Method for cultivating insect-resistant transgenic rice T1c-19
A transgenic rice technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of finding resistance gene resources and achieve the effect of protecting the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1: Construction of expression vector
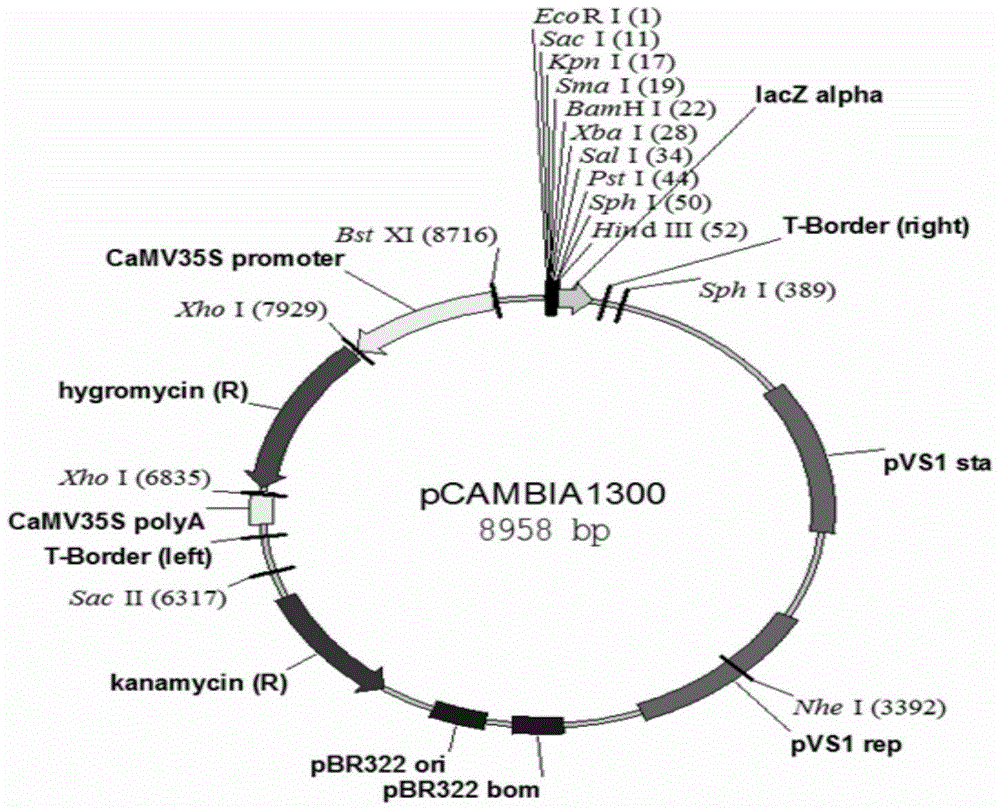
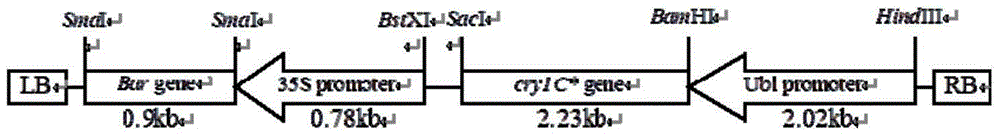
[0064] Firstly, pCAMBIA1300 plasmid (gifted by the Center for the Application of Molecular Biology in International Agriculture, Australia) was digested with XhoI restriction endonuclease, the large fragment was recovered, and cut into blunt ends with nuclease. At the same time, the pTW-a plasmid was digested with SmaI enzyme, and a small fragment (bar gene) was recovered. After ligating the recovered large and small fragments, Escherichia coli was transformed, positive clones containing the bar gene were selected, and the obtained vector was named intermediate vector pBar13.
[0065] Then cut the Ubi promoter from the pUBC plasmid with HindIII / BamHI double enzyme digestion (the direction of action of the Ubi promoter is SacI site → BamHI site), and insert it into the multiple cloning site of the pBar13 vector to form a pBar-Ubi intermediate carrier. At the same time, use BamHI / SacI to completely excise cry1C (the dire...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2: Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation
[0067] The Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method refers to the method shown in the "Agrobacterium-mediated Genetic Transformation Operation Manual" published by the State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement of Huazhong Agricultural University and the article published by Professor Lin Yongjun (Lin and Zhang 2005). The transformation recipient was the embryogenic callus induced from mature seeds of rice variety "Minghui 63" (gifted by Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences).
