Multi-sensor fusion for robust autonomous filght in indoor and outdoor environments with a rotorcraft micro-aerial vehicle (MAV)
An outdoor environment and sensor technology, used in unmanned aerial vehicles, aircraft, micro-aircraft, etc., can solve problems such as sensor failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
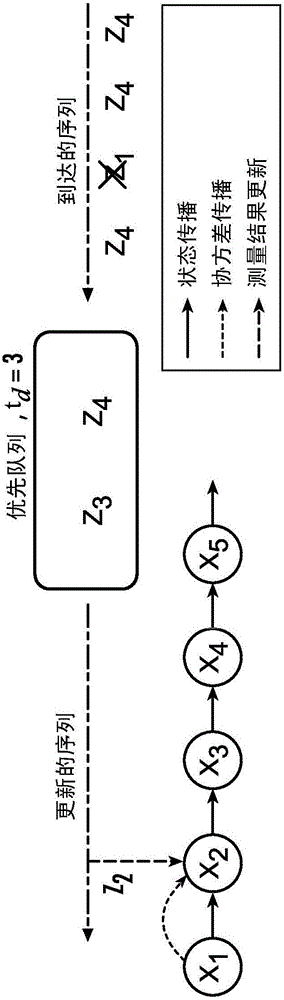
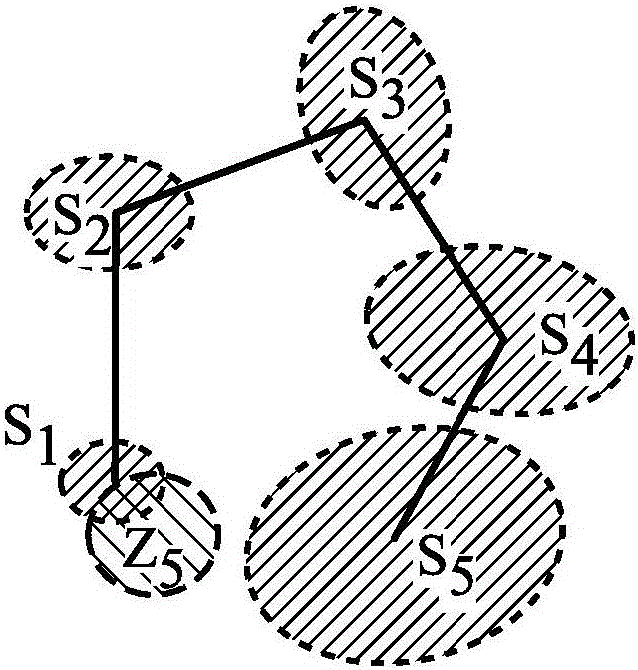
[0036] Rotary-wing Micro Aerial Vehicles (MAVs) are ideal platforms for surveillance and search and rescue in confined indoor and outdoor environments because of their small size, excellent mobility, and hovering capabilities. In such missions, it is important for the MAV to be able to fly autonomously to minimize operator workload. Robust state estimation is critical for autonomous flight, especially because of the inherently fast dynamics of MAVs. Due to cost and payload constraints, most MAVs are equipped with low-cost proprioceptive sensors (eg, MEMS IMUs), which cannot be used for long-term state estimation. Therefore, exteroceptive sensors (such as GPS, video cameras, and laser scanners) are often fused with proprioceptive sensors to improve estimation accuracy. In addition to the well-developed GPS-based navigation techniques [1, 2], there are recent studies on the use of laser scanners [3, 4], monocular cameras [5, 6], stereo cameras [7, 8] and RGB-D sensor [9] from ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap