Contour construction algorithm on the basis of point by point increasing of ground object scattered points
A technology of scattered points and ground objects, applied in the field of geographic information science, can solve problems such as slow speed and unreliable results, and achieve the effect of overcoming self-intersection and overcoming the explosive expansion of time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
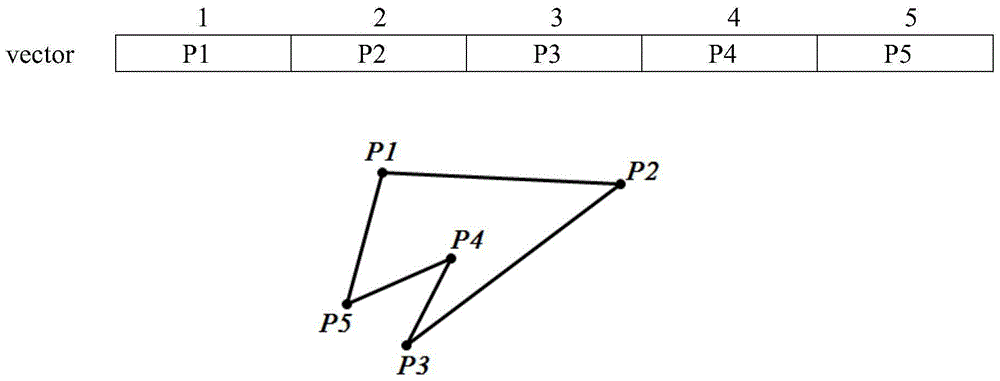
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, a contour construction algorithm based on the point-by-point increase of scattered points of ground objects includes the following steps:
[0026] S1, store the measured n sparse shape points of ground objects in the container vector of size n in sequence, and the n sparse shape points occupy the n positions of the container in turn, and label the n sparse shape points of ground objects as P1, P2,...Pn, a closed polygon scheme in which adjacent sparse shape points are connected to form the contour of the ground object.
[0027] S2, the initial number of iterations i=0, and the initial best criterion function value J_best=inf, inf is set according to the empirical value, generally can be set to 10 6 .
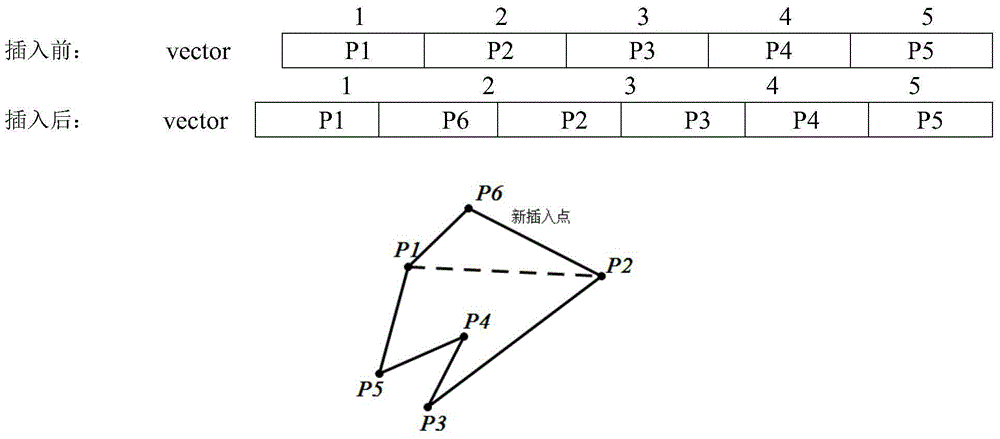
[0028] S3, randomize the positions of the n sparse shape points of the ground objects in the container vector. If there are 5 spars...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com