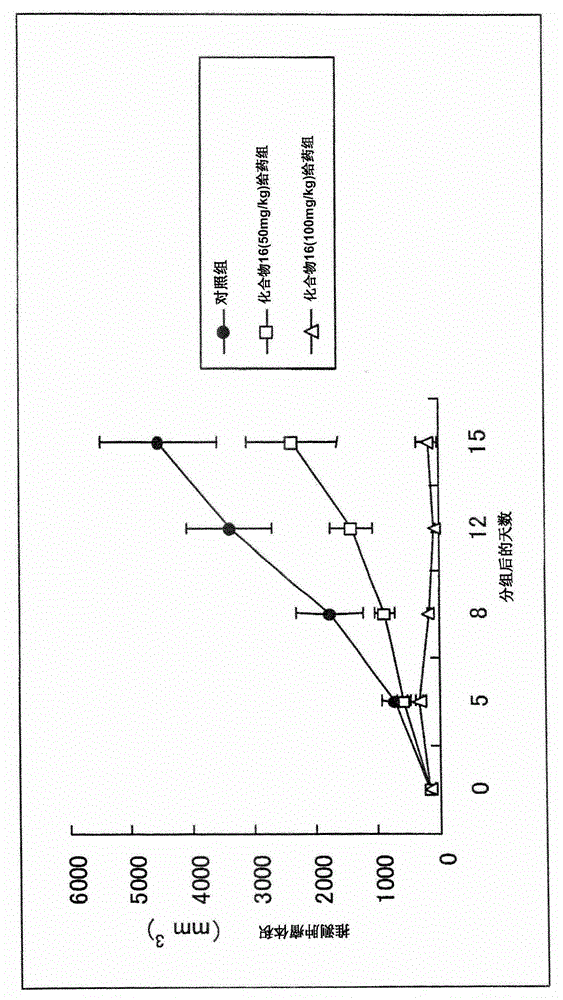
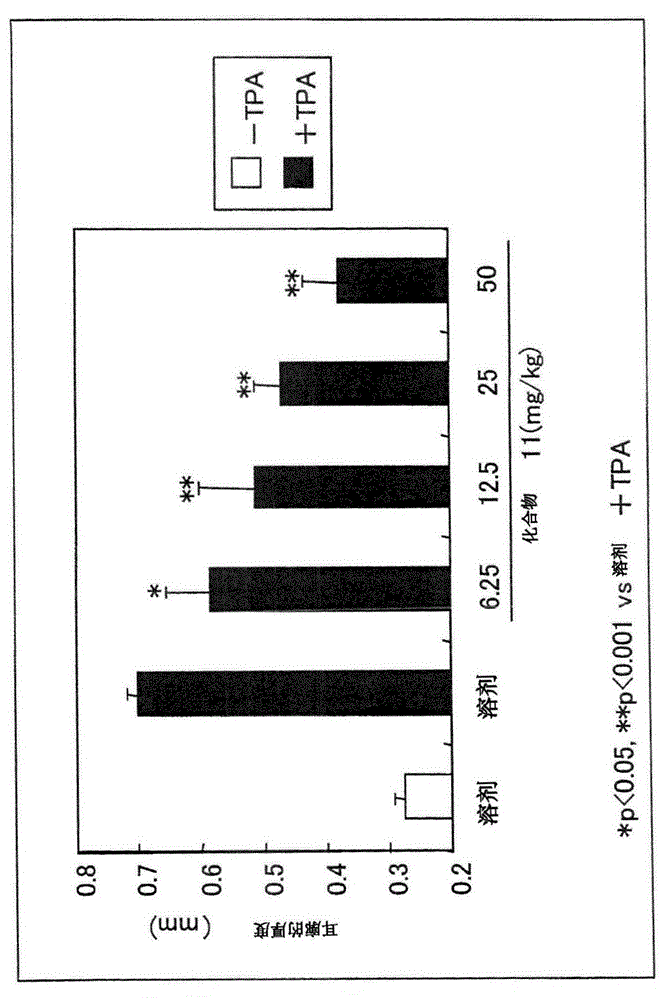
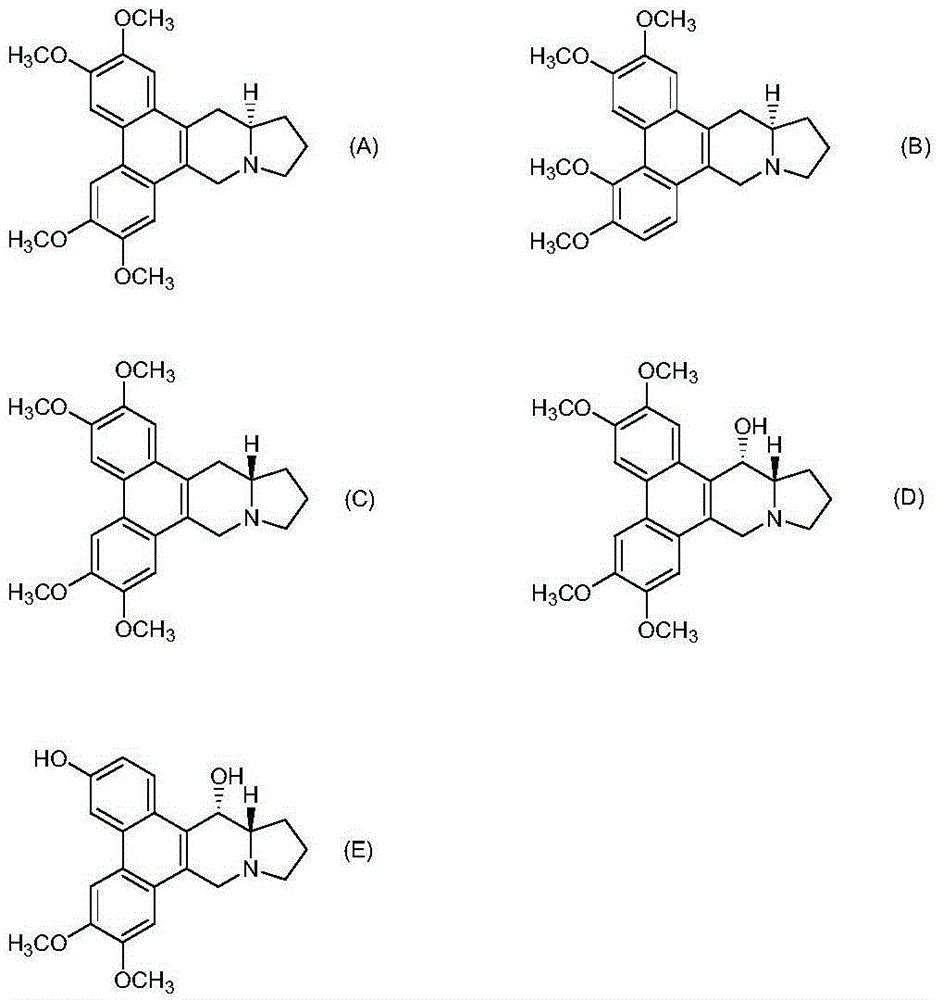
Phenanthroindolizidine compound and NF kB inhibitor containing same as active ingredient
A technology of active ingredients and compounds, which is applied in the field of novel phenanthrene indolizidine alkaloid compounds or their salts, can solve the problems of strong cytotoxicity and heterogeneity, achieve excellent solubility, small side effects, and excellent NFκB inhibitory effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0149] Hereinafter, examples are shown and the present invention will be described in more detail, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
[0150] The phenanthrene indolizidine alkaloid of the present invention is synthesized according to the reaction pathway of the following steps 1-10. When the substituent represented by R needs to be protected, an appropriate protecting group is used for the reaction.
[0151]
Synthetic example 1
[0153] Synthetic R 1 ~R 6 Compounds represented by the following groups. The operations of Steps 1 to 10 are shown below.
[0154] Compound 1
[0155] R 1
R 2
R 3
R 4
R 5
R 6
H
Oh
H
OCH 3
OCH 3
OCH 3
[0156] Step 1: Synthesis of stilbene
[0157] In an eggplant-shaped flask, in 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetonitrile 5.0g (24.1mmol) and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde 5.1g (24.1mmol, 1.0eq.) in ethanol 150mL suspension, under argon In an air atmosphere, 