P2P live broadcast system and method for reducing repetition of encoded segments
A fragment and encoding technology, applied in the field of live broadcast, can solve problems such as affecting user experience, slow process, and aggravating freeze, to reduce the risk of freeze, ensure smooth playback, and reduce the probability of receiving repeated encoded clips.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
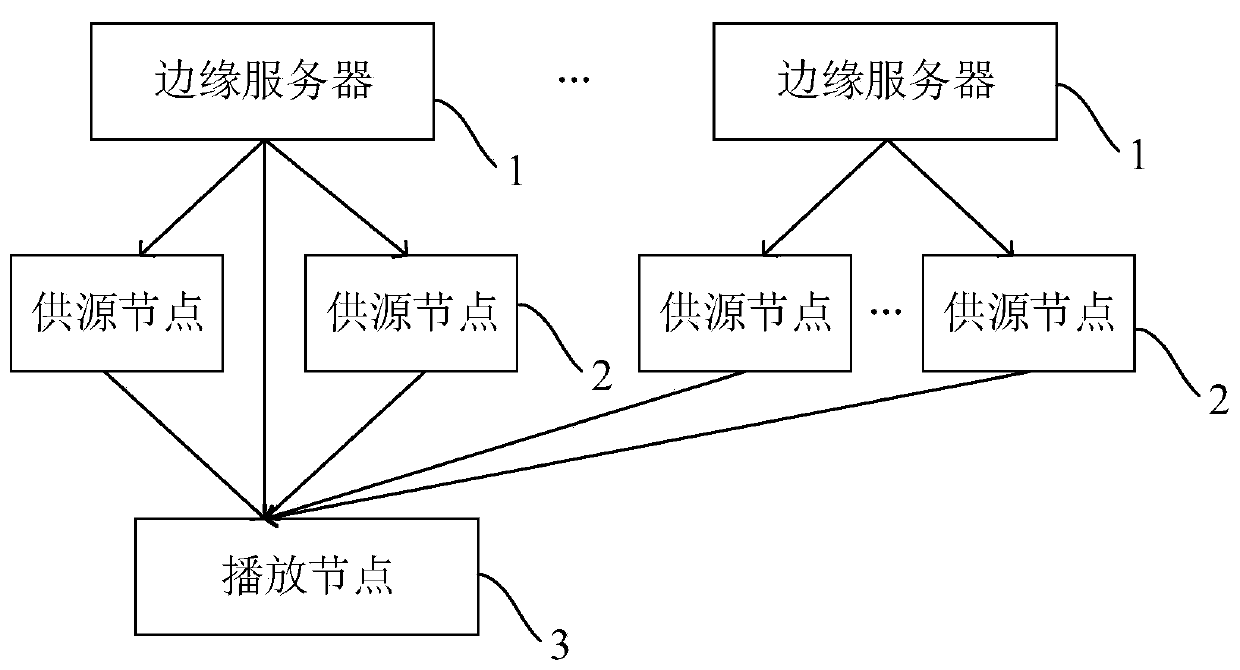
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, the P2P live broadcast system of this embodiment includes: an edge server 1, a source node 2 and a playback node, each edge server 1 is connected to a plurality of source nodes 2 respectively, and each source node 2 is connected to a plurality of source nodes. The playback nodes 3 are connected in communication, and each playback node is also connected in communication with multiple supply nodes 2 . During the live video broadcast, the edge server divides the acquired video data into several data blocks, and divides and encodes each data block into several coded segments. Specifically, the edge server divides each data block into k original fragments of the same size, and then encodes the k original fragments through erasure codes to generate N-k redundant coded fragments, and divides the N coded fragments into distribution Coding Snippets and Supplementary Coding Snippets. The edge server distributes the distribution code segment to the sou...
