Debris flow material source dynamic reserve calculation method under rainfall condition
A reserve calculation and debris flow technology, applied in calculation, water conservancy engineering, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems such as the lack of calculation standards and methods for dynamic reserves, the interpretation of static and dynamic reserves of debris flow after earthquakes, and the failure of debris flow prevention and control projects. Achieve the effect of avoiding similarity problems and avoiding particle size effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
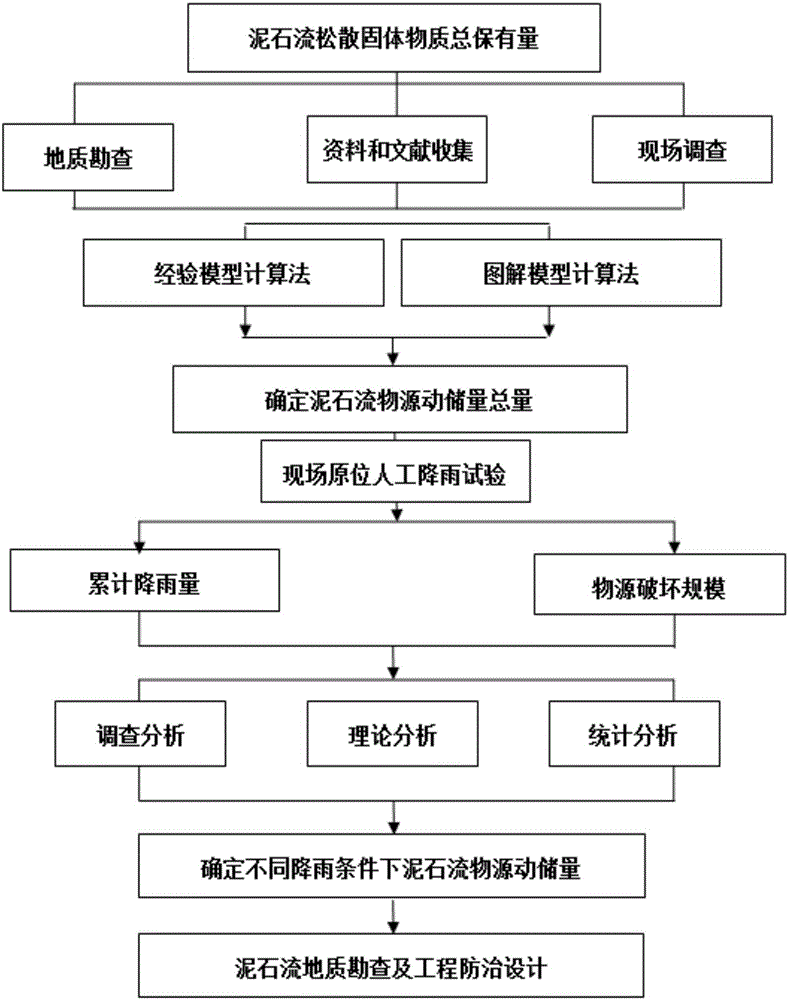
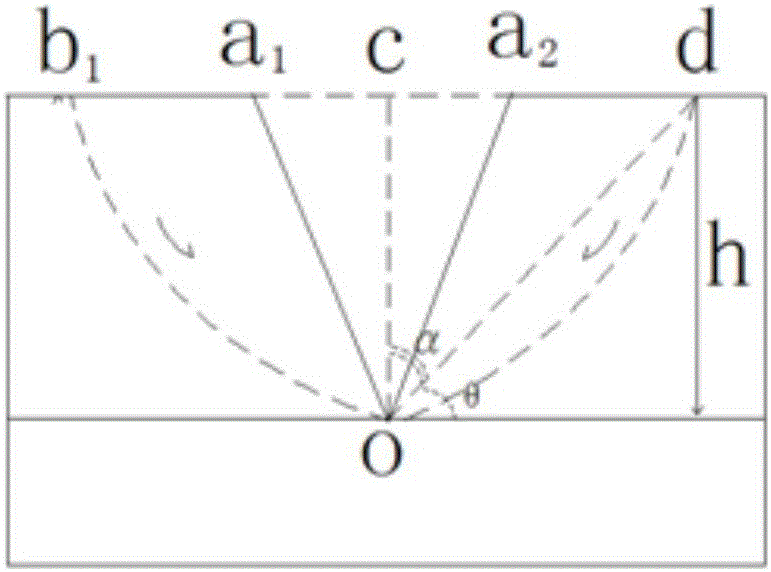
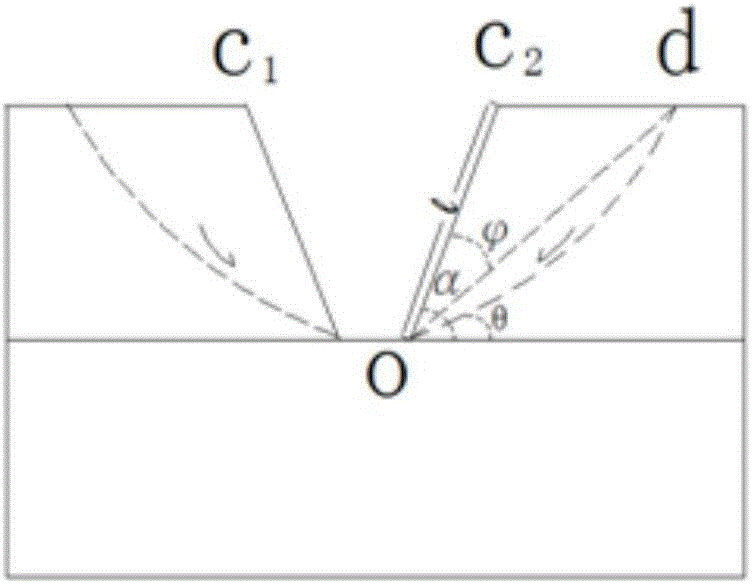
[0033] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. See the specific process figure 1 .
[0034] The debris flow in the dry ditch of Hongcun Village in Dujiangyan is located in the Baisha River Basin of Dujiangyan City in the episeismic area of the Wenchuan Earthquake. It is a typical debris flow after the earthquake. 2 (to the downstream Baisha River), the main ditch has a total length of 1.972km and an elevation of 1773-920m. The plane shape of the valley is V-U shape; the elevation of the valley bottom is 1640-1150m, and the relative height difference is 490m. The slopes on both sides of the valley are generally 30-40°. Among them, the valley in the upstream formation area is about 1121m long, with an average vertical slope of 530.78‰; the channel in the circulation area is about 219m long, with an average vertical slope of 273.97‰; the valley in the accumulation area is about 632m long...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com