Terminal identifier allocation method, device and system
A terminal identification and distribution method technology, applied in wireless communication, network data management, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to use the same C-RNTI, and achieve the effect of reducing signaling interaction and delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
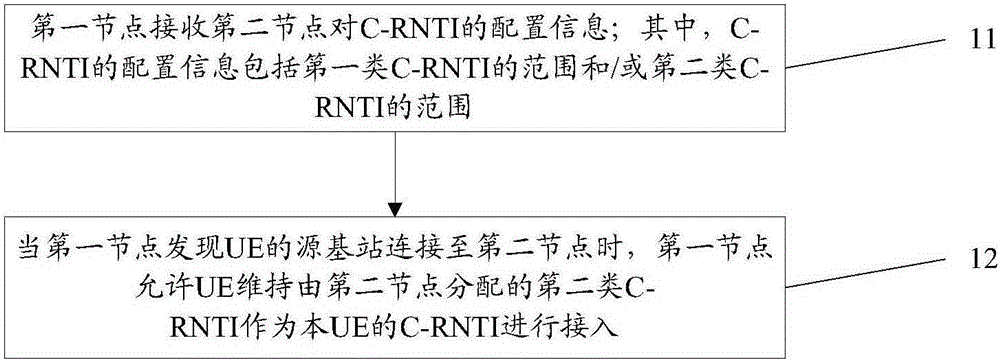
Examples
Embodiment 1
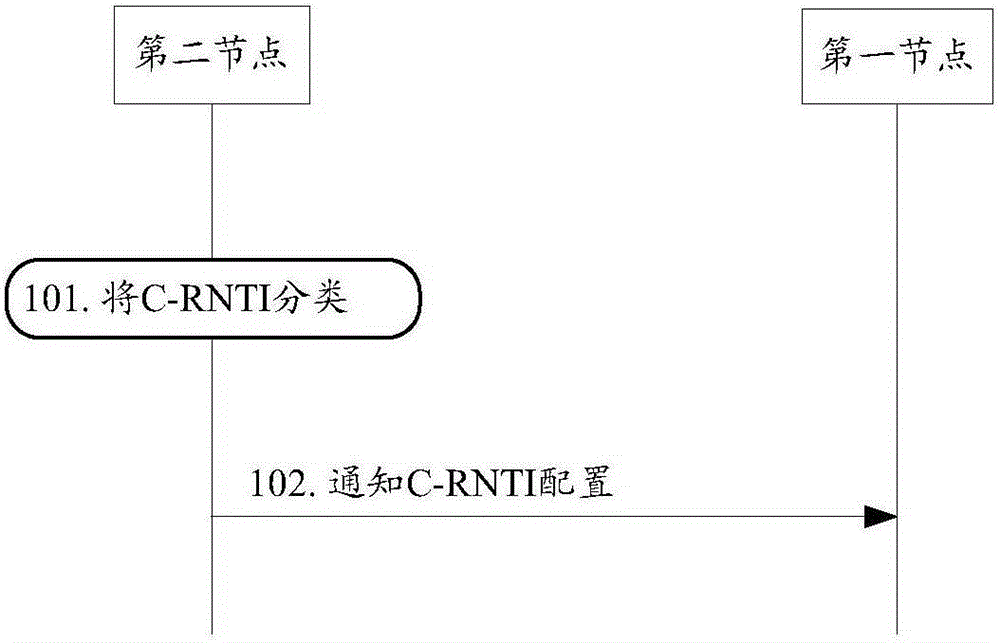
[0046] image 3 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. It should be noted that this embodiment only describes the process in which the second node notifies the first node of the configuration information of the C-RNTI, and the description of other irrelevant steps is omitted. Such as image 3 As shown, the specific description of this embodiment is as follows:
[0047] Step 101: The second node divides the C-RNTI into the first type of C-RNTI and the second type of C-RNTI; in this embodiment, the second node can modify the configuration information of the C-RNTI according to the following parameters: The number of UEs that have been accessed, the number of UEs requesting random access within a period of time, and the number of UEs that have not been assigned a C-RNTI among UEs requesting random access within a period of time;
[0048] Step 102: the second node notifies the first node of C-RNTI configuration information, where the C-RNTI configuration i...
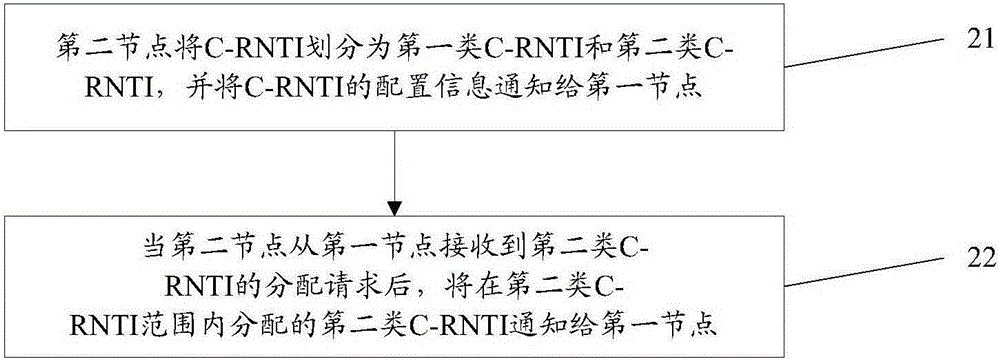
Embodiment 2
[0051] Figure 4 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 2 of the present invention. It should be noted that this embodiment specifically describes the process of performing random access in UE initial access or connection re-establishment scenarios, omitting descriptions of steps unrelated to this embodiment, and, in this embodiment, UE No C-RNTI is allocated before access, and a C-RNTI needs to be obtained through random access. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the specific description of this embodiment is as follows:
[0052] Step 201: UE sends a random access preamble to the first node;
[0053] Specifically, the UE first selects a preamble (Preamble), and sends the preamble to the first node according to the random access resource information configured by the system;
[0054] Step 202: the first node sends a random access response message Msg2 to the UE;
[0055] Here, the random access response message Msg2 may include a preamble identifier corresponding to the random access ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Figure 5 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 3 of the present invention. It should be noted that this embodiment specifically describes the process in which the target first node requests the target second node to allocate a second type of C-RNTI when the UE is handed over to the target first node and the target first node is connected to the target second node , the description of steps irrelevant to this embodiment is omitted, and, in this embodiment, the source base station may be any access network node that provides air interface access and the source base station is not connected to the target second node. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the specific description of this embodiment is as follows:
[0069] Step 301: the source base station sends a handover request message to the target first node, and the message includes handover preparation related messages;
[0070] Step 302: The target first node refers to the handover request message, and performs an admission dec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com