Method and device for monitoring an energy feed-in point of an energy supply network
An energy supply and feed-in point technology, applied in the field of energy feed-in points and equipment for monitoring energy supply networks, can solve problems such as difficulties and achieve the effect of avoiding deficiencies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
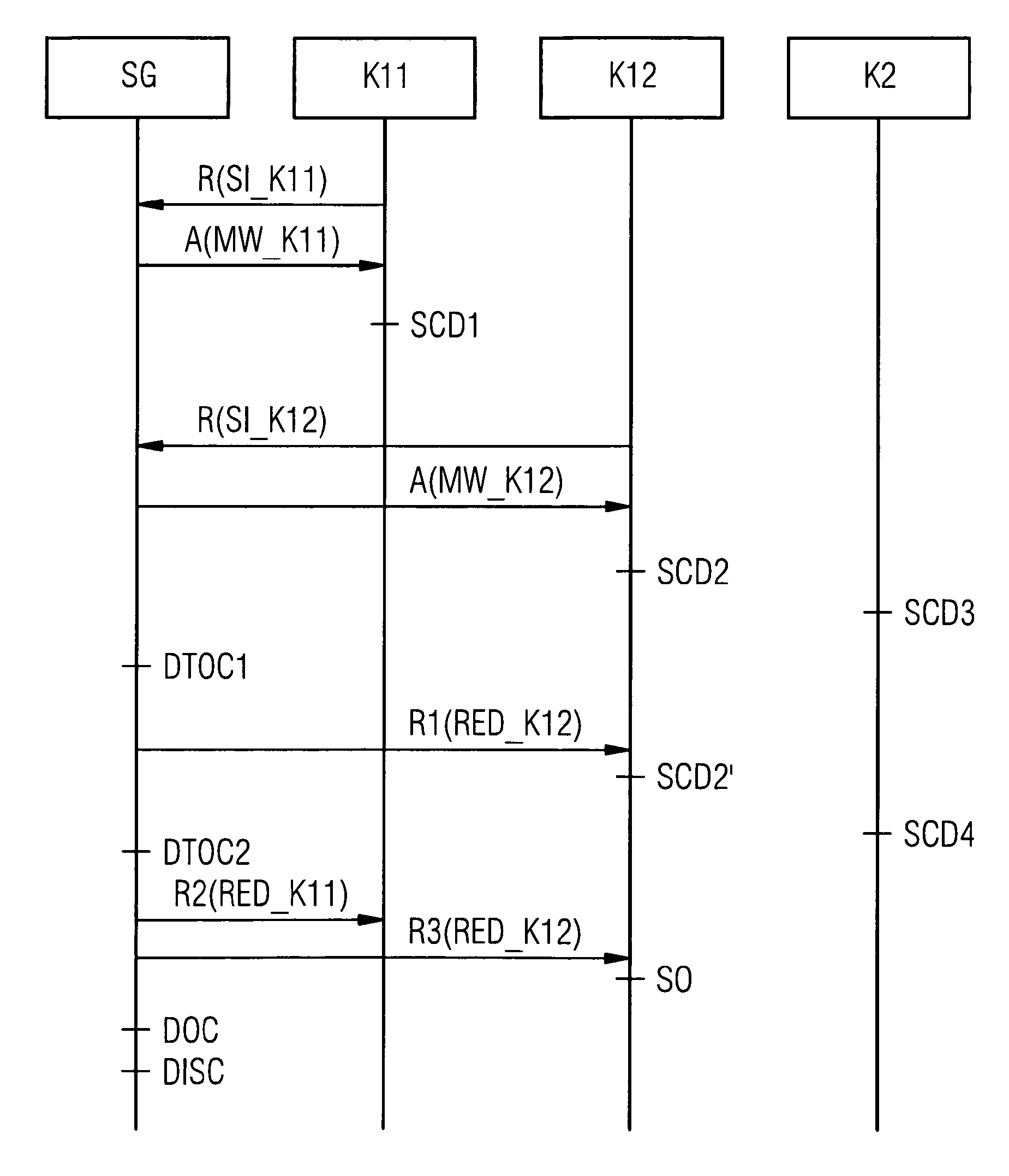
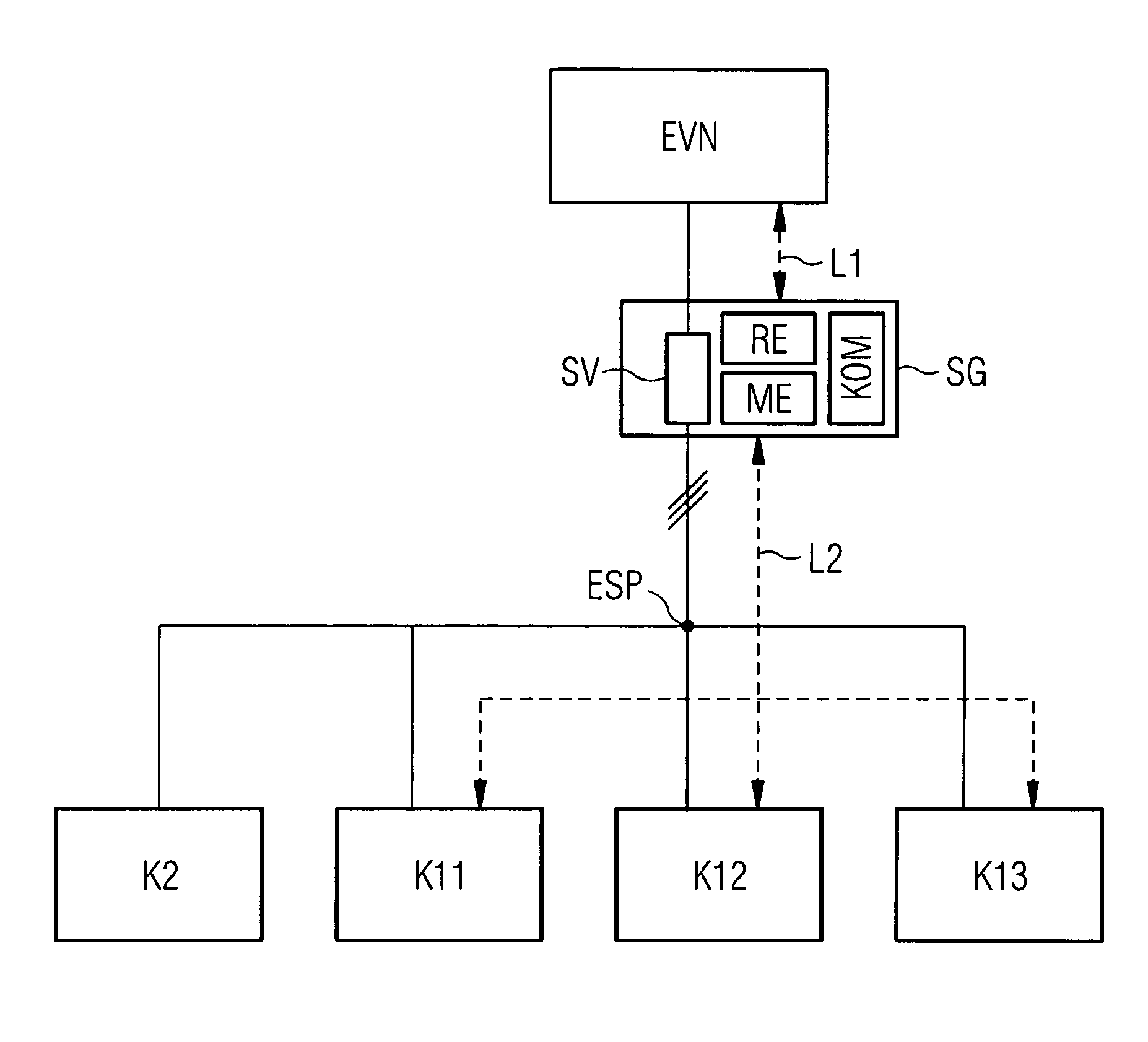
[0038] figure 1 A schematic diagram of a device according to the invention for monitoring an energy feed-in point ESP of an energy supply network EVN is shown. The device is a protective device SG, which can be considered as a combination of a power monitoring device and a protective switch. The protective device SG is arranged between the energy feed-in point ESP and the energy supply network EVN. By way of example only, the line between the protective device SG and the energy feedpoint ESP is configured in three phases, whereby the nodes K11 , K12 , K13 and K2 connected to the energy feedpoint ESP are supplied with a voltage of 400 V, for example. Likewise, the lines connecting the nodes K11 , K12 , K13 , K2 to the protective device SG can be implemented as single-phase. In this case, the nodes K11 , K12 , K13 , and K2 are supplied with a supply voltage of, for example, 230V. The stated voltage values apply to the energy supply network in the low-voltage range in German...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com