Embodiment 2
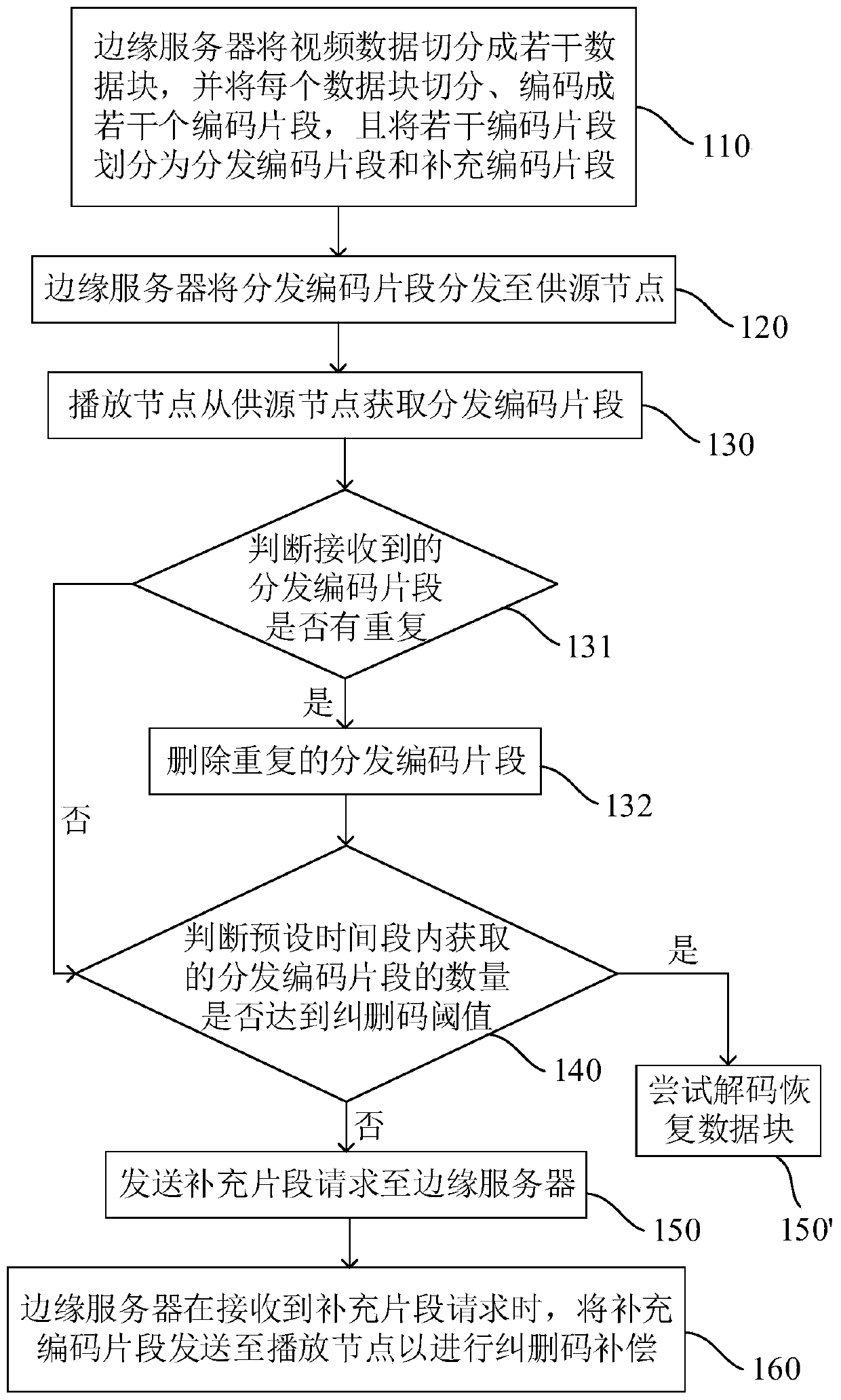
[0053] Embodiment 2 is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that this embodiment provides another way to prevent the playback node from obtaining duplicate distributed coded segments. Specifically, in this embodiment, all distributed coded segments in a data block have different coded IDs (supplementary coded segments also have different coded IDs, which are independent from the distributed coded segments), but the coded IDs in each data block are the same, for example, the encoding ID in data block 1 is: distribution encoding segment 1, distribution encoding segment 2, ..., distribution encoding segment n; the encoding ID in data block 2 is also: distribution encoding segment 1, distribution encoding segment 2, ..., distribute the encoded segment n. The edge server assigns a fixed code ID to each source node, and sends the distribution code segment corresponding to the code ID to the corresponding source node, that is, the source node only receives the distribution code...
