Carbon dioxide drive oil reservoir production method capable of realizing stage control on fluidity
A technology of hierarchical control and production methods, applied in the direction of production fluid, earthwork drilling and production, wellbore/well components, etc., which can solve the problems of fluid production decline, viscous fingering and channeling, and increase the difficulty of sealing gas channeling and other issues to achieve the effect of improving the mobility ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
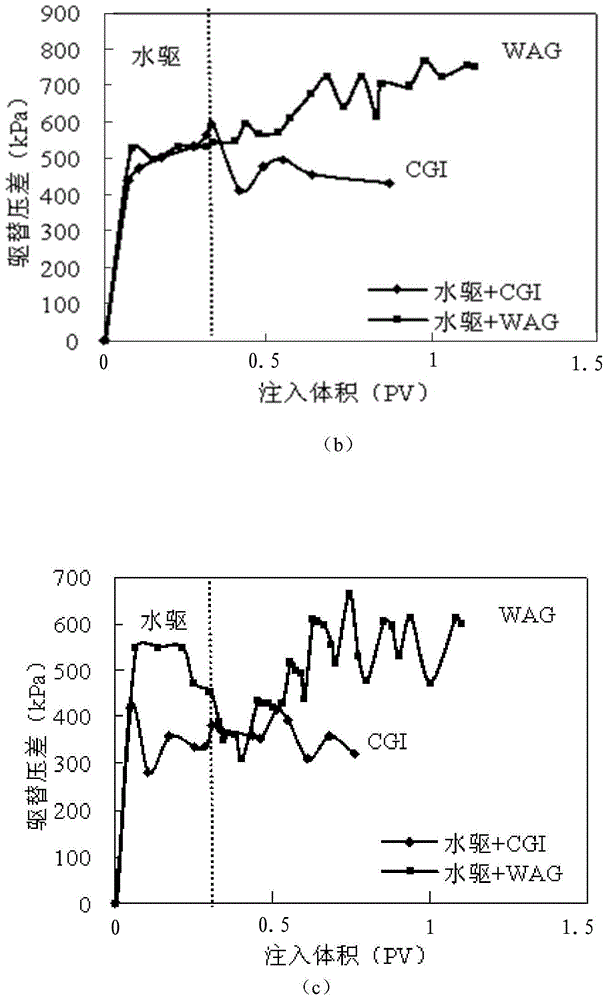
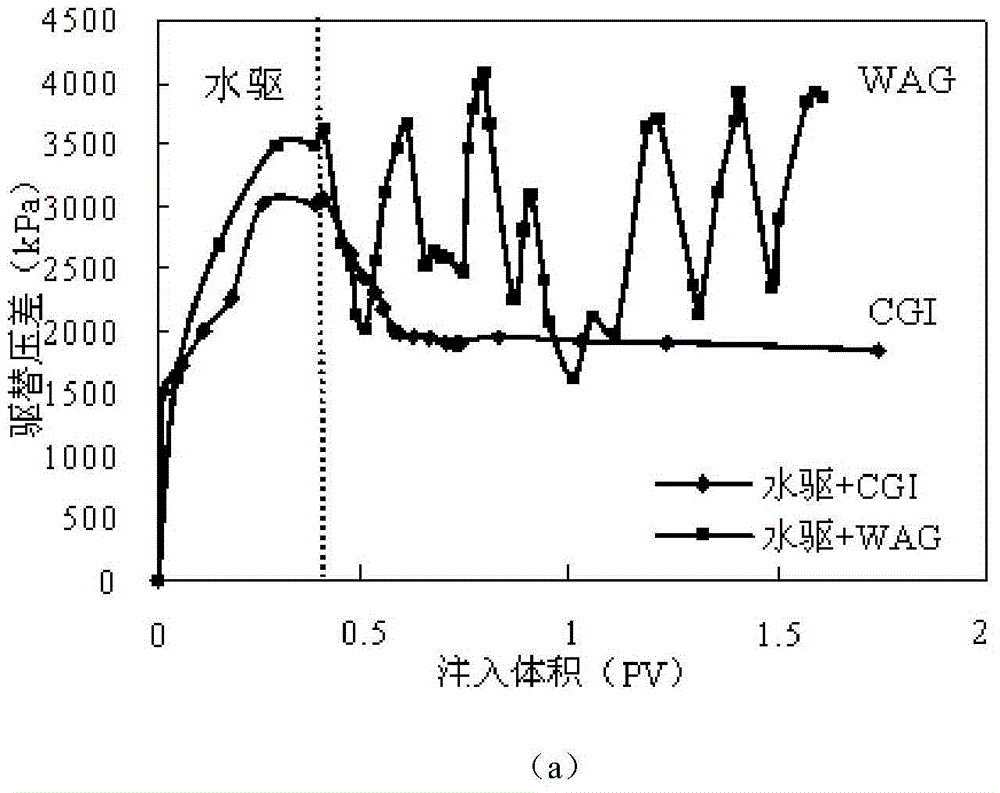
[0030] Homogeneous natural cores and heterogeneous cores with a permeability difference of 10 and 30 were selected for water flooding + CO 2 Continuous gas flooding and water flooding + water-gas alternating injection (WAG) experimental research, comparing the oil displacement effects of injection methods, and analyzing the mobility control effect of gas-water alternation. The specific operation process of the experimental example is as follows:
[0031] 1) Select cores that meet the requirements for drying, measure the length, width and height, and calculate the apparent volume.
