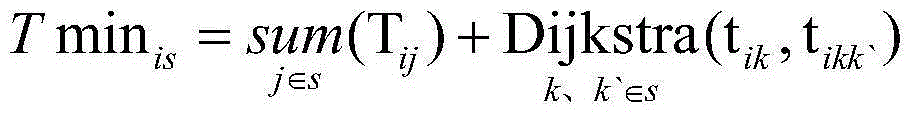Power transmission line ice-melting decision method based on shortest path algorithm and 0/1 decision
A shortest path algorithm and transmission line technology, applied in the field of power transmission and distribution, can solve the problems of high decision-making risk and long decision-making time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
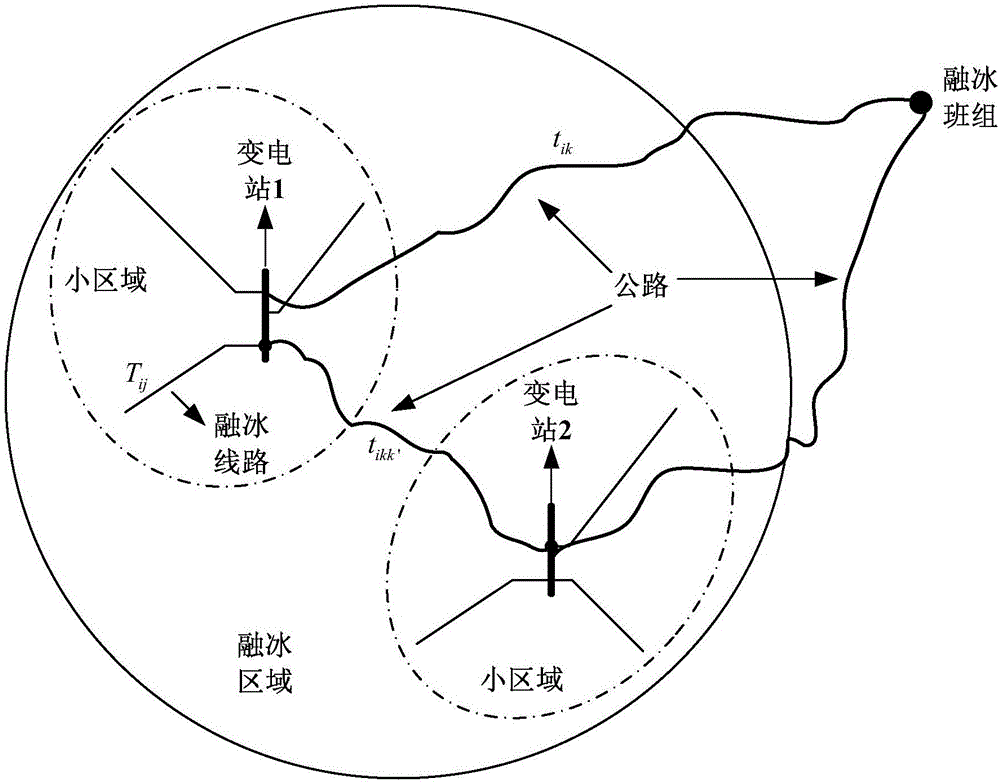
[0041] A decision-making method for icing transmission lines based on the shortest path algorithm and 0 / 1 decision, comprising the following steps: (1) Divide the area of the ice-covered line. According to the coordinates of the ice-covered line and the coordinates of the adjacent substation, calculate the distance between the ice-covered line and the adjacent substation, and divide the ice-covered line closer to a substation into the same area with the substation as the center, so that the ice-covered line is divided into For several small areas, since the number of small areas is greater than the number of teams, several adjacent small areas belonging to the same unit are merged into one large area until the number of ice-melting areas is equal to the number of ice-melting teams.
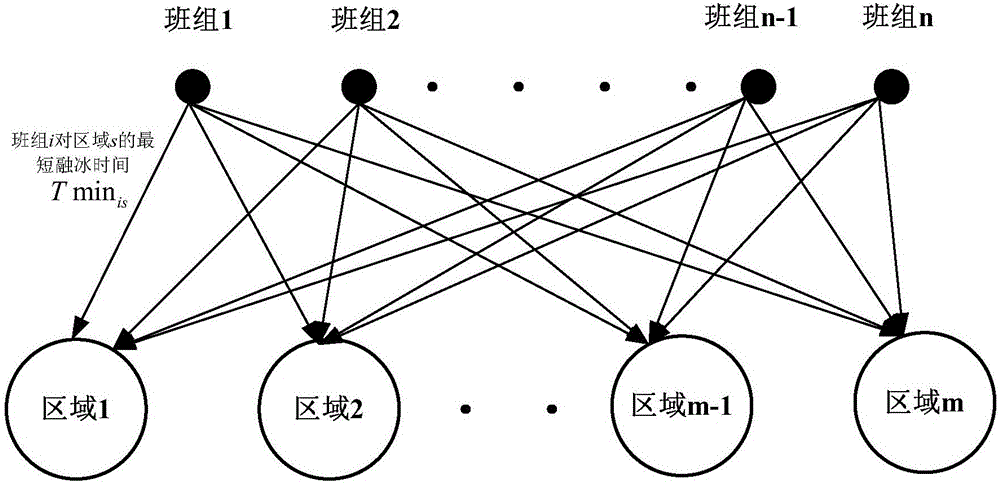
[0042] (2) Calculate the ice-melting time of each team for a single ice-covered line. According to the meteorological factors such as the number of personnel in each team, the type and capacity ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] (1) Divide the ice-covered line area. According to the coordinates of the ice-covered line and the coordinates of the adjacent substation, calculate the distance between the ice-covered line and the adjacent substation, and divide the ice-covered line closer to a substation into the same area with the substation as the center, so that the ice-covered line is divided into Several small areas, the number of small areas is less than the number of teams.
[0053] Steps (2)-(7) are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0055] (1) Divide the ice-covered line area. According to the coordinates of the ice-covered line and the coordinates of the adjacent substation, calculate the distance between the ice-covered line and the adjacent substation, and divide the ice-covered line closer to a substation into the same area with the substation as the center, so that the ice-covered line is divided into Several small areas, the number of small areas is equal to the number of teams. Steps (2)-(7) are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com