Self-paced matrix decomposition method based on Pareto optimization
A matrix decomposition and matrix technology, applied in genetic models, instruments, computing models, etc., can solve problems such as poor matrix decomposition and local minima
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] This embodiment provides a figure 1 The self-stepping matrix factorization method based on Pareto optimization shown includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1) Input the matrix Y∈R to be decomposed m×n , population size N p and step size information, the matrix index set of the non-missing data in the matrix Y to be decomposed is Ω, and the step size information includes the initial step size k 0 and step increment μ;
[0041] Step 2) Decompose the matrix Y to be decomposed to obtain the initial matrix U 0 ,V 0 , calculate the matrix element loss value, and then according to the weight distribution method f(w ij ; k) and random method to generate a population size of N p The initial weight population P 0 And calculate the two objective function values corresponding to the population individual, at this time And set the iteration termination number G max , where U 0 ∈R m×r ,V 0 ∈R r×n ,r0 Increase μ successively to get, w ij Indicates the weight of t...
Embodiment 2
[0052] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a self-step matrix decomposition method based on Pareto optimization, including the following steps:
[0053] Step 1) Input matrix Y, population size N p and step information:
[0054] Randomly generate elements Y of matrix Y ij Obey the Gaussian distribution N(0,1), and then 40% of them are selected as missing data, 20% of the data is added to the uniformly distributed noise disturbance on [-20,20] and 20% of the data is added to Gaussian noise ~ N(0,0.01) Disturbance; step size information includes initial step size k and step size increment μ;
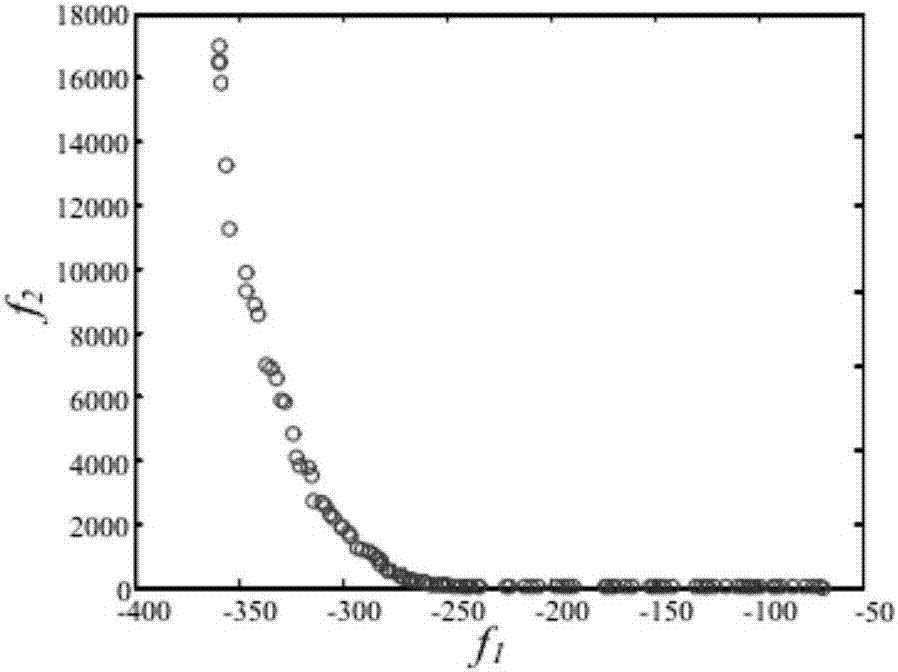
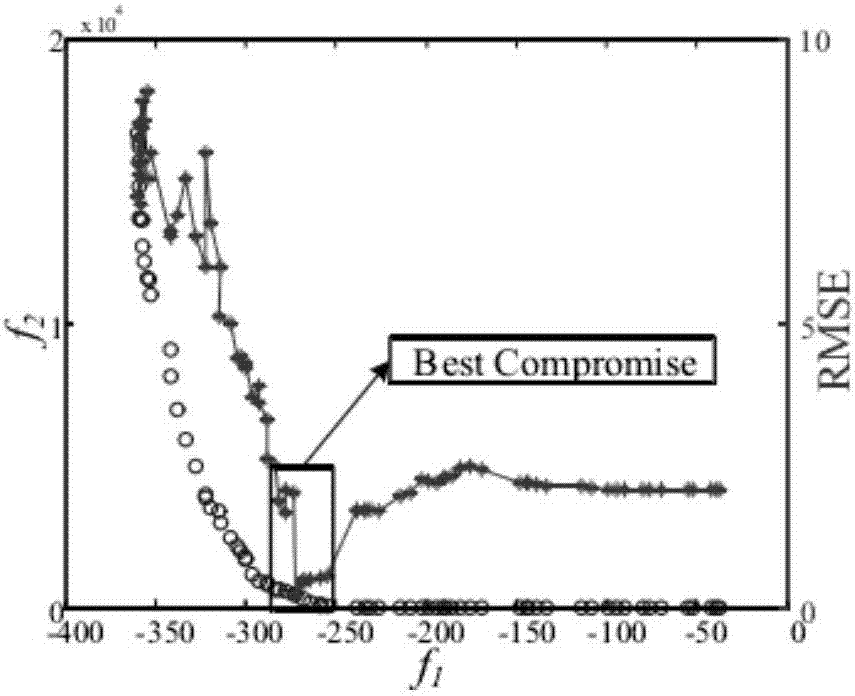
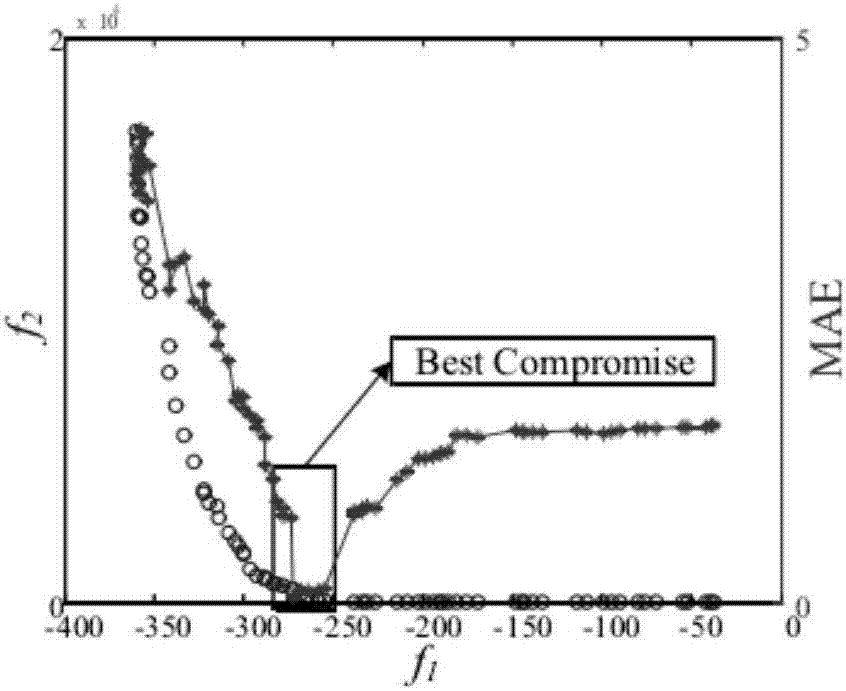
[0055] Step 2) Decompose Y to get the initial matrix U 0 ,V 0 , calculate the loss and generate the initial weight population P 0 And set the iteration termination number G max : Population P 0 Schematic figure 2 ;
[0056] Use the traditional matrix decomposition method to get the initial matrix U 0 ,V 0 , the matrix U 0 ,V 0 Substituting the loss function ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com