Real-time subtitle display method and system
A technology of subtitles and screens, applied in the field of real-time subtitle display methods and systems, which can solve problems such as the small amount of information transmitted, the inability to re-view subtitle texts on the spot, and the inability to meet application requirements, so as to achieve the effect of improving intelligibility and improving effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0082] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the solutions of the embodiments of the present invention, the embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings and implementations.
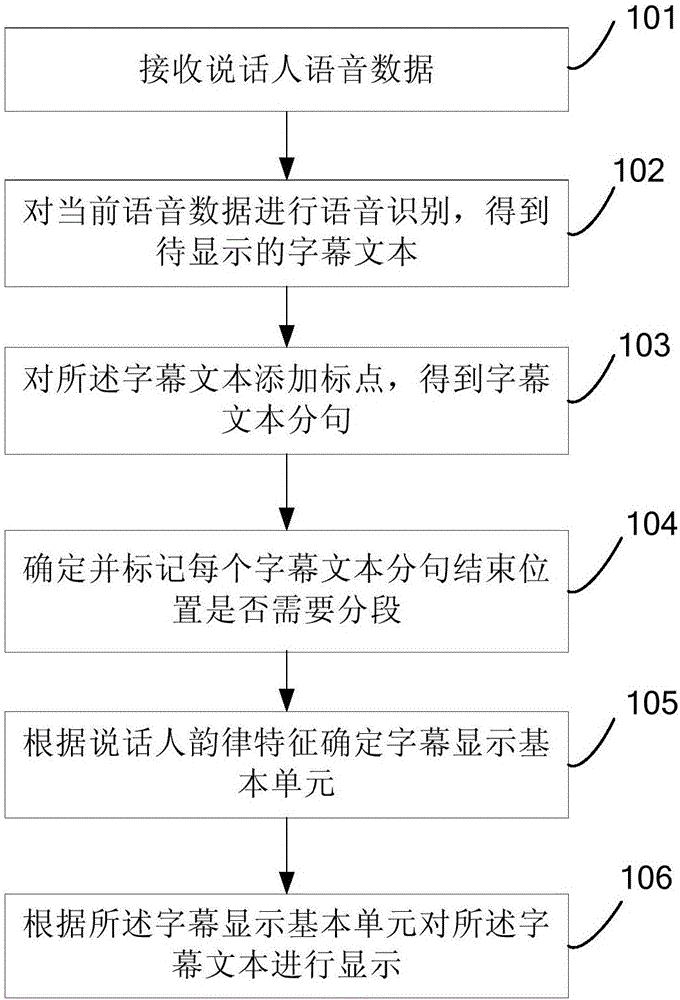
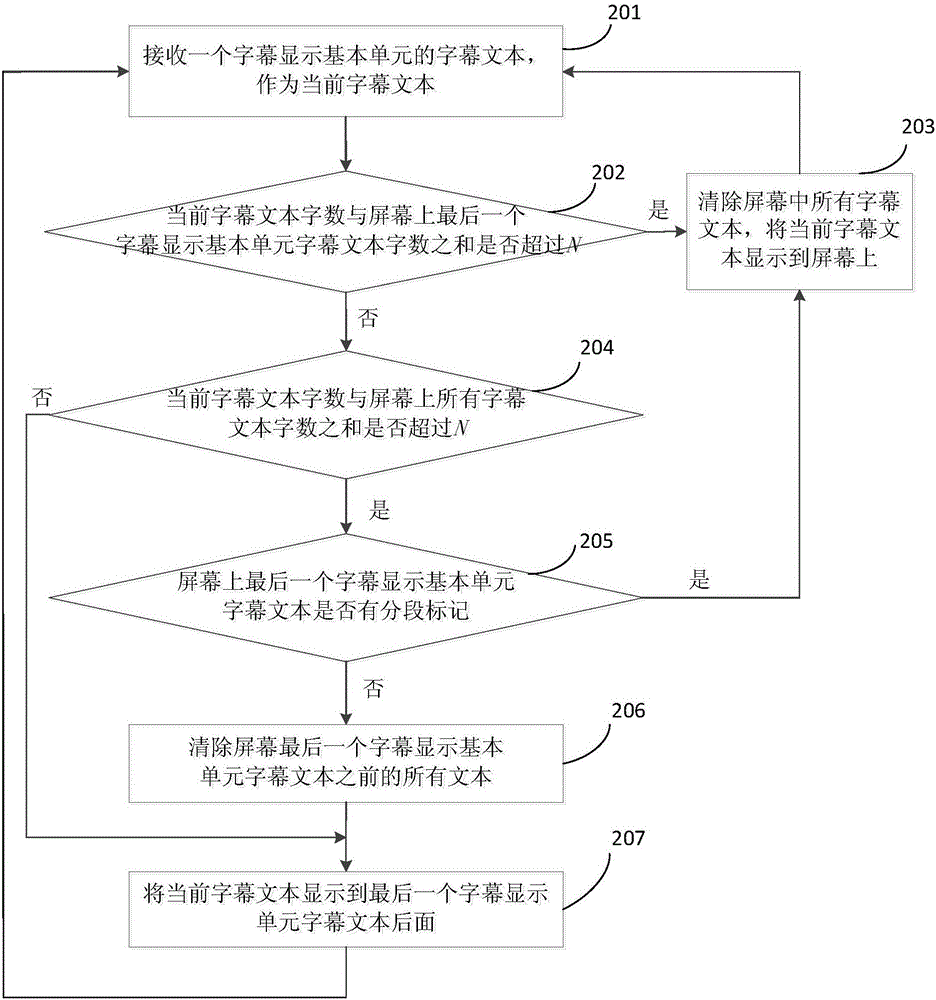
[0083] Aiming at the problems existing in the existing subtitle display method, an embodiment of the present invention provides a real-time subtitle display method and system, which adds punctuation to the recognized subtitle text to be displayed, obtains subtitle text clauses with complete semantics, and determines and marks the subtitle text. Describe whether the end position of the subtitle text sentence needs to be segmented, and then determine the basic unit of subtitle display according to the prosodic characteristics of the speaker, and display the subtitle text sentence according to the basic unit of subtitle display, thereby increasing the context of subtitle text display and greatly improving the speaker...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com