A kind of qrl code used for plane continuous positioning and its continuous positioning method
A code block and line coding technology, which is applied to record carriers, instruments, and calculations used in machines, can solve problems such as increased costs, increased camera data traffic and processing load, and achieves high positioning accuracy, reduced granularity, and code. The effect of increased block resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
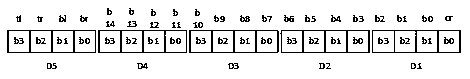
[0065] The so-called QRL code actually involves two concepts: QRL layout and QRL unit; among them, the QRL unit is the basic unit for the complete recognition of the QRL code, and the QRL layout is an arbitrary shape formed by arranging multiple QRL units continuously according to the same rules. picture of. Each QRL unit contains two positioning patterns (Finder Pattern), a row encoding sub-block (RowEncoding) and a column encoding sub-block (Column Encoding); the positioning pattern is exactly the same as the positioning pattern of the QR code, and its The length of each side is 7 code block units, and they are arranged according to the ratio of vertical and horizontal 1:1:3:1:1 (black / white / black / white / black). There is no difference in appearance between row-coded sub-blocks and column-coded sub-blocks. They are collectively referred to as row-column codes. There are two specifications of 9*9 and 7*7. The row-column codes of 9*9 specifications are arranged in 9*9 code block...
Embodiment 2
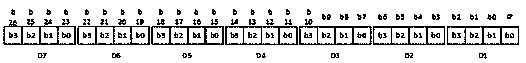
[0096] This embodiment provides a QRL layout example with 7*7 specification row and column coding, such as Figure 23 shown. Compared with Embodiment 1, this embodiment is identical except that the specification of row and column coding is changed from 9*9 to 7*7. However, changes in the row and column encoding specifications will result in changes in the value of minNumPixels, such as Figure 24 Shown:
[0097] minNumPixels>=(7+1+7+1+7)* *mResolution= 32.5*mResolution = 32.5 code block units
[0098] The above calculations show that when the 7*7 row and column encoding is used and separated into 1 code block unit, compared with the situation where the QR code is used for positioning applications, the image array covers at least 61 code blocks on one side, and the same camera , the number of code block units required by the QRL code is reduced by 47%, that is to say, the code block resolution can be nearly doubled.
[0099] The structure of the row-coded sub-block and t...
Embodiment 3
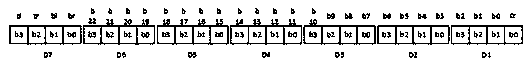
[0104] This embodiment shows the situation where multiple layouts are used in an application, such as Figure 33 shown. In the figure, we call the layout on the left as layout 1 and the layout on the right as layout 2. Use completely different row and column coordinate ranges in the two layouts, and have completely independent X'O'Y' coordinate systems. When the mover moves and locates in the same layout, the situation is the same as that of embodiment 1 or embodiment 2. If the mover needs to enter layout B from layout A, what should be done, the answer is to use the boundary flag. For example, if the current QRL unit is R940 / C303, you will find that the tl, tr, and br bits of R940 are 0, indicating that the upper and right sides of R940 are the border; in order to enter layout 2, the mover must first turn off the QRL code recognition function, so that the mover The child "freely" moves a certain distance to the right, upper right or lower right, and does not turn on the QR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com