Lens driving device
A lens driving device and lens technology, applied in installation, instrumentation, optics, etc., can solve the problems of difficult size control, easy warping and deformation of the outer edge of the coil, and difficulty in wire routing, and achieve the effect of low process requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] The lens driving device of the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
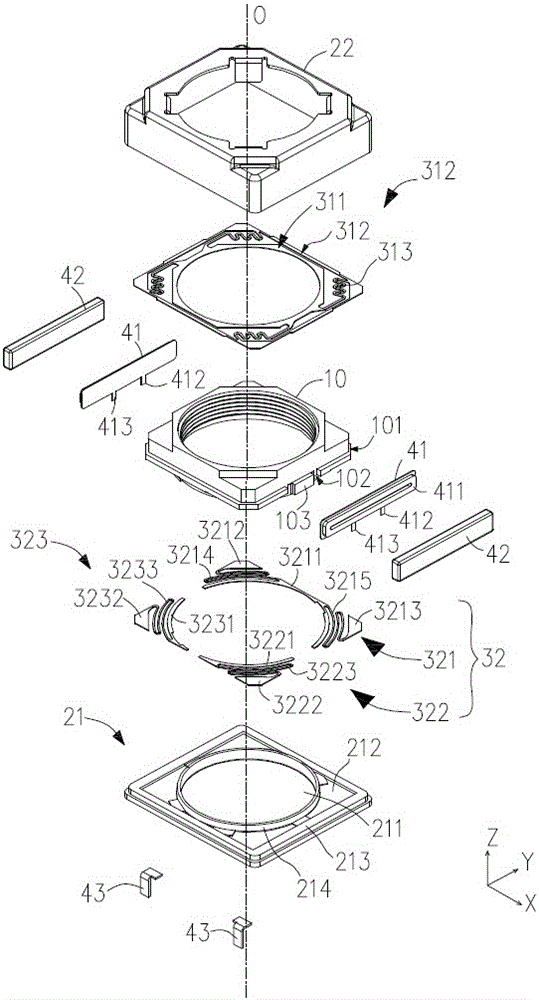
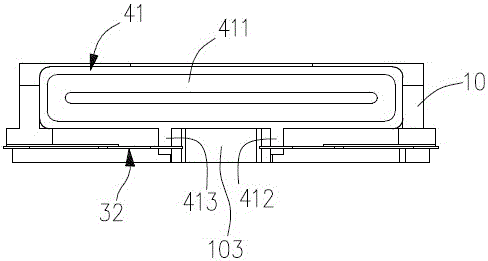
[0015] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, in a preferred embodiment, the lens driving device of the present invention mainly includes a lens holder 10 for holding an unillustrated lens, a base 21 and a front cover 22 that is fastened on the base 21. A case, a spring member for suspending the lens holder 10 on the case and enabling it to move in the optical axis direction O of the lens, and an electromagnetic drive mechanism 40 for driving the lens holder to move in the optical axis direction of the lens.
[0016] Hereinafter, in this specification, the optical axis direction O of the lens is referred to as the Z-axis direction, and the subject side is referred to as the Z-axis front (+Z side or +Z direction). In addition, two axes which are orthogonal to each other and are orthogonal to the Z-axis, respective...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com