Application of protein inhibitor t323 in antifertility
An anti-fertility, small molecule inhibitor technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, achieves good activity, novel structure, and improved screening accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
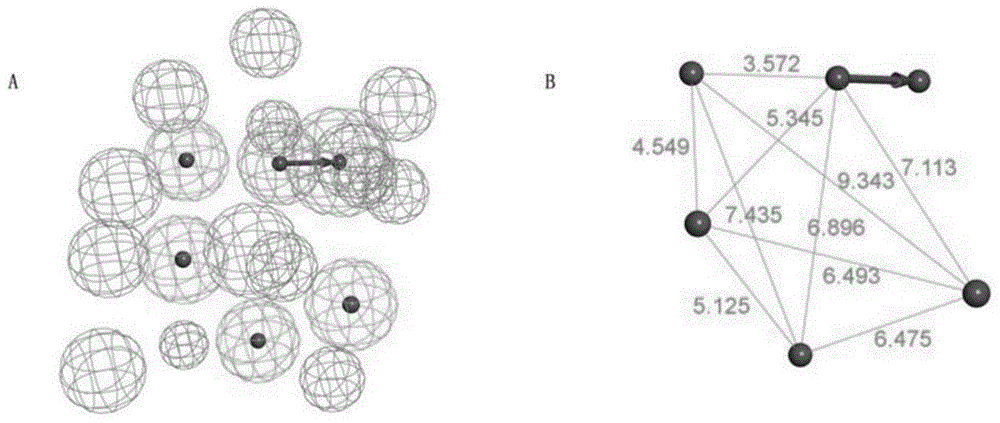
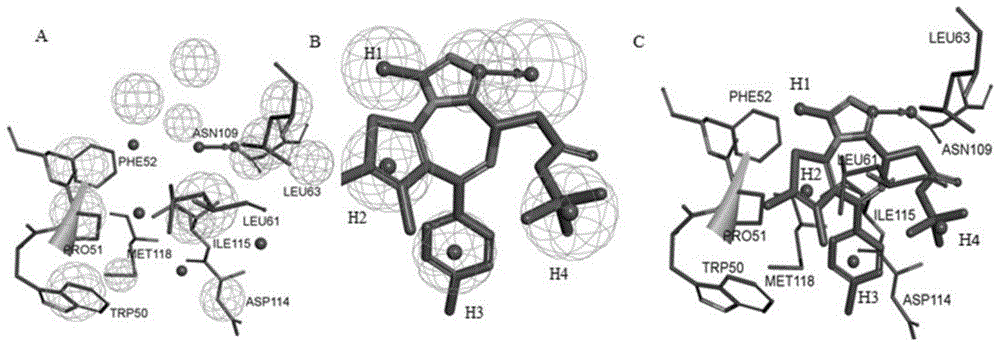
[0050] The construction of embodiment 1 pharmacophore model
[0051] 1. Download the three-dimensional structure file of the co-crystal active conformation of human BRDT and JQ1 from the PDB database and input it into Discovery Studio 3.0 software, figure 1 The domain map of BRDT and the enantiomers of compound JQ1 are shown;
[0052] 2. Use the pharmacophore building block of Discovery Studio 3.0 to construct a pharmacophore model based on the interaction between BRDT and JQ1 complex, remove water molecules, add hydrogen bonds to form receptor structures;
[0053] 3. Set each parameter condition, set the parameters of the minimum structural feature and the maximum structural feature to 4 and 6 respectively, set the lipophilic site density parameter to 15, and set the polar site parameter to 20;
[0054] 4. Identify the active site according to the interaction mode between the acetyl-lysine binding pocket JQ1 and BRDT, cluster all the action sites, and obtain a pharmacophore ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 drug class prediction
[0060] 1. Materials
[0061] The compound database of the National New Drug (Microbial) Screening Laboratory of the Institute of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the self-developed microbial natural product database MNPD.
[0062] 2. Lipinski's five-rule screening compound library
[0063] 80,000 compounds from the compound library were screened using Lipinski's rule of five to screen out compounds with toxic groups and active groups.
[0064] 3. Calculate the ADMET properties of the compound
[0065] Predict the properties of the compounds screened by Lipinski's five rules in terms of water solubility, human intestinal absorption, blood barrier permeability, cytochrome P4502D6 inhibition, liver toxicity, and plasma protein binding rate, and select a relative molecular mass below 500 , Calculate the compounds whose lipid-water partition coefficient CLgP is less than 5, the number of hydrogen bond ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 virtual screening based on pharmacophore model
[0069] The constructed pharmacophore model was input as a 3D query structure into the compound database (76984) filtered by Lipinski's five rules and predicted by ADMET for high-throughput virtual screening, and compounds matching more than half of the pharmacodynamic characteristic elements were retained. Finally, 270 qualified compounds were screened out.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com