Embodiment 3
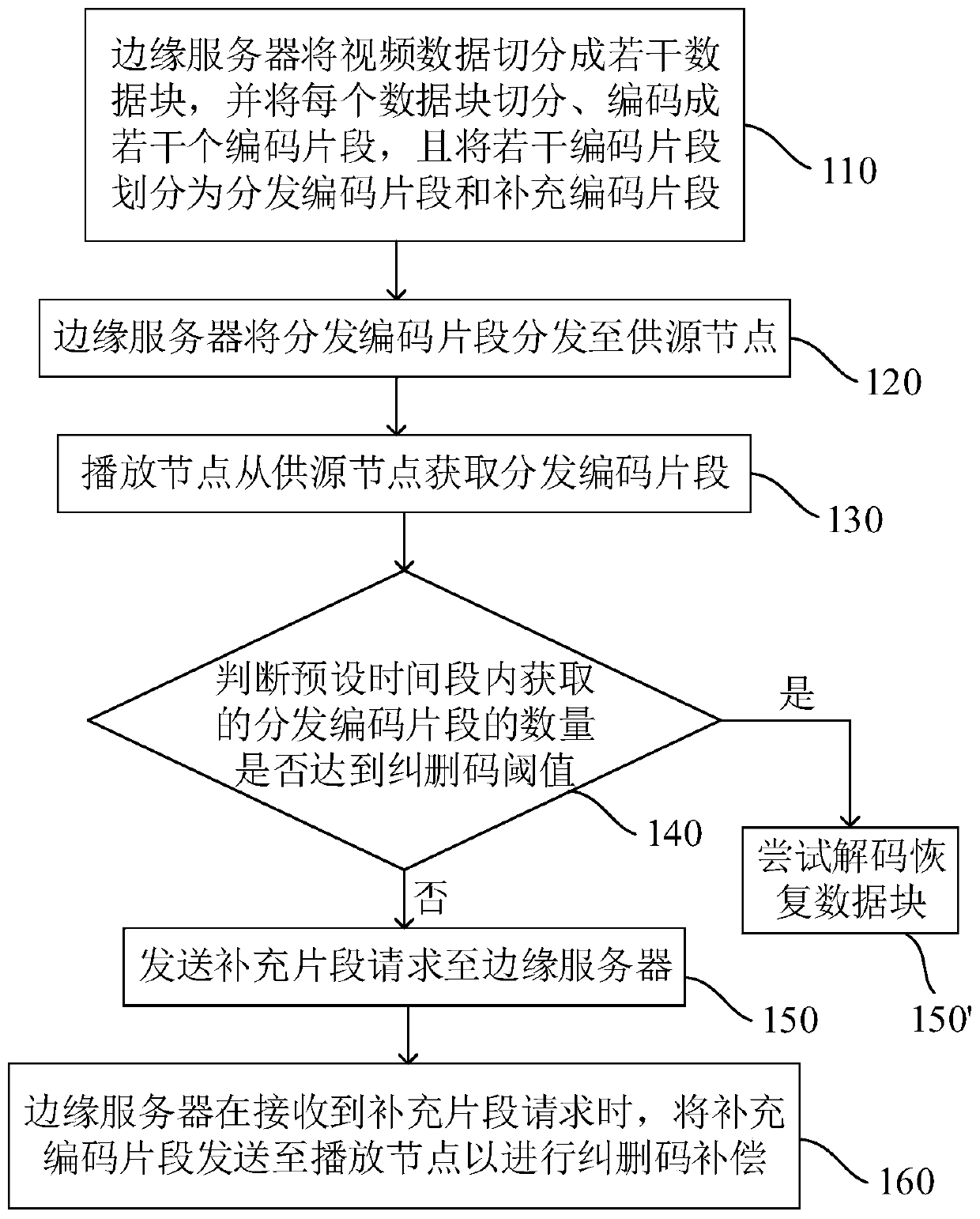
[0056] Such as figure 2 As shown, the P2P live broadcast method of the present embodiment includes the following steps:
[0057] Step 110, the edge server divides the video data into several data blocks, and divides and encodes each data block into several coded segments, and divides the several coded segments into distribution coded segments and supplementary coded segments.
[0058] Wherein, when dividing the coded segments, it is preferable to make the number m of supplementary coded segments not less than the erasure code threshold k. This is because, if a playback node fails to obtain any distributed coded fragments, all coded fragments need to be supplemented from the edge server, so it must be ensured that k<m<N. In addition, when dividing coded segments, it is best to make the number of distributed coded segments much larger than the number of supplementary coded segments, so as to reduce the probability of duplication during P2P exchange.
[0059] Step 120, the edg...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com