Cross-visual-angle gait identification method based on tensor simultaneous discriminant analysis
A discriminant analysis and gait recognition technology, applied in the field of pattern recognition and machine learning, can solve the problems of weakening the effectiveness of classic gait recognition algorithms, serious self-occlusion, and differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
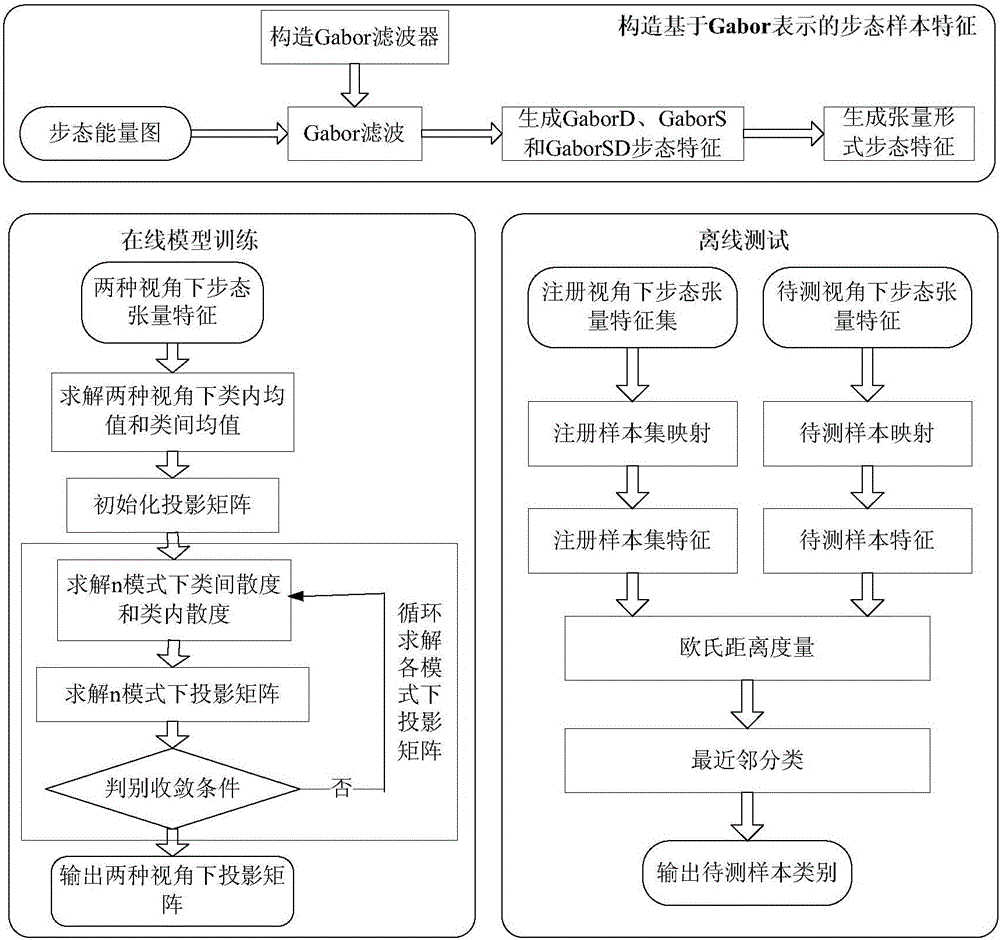
[0085] A cross-view gait recognition method based on tensor simultaneous discriminant analysis, such as figure 1 As shown, including building Gabor-based gait features, online model training and offline testing;
[0086] The method for said construction based on the gait feature represented by Gabor comprises:
[0087] First, construct a two-dimensional Gabor filter;
[0088] Secondly, perform Gabor transformation on the gait energy map features;
[0089] Finally, the two-dimensional Gabor filter direction, scale and these two aspects are respectively summed to generate GaborD, GaborS and GaborSD gait features;
[0090] The method for online model training includes:
[0091] First, the gait features under the two perspectives are written in the form of tensors;
[0092] Then, through tensor simultaneous discriminant analysis, the inter-class divergence of gait features under the two views is maximized, and the intra-class divergence of the two views is minimized, and each ...
Embodiment 2
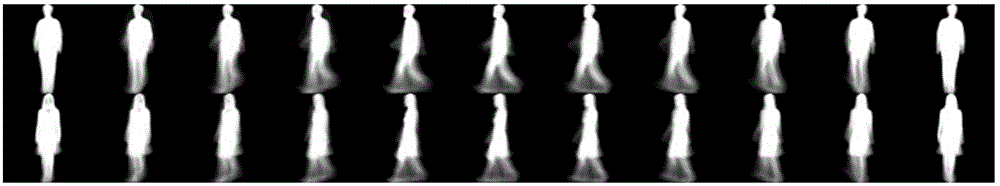
[0098] A cross-view gait recognition method based on tensor simultaneous discriminant analysis as described in Example 1, the difference is that in the method of constructing the gait feature based on Gabor representation, as figure 2 and image 3 As shown, the Gabor-based gait features include GaborS, GaborD and GaborSD, such as Figure 5, use the gait energy map to generate the above three gait features, and write them in the form of tensor respectively. The gait features based on Gabor representation in the above tensor form are collectively referred to as gait tensor features based on Gabor representation;
[0099] First, perform Gabor transformation on the gait energy map features, and sum them according to the direction and scale direction, respectively, to obtain GaborD, GaborS and GaborSD features, and their mathematical description is as follows:
[0100] The two-dimensional Gabor function is defined as the product of an elliptic Gaussian envelope and a complex plan...
Embodiment 3
[0111] A cross-view gait recognition method based on tensor simultaneous discriminant analysis as described in Embodiment 2, the difference is that in the online model training method, the gait tensor feature represented by Gabor is based on Gabor The tensor form of the expressed gait features GaborD, GaborS and GaborSD, which is represented by cursive symbols below; the model training is to find the gait tensor features expressed by Gabor based on samples from different perspectives in the common subspace with the largest inter-class distance , the mapping form with the smallest intra-class distance, its mathematical description is as follows:
[0112] Assume that the gait tensor feature of the i-th sample of the c-th class based on the Gabor representation under the viewing angle θ is angle of view The gait tensor feature of the jth sample of the next c-th class based on Gabor representation is Then the training sample sets composed of all samples from the two perspecti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com