Photodynamic antibacterial cellulose material and preparation method thereof
A photodynamic antibacterial and antibacterial fiber technology, applied in fiber processing, plant fibers, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitability for industrial production, limited, and restricting the development of photodynamic antibacterial fibers.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
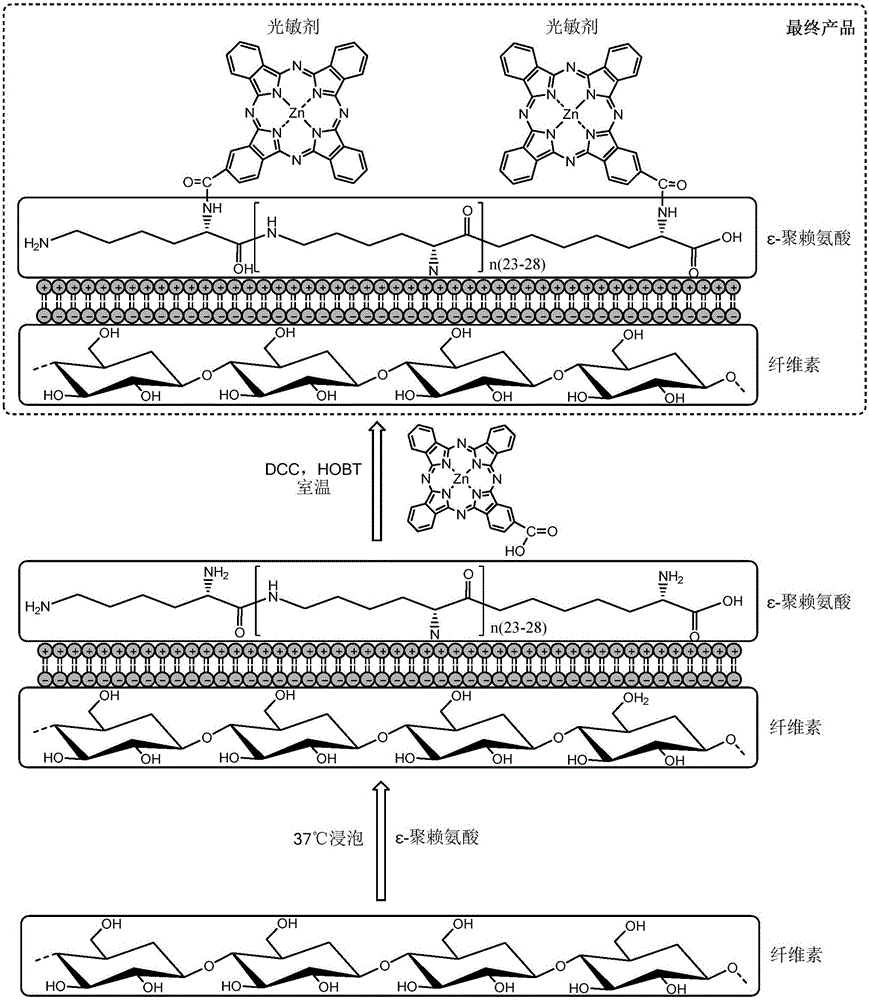
[0058] Preparation of zinc phthalocyanine-ε-polylysine cellulose
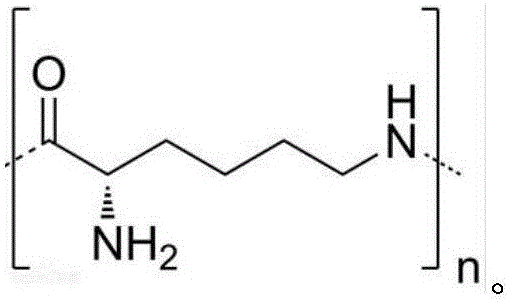
[0059] 1. Soak 1g of cellulose fabric in 50ml of 1g / L ε-polylysine (containing 25-30 L-lysine residues) aqueous solution at 37°C, take it out after 30 minutes, and wash it with water Remove unadsorbed ε-polylysine from the fabric and dry it for later use.
[0060] 2. Dissolve 0.06mmol (37.32mg) β-monocarboxy substituted zinc phthalocyanine in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent, add 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT) and twice the molar equivalent The N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) was activated for 30 minutes, then added to the cellulose fabric prepared in the first step and reacted at room temperature for 24 hours, and the unreacted β-monocarboxyl substituted phthalein was washed away with DMF Zinc cyanine, and then wash the fabric 3 times with clear water, and dry to obtain zinc phthalocyanine-ε-polylysine cellulose.
Embodiment 2
[0062] Preparation of zinc phthalocyanine-ε-polylysine cellulose microspheres
[0063] 1. Soak 1g of cellulose microspheres in 50ml of 45g / L ε-polylysine (containing 25-30 L-lysine residues) aqueous solution at 10°C, take it out after 90 minutes, and rinse with water Wash to remove unadsorbed ε-polylysine, and dry it for later use.
[0064] 2. Dissolve 0.12mmol (74.64mg) β-monocarboxy substituted zinc phthalocyanine in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent, add 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT) and twice the molar equivalent The N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) was activated for 20 minutes, then the cellulose microspheres prepared in the first step were added and the reaction was shaken at room temperature for 12 hours, and the unreacted β-monocarboxyl substitution was washed away with DMF. The zinc phthalocyanine was washed three times with clear water, and dried to obtain the zinc phthalocyanine-ε-polylysine cellulose microspheres.
Embodiment 3
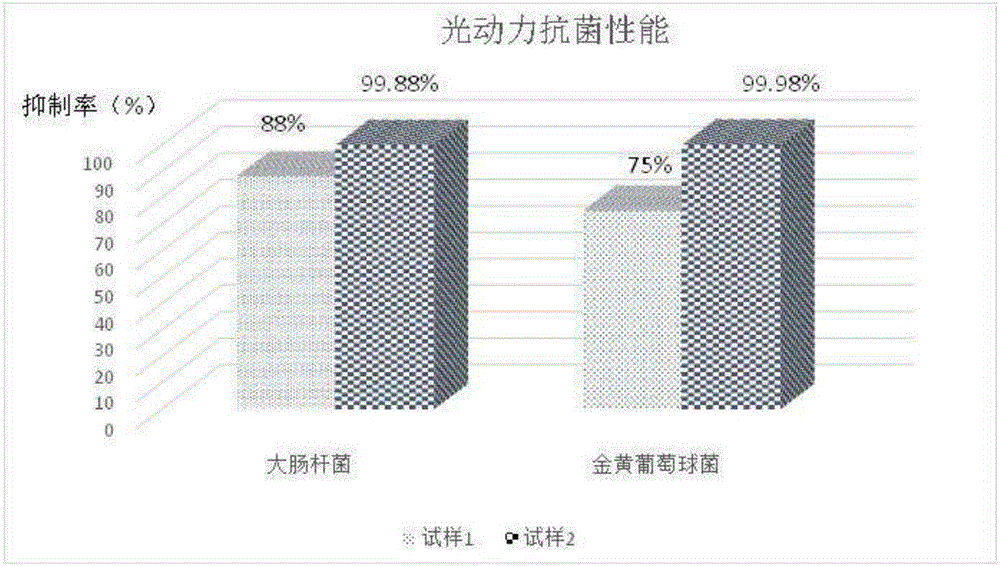
[0066] Photodynamic antibacterial properties of zinc phthalocyanine-ε-polylysine cellulose materials
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com