[0032] 2) Vacuumize, saturate the formation water, and calculate the pore volume.
[0033] 3) Control the experimental temperature to the reservoir temperature of 60°C, saturate the simulated oil to irreducible water saturation, and calculate the original oil saturation.
[0034] 4) The outlet pressure was controlled at 6MPa through the back pressure valve, and the water flooding experiment was ca...
experiment example 2
[0046] Heterogeneous rock cores with a permeability difference of 30 and 100 were selected to carry out plugging experiments with small-molecule aliphatic amines respectively to study the effect of small-molecule amines on CO 2 The degree of improvement in the oil displacement effect. In this embodiment, ethylenediamine is selected as the plugging agent. Ethylenediamine (H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2 ) is a small molecular organic amine. It is a colorless and transparent viscous fluid with a pungent odor. Its melting point is 8.5°C, its boiling point is 116.5°C, and its relative density is 0.8995 at 20°C. It is soluble in water , Slightly soluble in ether. As a strong base, ethylenediamine can react with CO 2 The reaction produces ammonium carbamate, which has high viscosity and good plugging performance. The specific operation process of this experiment example is as follows:
[0047] 1) Select cores that meet the requirements for drying, measure the length, width and height, a...
experiment example 3
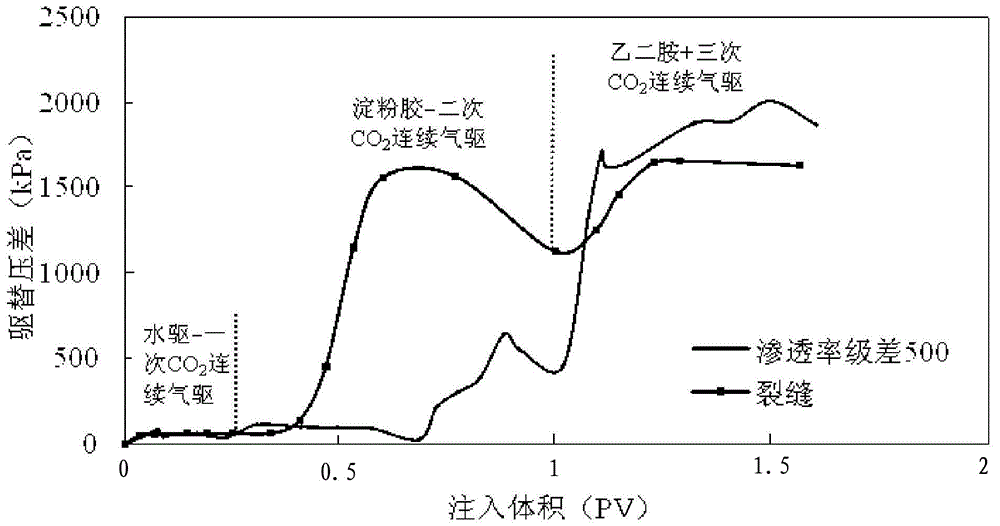
[0060] Heterogeneous rock cores with a permeability difference of 500 and natural rock cores with fractures were selected to carry out the sealing experiments of modified starch gel + small molecule aliphatic amine to study the effect of this measure on CO 2 The degree of improvement in the oil displacement effect. The formulation of the starch gel used in this embodiment is shown in Table 3, and the small molecule aliphatic amine used is ethylenediamine.
[0061] Table 3 modified starch gel formula
[0062]
[0063] The specific operation process of this experiment example is as follows:
[0064] 1) Select cores that meet the requirements for drying, measure the length, width and height, and calculate the apparent volume.
[0065] 2) Vacuumize, saturate the formation water, and calculate the pore volume.
[0066] 3) Control the experimental temperature to the reservoir temperature of 60°C, saturate the simulated oil to irreducible water saturation, and calculate the ori...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com