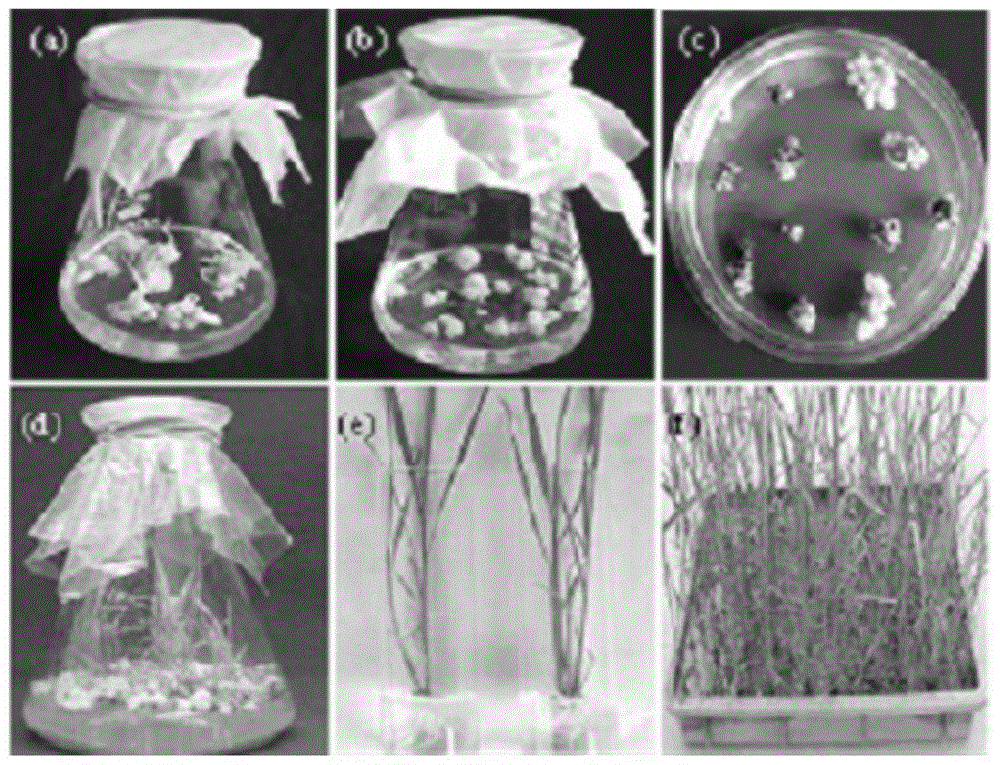
[0068]After mature seeds were induced in the dark for 7 days, a pale yellow embryogenic callus grew between the embryo and endosperm. After 40 days of culture, the embryogenic callus was isolated and proliferated on the subculture medium. Then, the engineered bacteria containing the transformation vector pBar13-Cry1C were used to infect the embryogenic callus, and after co-cultured at 28°C for 3 days, they were cultur...
Embodiment 3
[0133] Example 3: PCR detection of transgenic positive plants
[0134] Extraction of T by a small amount of genomic DNA extraction 0 The DNA of transgenic leaves was analyzed by PCR, and the primers for amplifying the cry1C* gene were F: 5'-ttctactggggaggacatcg-3' (SEQ ID NO: 6), R: 5'-cggtatctttgggtgattgg-3' (SEQ ID NO: 7), and the amplified The product is 602bp.
[0135]PCR reaction system: total reaction system is 20μl, DNA template 30-50ng, 10×buffer2.0μl, 2mMdNTP1.5μl, 25mMMgCl 2 2.0 μl, 0.4 μl each of 10 μM primers (F / R), 1 U of Taq enzyme, plus sterilized ddH 2 0 to 20 μl.
[0136] PCR reaction program: 94°C, denaturation for 3min; 94°C, denaturation for 1min, annealing at 57°C for 1min, extension at 72°C for 1.5min, 35 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10min.
[0137] Detection of PCR products: the amplified products were electrophoresed on 0.8% agarose gel, stained with EB, observed and photographed by an ultraviolet analyzer.
[0138] Extraction method of a small am...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com