Boundary unicursal method for processing polygon multiplex inclusion relation
A polygonal and relational technology, applied in the field of border organization of complex polygons, can solve problems such as layered capping, data redundancy, etc., and achieve the effect of ensuring correctness and avoiding complexity and redundancy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to make it easier for those skilled in the art to understand and implement the present invention, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
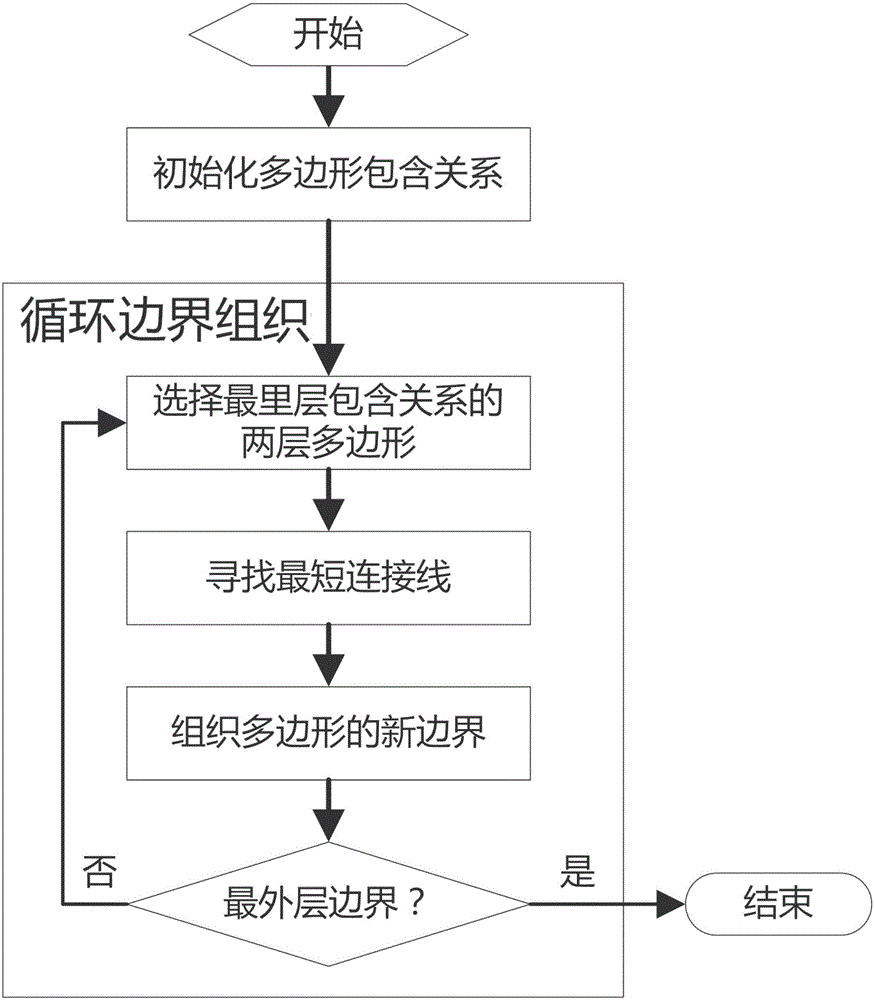
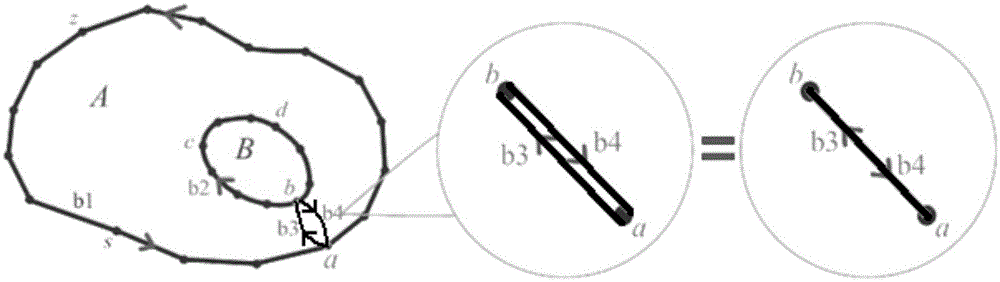
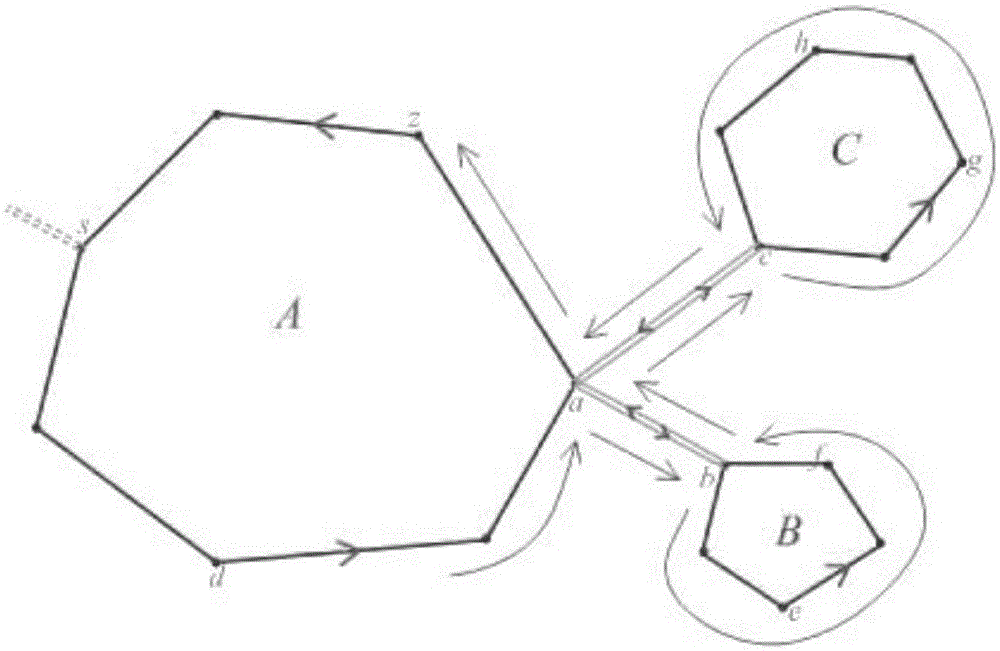
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a schematic flow chart of the present invention. Through five steps, the polygon of the target object in a certain area is judged by the plane geometric coordinates and specific target attributes to determine the multiple inclusion relationship of the polygon of the target polygon. And find the shortest connecting line according to the definition and principle of the shortest connecting line, iteratively carry out the boundary organization of the two-layer containment relationship from the inside to the outside, until all the effective boundaries of the target polygons are connected and organized in one stroke, so as to solve the problem of polygons with multiple containment relationships. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com