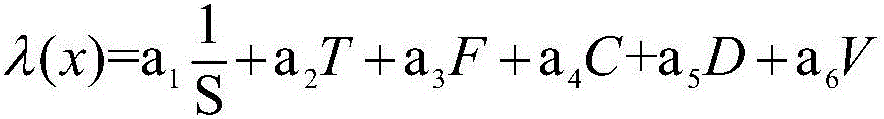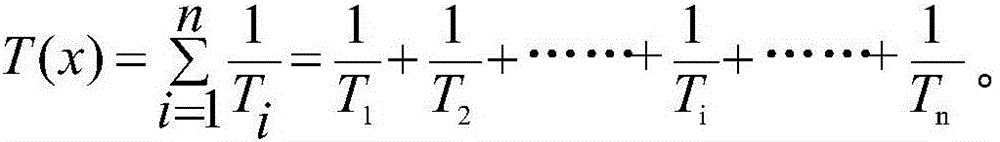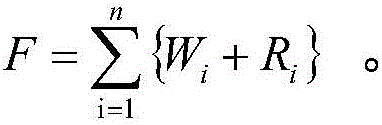Data value degree calculation method based on analytic hierarchy process
A technique of analytic hierarchy process and calculation method, which is applied in the direction of calculation, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., and can solve problems such as low accuracy and low storage efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] This embodiment provides a data value calculation method based on the analytic hierarchy process. The calculation formula of the value λ of data x is as follows:
[0054] λ ( x ) = a 1 1 S + a 2 T + a 3 F + a 4 C + a 5 D + a 6 V
[0055] ①S represents the data size; for a storage system that has reached the PB level, it is impossible to use a high-performance disk array with high cost. Therefore, for a storage system built with hybrid disks, small and hot files are more suitable for storage in In high-performance disk arrays with high performance and limited capacity, the unit is megabytes;
[0056] ②T represents the access time interval; the newly created or recentl...
Embodiment 2
[0070] As a supplement to Example 1, the calculation method of the expected value V of the data is:
[0071] Step 1: Assume that users who have accessed data x are represented by G, and other users are represented by H, then:
[0072] G={g 1 , g 2 ,...,g n}
[0073] H={h 1 ,h 2 ,...,h m}
[0074] Said n and m are the total number of users;
[0075] Step 2: Calculate the similarity of G and H elements to obtain a similarity matrix:
[0076] S i m ( G i , H j ) = S 11 S 12 ... S 1 m S 21...
Embodiment 3
[0084] As a further supplement to Embodiment 1 or 2, the constructed judgment matrix P is as follows:
[0085] P = 1 3 3 1 3 1 5 1 3 1 3 1 1 1 1 15 1 9 1 3 1 1 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com