A kind of Burkholderia and its application in the prevention and treatment of Panax notoginseng soil-borne diseases
A Burkholderia and Panax notoginseng soil technology, applied to Burkholderia strains and its application in the prevention and treatment of Panax notoginseng soil-borne diseases, can solve the problems of high cost, unsatisfactory effect, allergic reaction, etc., and achieve high safety sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
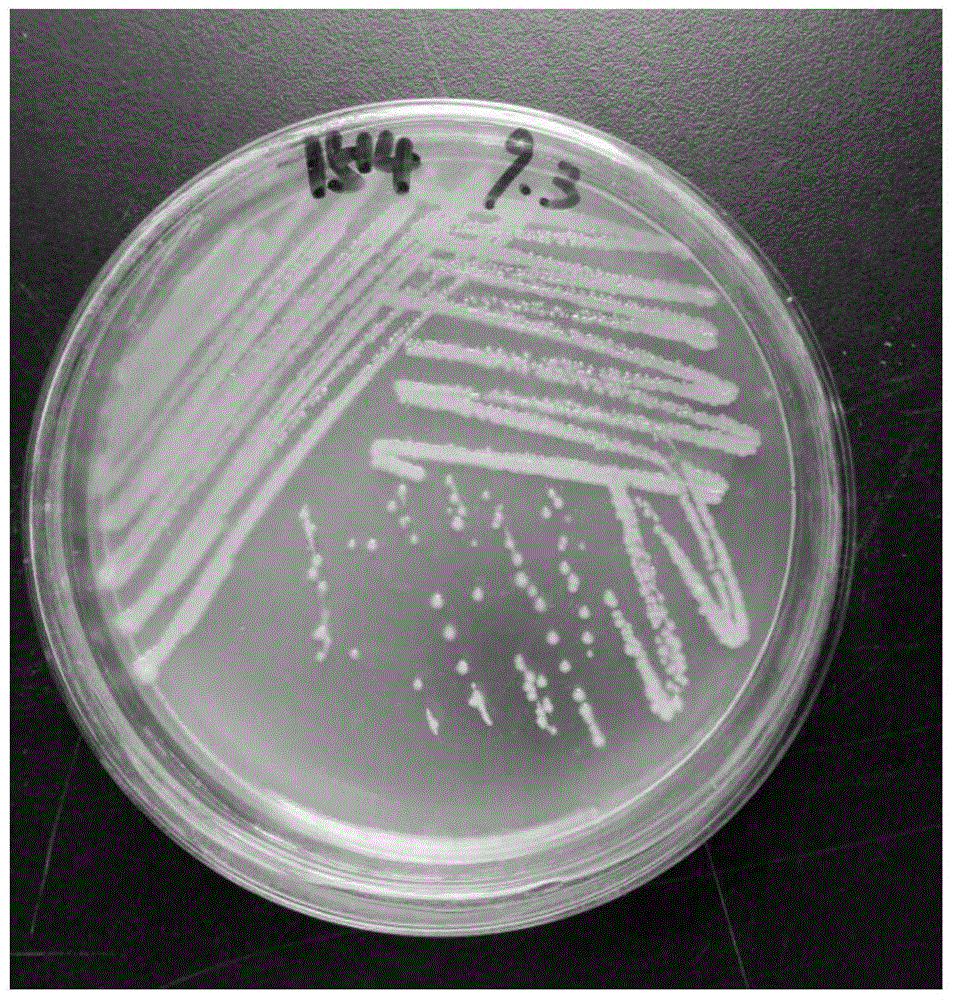
[0031] The rhizosphere soil of Panax notoginseng in a field of Panax notoginseng in Wenshan area, Yunnan Province was collected for related experiments. The specific steps are as follows:
[0032] (1) Soil sample treatment: prepare a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask, pure water, and glass beads for 1 hour. Put the glass beads into an Erlenmeyer flask filled with 20ml of sterile water, and take 2.0g of fresh soil samples into the Erlenmeyer flask, mix well, and shake at 150r / min for 45min at room temperature.
