A human-computer interaction force detection device
A detection device and human-computer interaction technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as low accuracy, poor stability, and poor human comfort, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
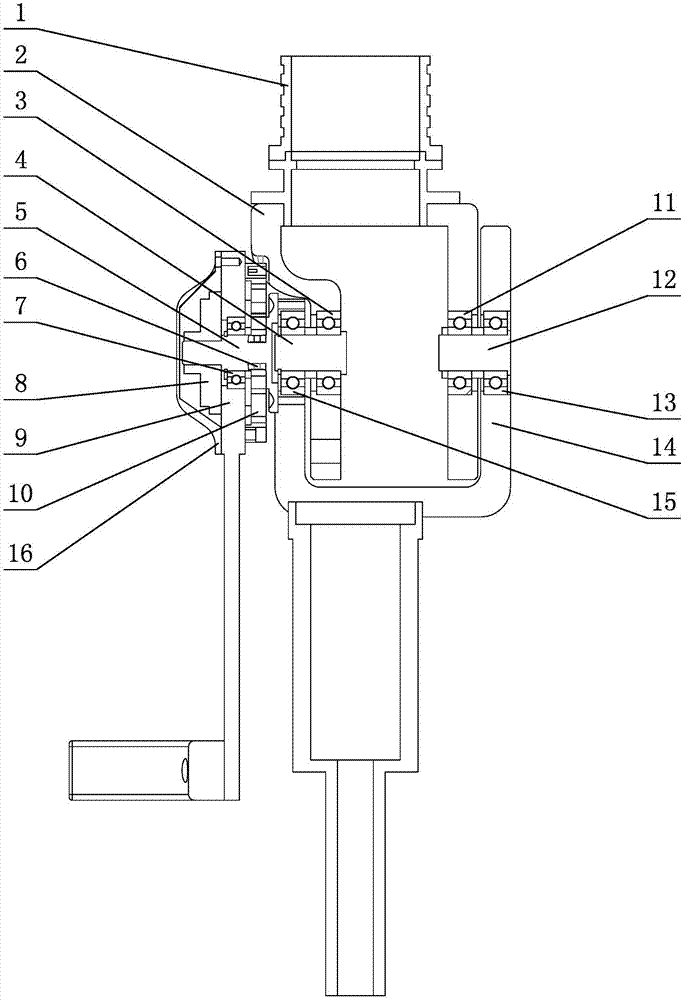
[0011] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a human-computer interaction force detection device described in this embodiment includes a first exoskeleton rod 1, a first joint head 2, a connecting shaft 5, a key 6, a second bearing 7, a magnetic encoder 8, a binding Binding rod 9, elastic body 10, second joint head 14, first connection assembly and second connection assembly, the lower end of the first exoskeleton rod 1 is connected to the upper end of the first joint head 2, and the outer side of the first joint head 2 is The wall is rotatably connected to the inner wall on one side of the second joint head 14 through the first connecting assembly, and the outer wall on the other side of the first joint head 2 is rotated to the inner wall on the other side of the second joint head 14 through the second connecting assembly. Connection, one end of the connecting shaft 5 is connected to the outer side wall of the second joint head 14 throug...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0012] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the first connection assembly of a human-computer interaction force detection device described in this embodiment includes a first bearing 3, a support shaft 4 and a fifth bearing 15, and the first bearing 3 is embedded in the first joint head 2 On the outer side wall of one side, the fifth bearing 15 is embedded on the inner side wall of the second joint head 14, one end of the support shaft 4 is inserted into the first bearing 3, and the other end of the support shaft 4 is inserted into the fifth bearing within 15. Other components and connections are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0013] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the second connection assembly of a human-computer interaction force detection device described in this embodiment includes a third bearing 11, an optical axis 12 and a fourth bearing 13, the third bearing 11 is embedded in the first joint head 2 On the outer side wall of the other side, the fourth bearing 13 is embedded on the inner side wall of the second joint head 14, one end of the optical axis 12 is inserted in the third bearing 11, and the other end of the optical axis 12 is inserted in the third bearing. In the four bearings 13. Other components and connections are the same as those in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com