160 mg (2.4 mmol, 0.1 eq.) of sodium ethoxide was added with stirring at room temperature, and heated to reflux (oil bath temperature: 85° C.). After 3 hours, the disappearance of the raw material was confirmed, and the reaction liquid was cooled with an ice bath. The precipitated solid was suction-filtered with a Buchner funnel and a suction filter flask, and washed with 100 mL of methanol (twice). Drying was carried out at 60° C. under reduced pressure to obtain 9....
Synthetic example 2
[0189] Synthetic R 1 ~R 6 Compounds represented by the following groups. The operations and the yield of each operation are shown below.
[0190] [Table 2]
[0191] Compound 3
[0192] R 1
R 2
R 3
R 4
R 5
R 6
H
Oh
H
H
H
H
[0193] Process 1
[0194] Yield: 92.0%
[0195] 1 HNMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 5.14 (2H, s), 7.02-7.08 (2H, m), 7.32-7.48 (9H, m), 7.62-7.68 (2H, m), 7.85-7.92 (2H, m)
[0196] Process 2
[0197] Yield: 84.3%
[0198] 1 HNMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 5.32(2H,),7.30-7.56(7H,m),7.68-7.80(2H,m),7.82-7.90(1H,m),8.13(1H,s),8.18-8.21(1H,m ),8.24-8.33(1H,m),8.54-8.64(1H,m)
[0199] Process 3
[0200] Yield: 94.2%
[0201] 1 HNMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 5.33(2H,s),7.34-7.57(5H,m),7.41(1H,dd,J=2.44,8.80Hz),7.68-7.77(2H,m),7.98(1H,d,J= 8.80Hz), 8.14(1H,d,J=2.44Hz), 8.54-8.64(1H,m), 8.21(11H,s), 9.36-9.44(1H,m), 10.33(1H,s)
[0202] Process 4
[0203] Yield: 98.8%
[0204] 1 HNMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com