Controlling transmission of pulses from a sensor
A sensor, a technology for transmitting pulses, used in the field of controlling the transmission of pulses from sensors, which can solve problems such as disrupting lighting control systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
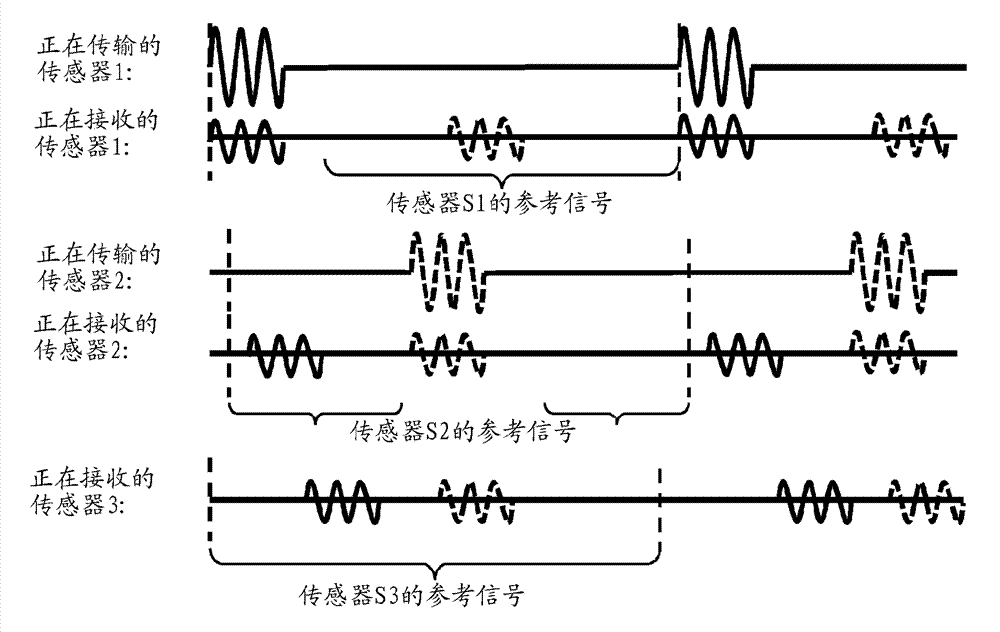
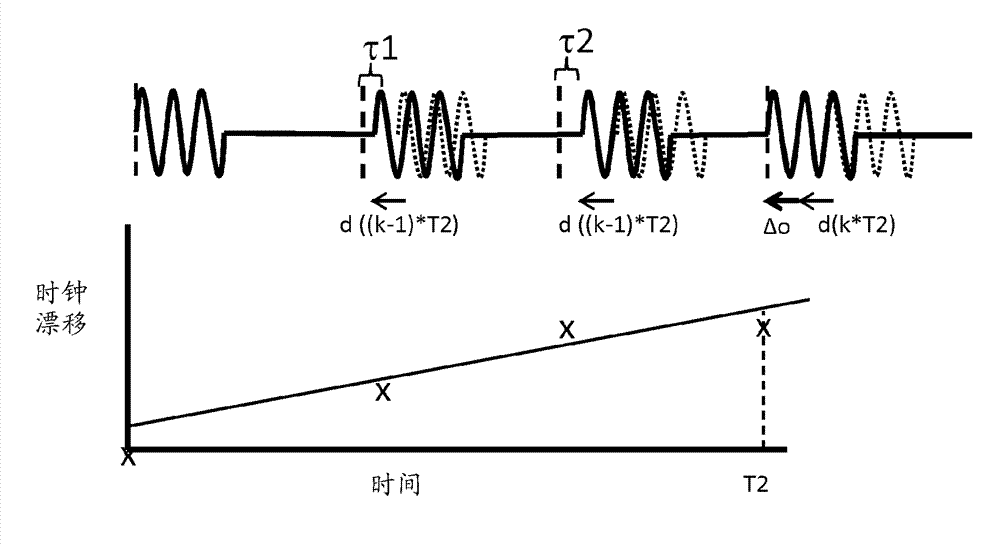
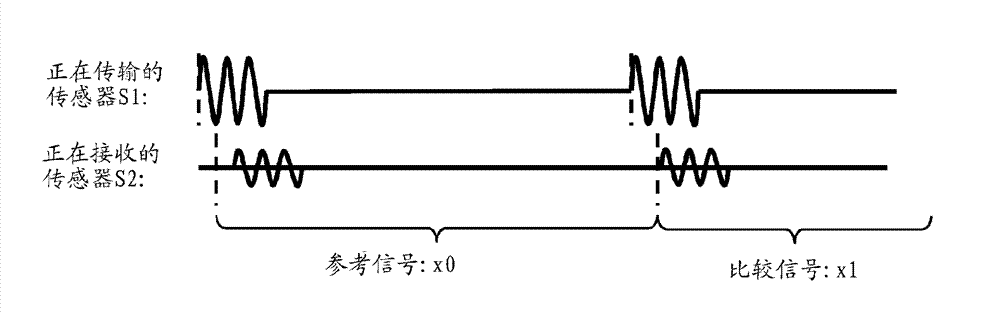
[0025] As an alternative to relying on a central controller or a single central element, it may be desirable to tend to involve some or all of the intelligence that will be embedded across the system in the lighting system, and functions similar to sensing are distributed in separate Between the units. In the following embodiments of the present invention, a distributed active sensing system for indoor presence detection (for example, based on an ultrasonic sensor modality) is provided, and the distributed active sensing system is installed in ( For example, as part of the lighting system) rarely or does not incur the overhead of trial operation. One of the challenges in active presence sensor systems is the potential for cross interference. To this end, time division multiplexing transmission protocol can be used. However, due to clock drift inherent in the sensor, the sensor may drift from its assigned time slot. An exemplary method to ensure slot synchronization is presen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com