Continuous time data protection method on solid state drive
A time data, solid-state hard disk technology, applied in the redundant operation of data error detection, response error generation and other directions, can solve the problem of occupying memory space, unable to restore data, affecting the normal read and write of hard disk, etc., to reduce The effect of reading and writing, the effect of overcoming incompleteness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
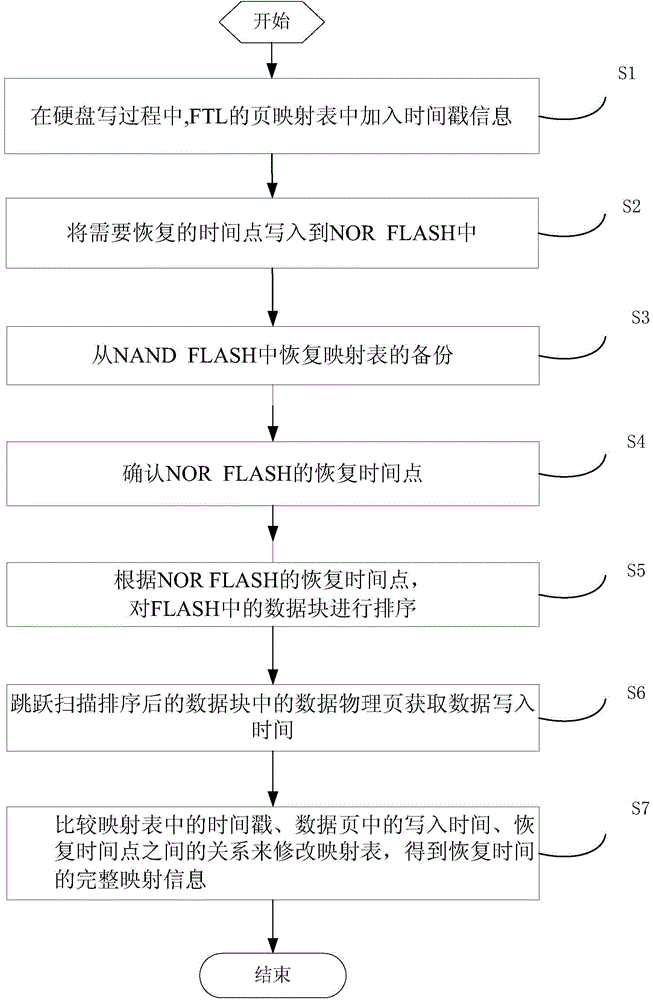
[0045] see figure 1 As shown, it is a flowchart of a continuous-time data protection method on a solid-state hard disk according to the present invention. The method comprises the steps of:
[0046] Jump scan the data physical page in the sorted data block to obtain the data writing time;
[0047] Compare the relationship between the timestamp in the mapping table, the write time in the data page, and the recovery time point to
[0048] Modify the mapping table.
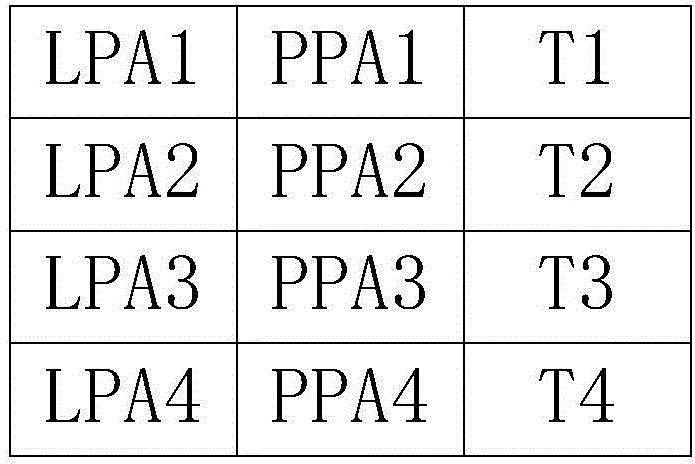
[0049] Step S1: During the writing process of the hard disk, time stamp information is added to the page mapping table of the FTL;
[0050] Step S2: Write the time point to be restored into NOR FLASH;
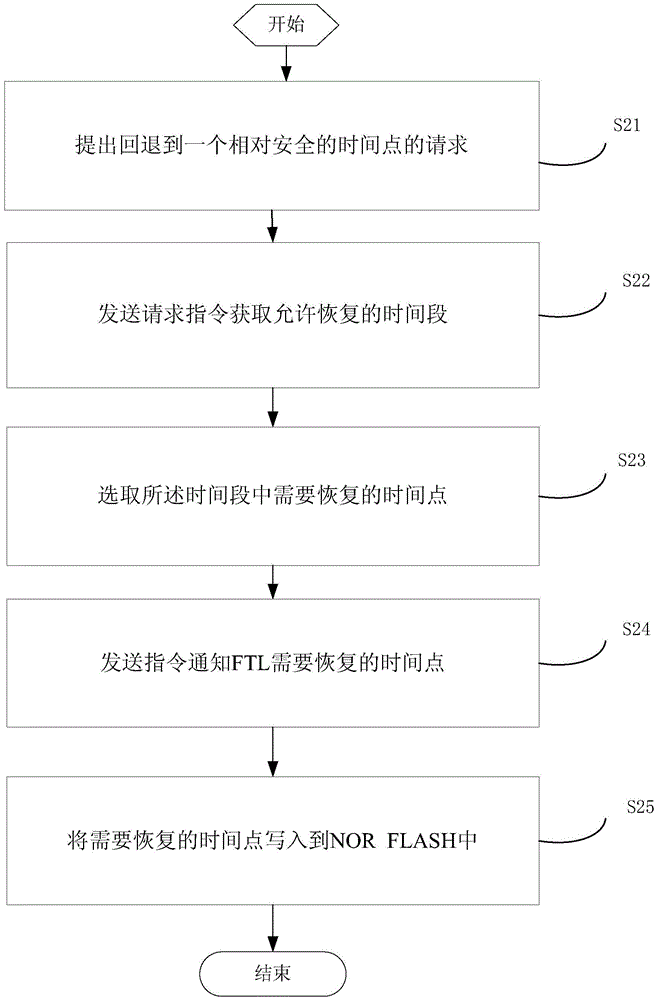
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, wherein, writing the time point that needs to be restored into NOR FLASH further includes the following steps: making a request to fall back to a relatively safe time point; sending a request instruction to obtain a time period that allows recovery; selecting the The time point ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com