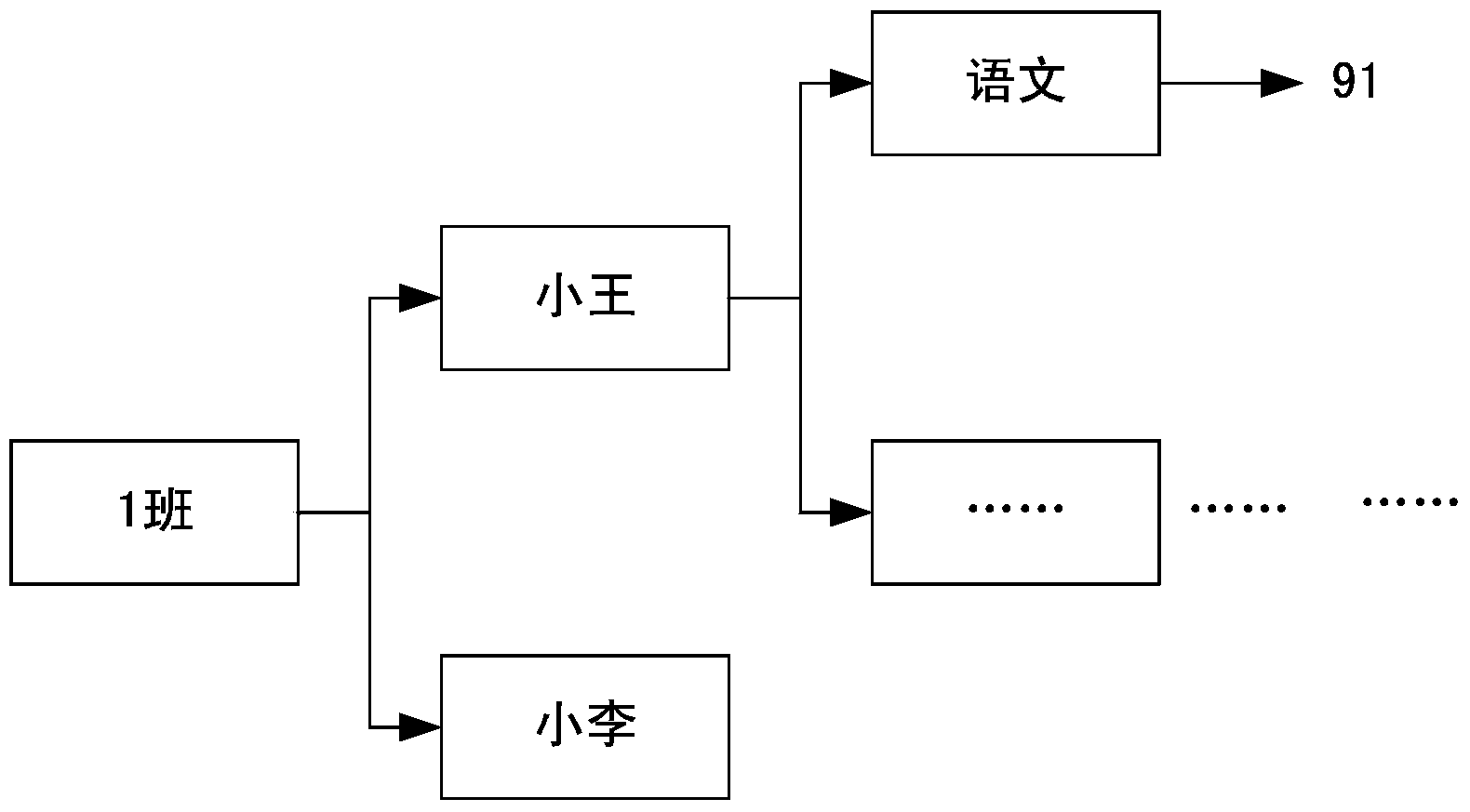
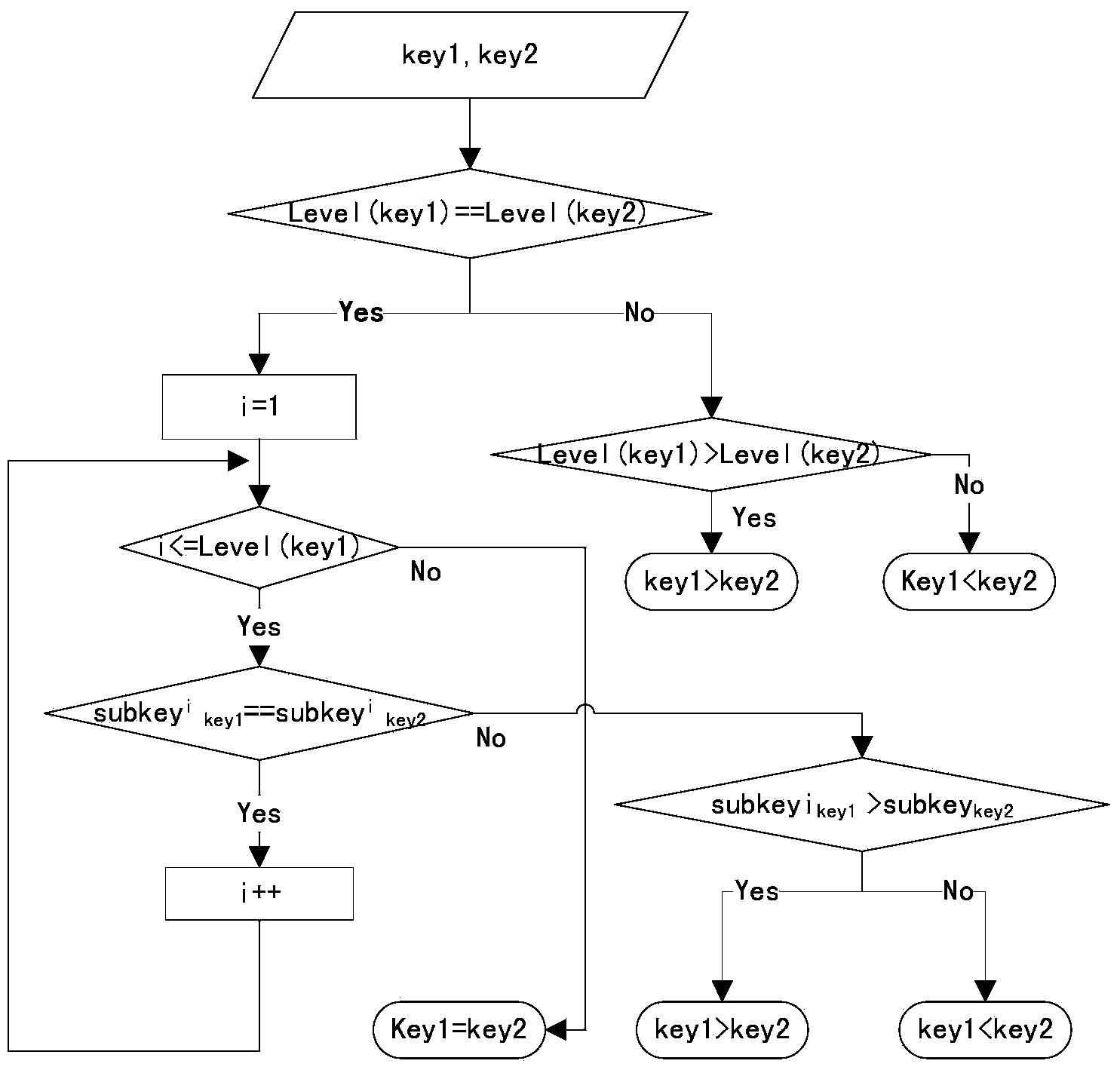
[0069] 1) Build a hierarchical key code naming rule in advance in the key-value database stored in an orderly manner. The hierarchical key code naming rule defines the key code as starting with a separator and consisting of alternating combinations of separators and substrings. The number of separators Indicates the series of key codes; determine the size comparison method between two legal key codes, the larger the series, the larger the key code, and the key codes with the same series are determined according to the string comparison;
[0070] 2) Receive the access request of the key-value database, if the access request is a data storage request, then jump to step 3), if the access request is a data query request, then jump to step 4);
[0071] 3) Determine the key code sorting position of the data sto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com