[0033] (2) Coating: Take 1 mL of the suspension in (1) and add 9.0 mL of sterile water, and serially dilute 3 times to obtain a dilution of 10 -4 Then take 120 μL of the sample solution and evenly spread it on the separation medium (beef extract peptone), and do three repetitions.
[0034] (3) Cultivation and purification: the coated plate was cultivated at 28°C for 3 days, and then a single colony was picked on the beef extract peptone medium to draw a line on the ISP2 agar...
Embodiment 2
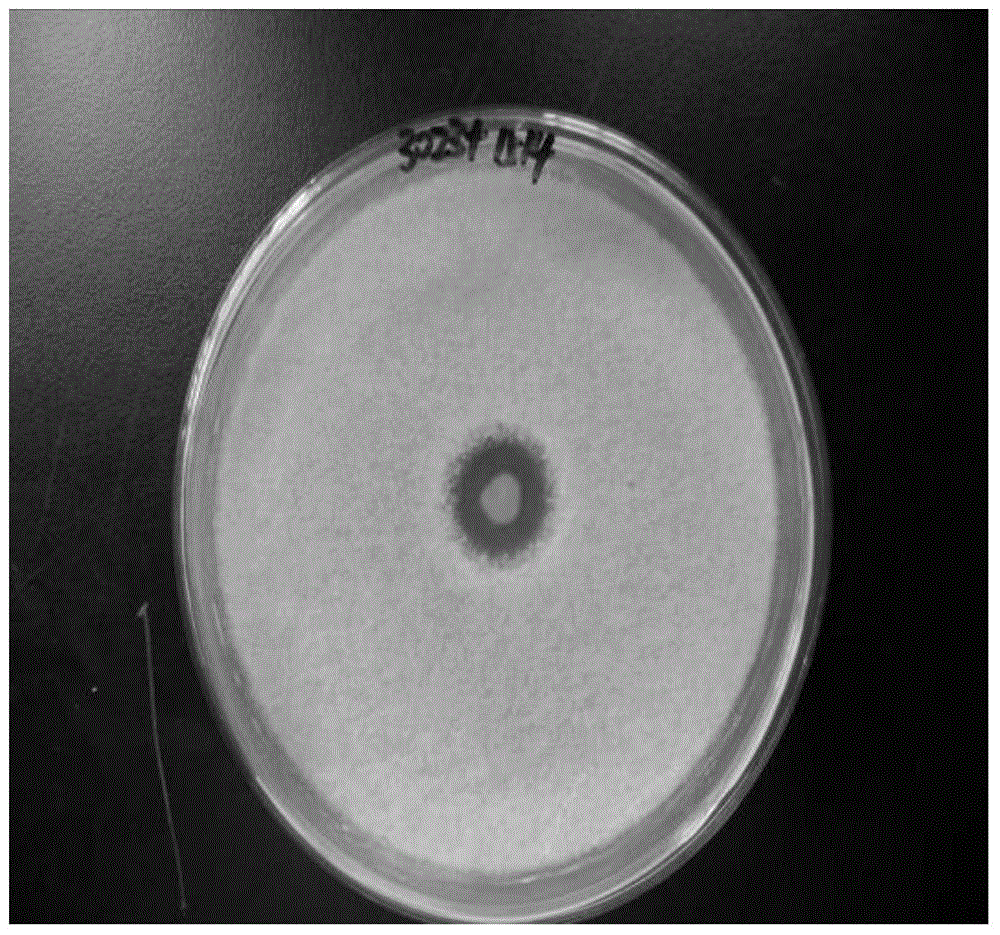
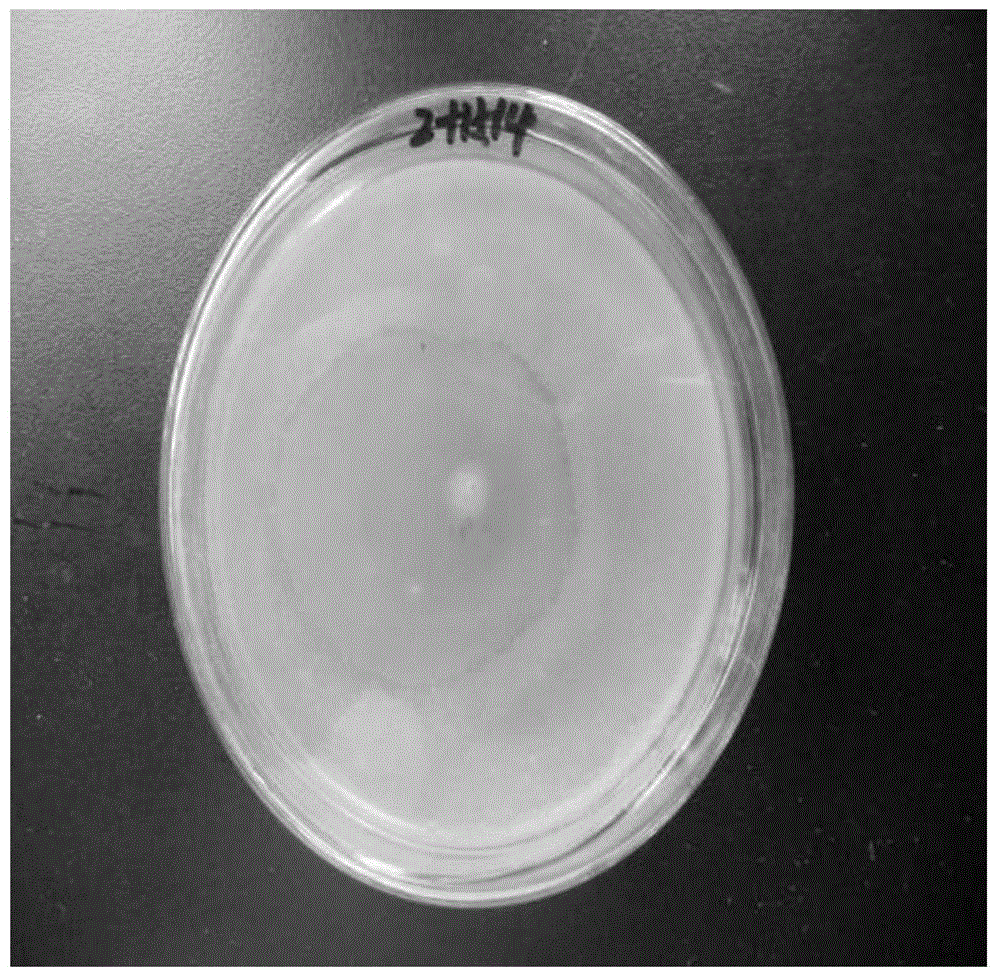
[0041] Antibacterial experiments were carried out using the strain with the preservation number CGMCC NO.9733: first culture this strain on a medium containing 0.8% polypeptone and 0.4% yeast extract for 2 days, then pick a single colony and transfer it to a shaker flask Cultivate it inside for 3 days; then use the water agar diffusion method to react its metabolites with plant pathogenic bacteria: Fusarium apicosum (Pathogen of Panax notoginseng), Fusarium wilt of banana, Botrytis cinerea, Tobacco red spot fungus, Black spot fungus of cabbage, Such as Figure 2-Figure 6 , found that its metabolites have a good antagonistic effect on plant pathogenic bacteria.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Culture the strain with the preservation number CGMCC NO.9733 on a medium containing 0.8% polypeptone and 0.4% yeast extract for 2 days, and prepare a glass test tube filled with sterile water; make the bacteria suspension solution, the bacterial suspension is OD 600 =1.62, then the prepared bacterial suspension was diluted 1:100 times for application. Prepare 3 replicates and a blank control, apply them to pots of Panax notoginseng grown normally under the same conditions, observe and record Panax notoginseng in 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months As a result, it was found that after 1 month, the plants of the control group had no significant difference compared with the plants of the test group; after 3 months, there were differences between the plants of the control group and the test group, showing For: 17.96% of the plants in the control group had symptoms of yellowing and edge atrophy, while only 4.23% of the plants in the test group had such symptoms; 29....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com