Flexible transmission device, adjustable spring, energy storage component, robot and locking device
A technology of flexible transmission and energy storage components, which is applied in the field of robotics and can solve problems such as damage to components or workers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
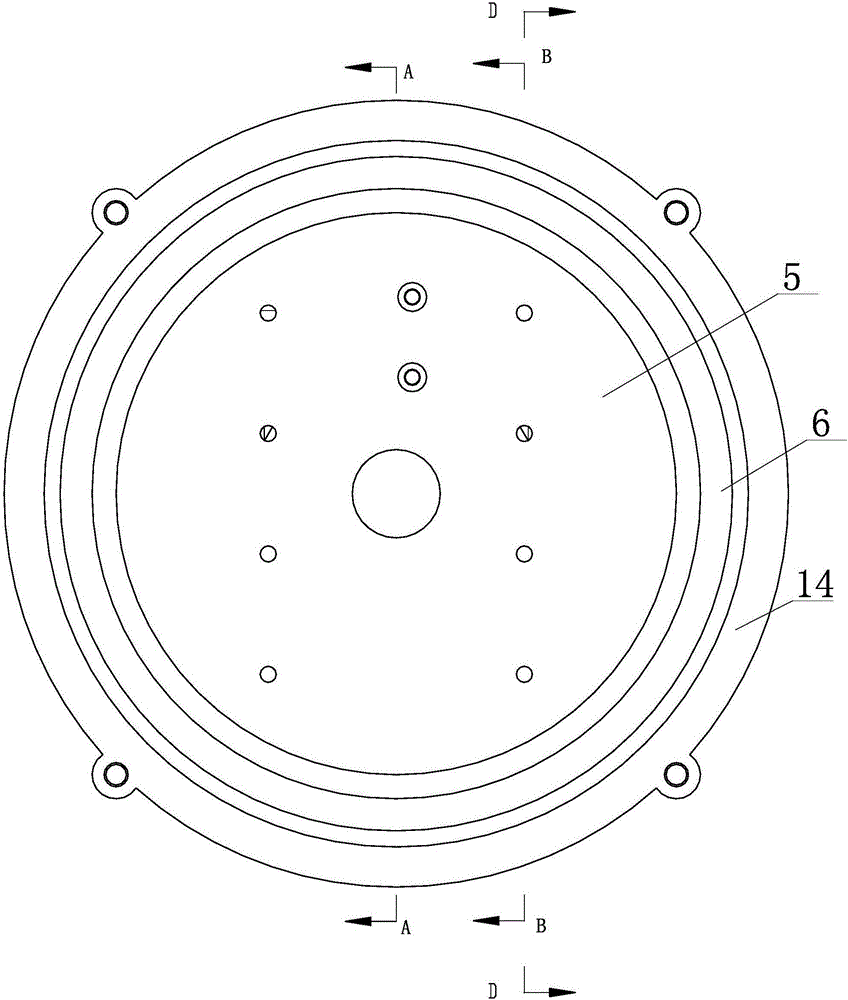
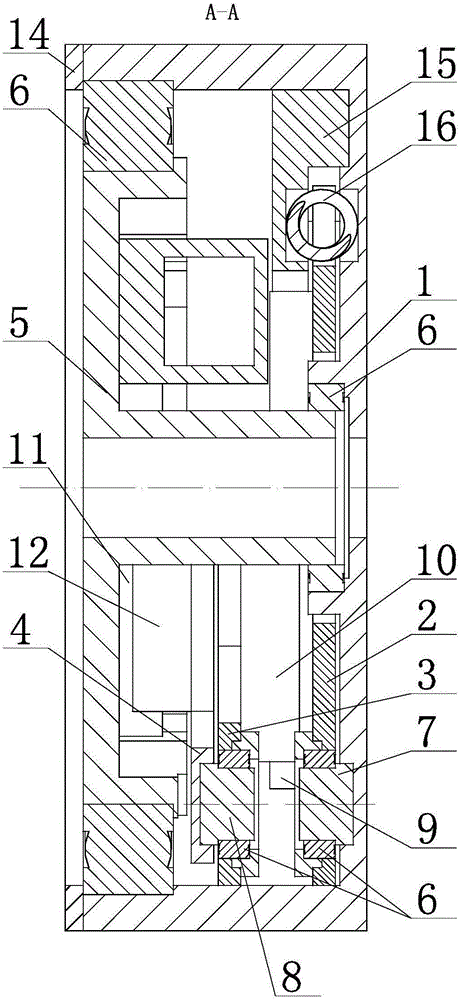
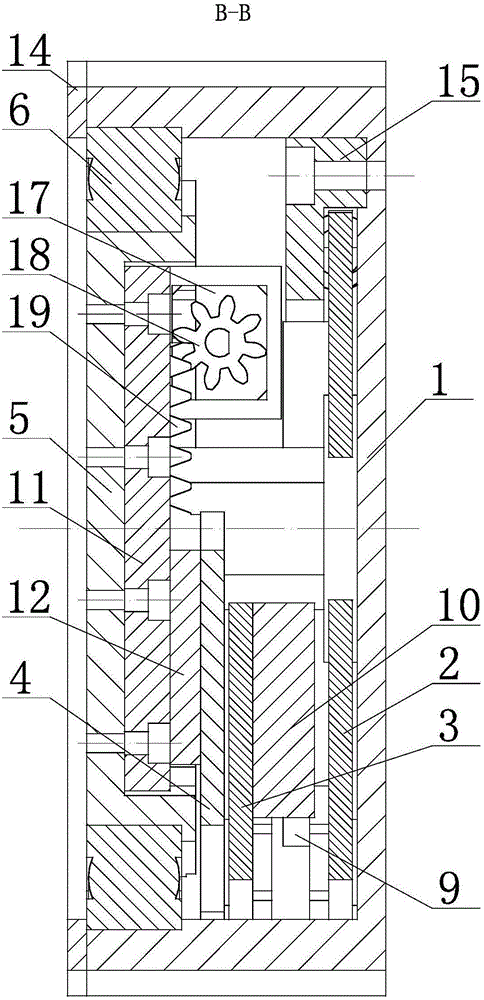
[0054] figure 1 It is the side view of the flexible transmission device of embodiment 1: figure 2 yes figure 1 A-A sectional view of ; image 3 yes figure 1 The B-B sectional view of; Figure 4 yes figure 1 D-D sectional view of ; Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the three-dimensional structure of the flexible driving device in embodiment 1 after the first end cover is removed; Figure 6 It is a side view of the schematic diagram of the mechanism of embodiment 1; Figure 7 It is the front view of the mechanism diagram of Embodiment 1.
[0055] In the figure, the meanings of each reference mark are as follows:
[0056] 1. First end cover; 2. First swing arm; 3. Second swing arm; 4. Third swing arm; 5. Second end cover; 6. Rolling bearing; 7. First shaft; 8. Second shaft ; 9, the first guide rail; 10, the first slider; 11, the second guide rail; 12, the second slider; 14, the pressure ring; 15, the first gland; 16, the compression spring; 17, the driving motor; 1...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of embodiment 2 where the flexible transmission device is cut along the middle of the second shaft 8 and viewed in the direction of the first end cover 1 . In the figure, the definitions of the reference numerals of the first embodiment are still used for the same reference numerals used in the drawings of the first embodiment. In the figure, the meanings represented by the newly appearing reference numerals in the accompanying drawings with respect to embodiment 1 are as follows: 20, tension spring;
[0081] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0082] In Embodiment 1, a compression spring 16 is provided to provide anti-rotation torque for rigid transmission. In fact, a pair of extension springs can also be provided—a first extension spring and a second extension spring, the first extension spring has a first end and a second end, and the second extension spring has a third end and a second end. The fourth ...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Figure 9 It is a schematic diagram of the movement of the mechanism in Embodiment 3. In the figure, the same reference numerals as in the drawings used in Embodiment 1 still follow the definition of the reference numerals in Embodiment 1.
[0086] In this embodiment, the corresponding relationship between each relative movement member and specific parts is as follows: the first relative movement member is the first end cap 1, the second relative movement member is the second end cap 5, and the third relative movement member is the third rocker. arm, the fourth relative movement member is the second rocker arm, the fifth relative movement member is the first rocker arm,
[0087] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in Embodiment 1, the driving motor 17 is installed on the second end cover 5, and the rack 19 meshing with the output gear 18 at the output end of the driving motor 17 is arranged on the third rocker. arm, and in this embodiment, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com