Management method, apparatus and system for remotely destroying private key
A management method and technology for private keys, applied in the management field of remote destruction of private keys, can solve problems such as communication tampering, hardware cost inconvenience, and inconvenience in use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
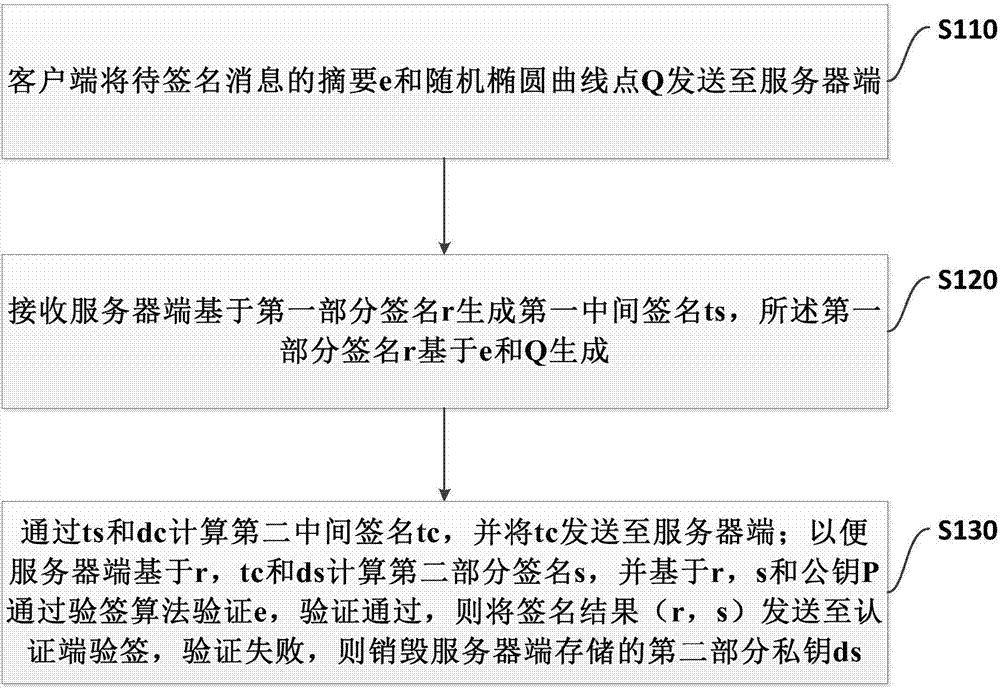
[0114] refer to figure 1 , figure 1 A flow chart of an embodiment of a management method for remotely destroying private keys provided by the present invention is shown. Wherein, the client stores the first part of the private key dc, the server stores the second part of the private key ds, and the first part of the private key and the second part of the private key are jointly operated to generate an electronic signature. Including: step S110 to step S130.
[0115] In step S110, the client sends the digest e of the message to be signed and the random elliptic curve point Q to the server.
[0116] In step S120, the receiving server generates a first intermediate signature ts based on the first partial signature r, and the first partial signature r is generated based on e and Q.
[0117] In step S130, calculate the second intermediate signature tc through ts and dc, and send tc to the server; so that the server calculates the second partial signature s based on r, tc and ds,...
Embodiment 2
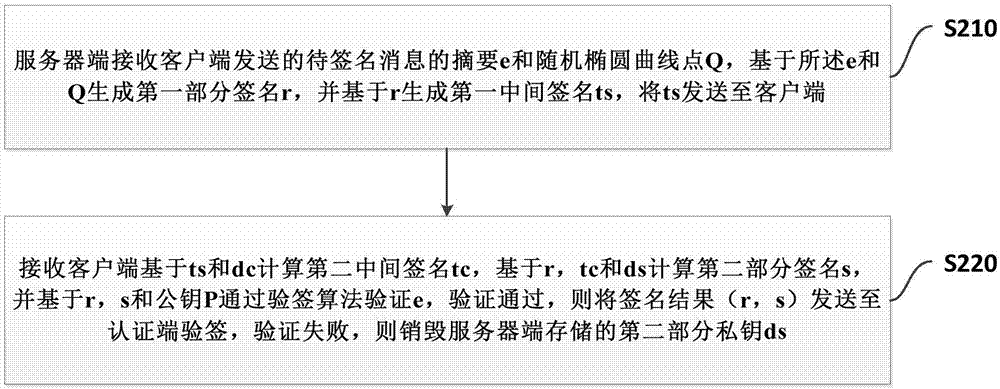
[0122] refer to figure 2 , figure 2 A flow chart of another embodiment of a management method for remotely destroying private keys provided by the present invention is shown. Wherein, the client stores the first part of the private key dc, the server stores the second part of the private key ds, and the first part of the private key and the second part of the private key are cooperatively operated to generate an electronic signature. The method includes: step S210 to step S220.
[0123] In step S210, the server receives the digest e of the message to be signed and the random elliptic curve point Q sent by the client, generates a first partial signature r based on e and Q, and generates a first intermediate signature ts based on r, and sends ts to to the client.
[0124] In step S220, the receiving client calculates the second intermediate signature tc based on ts and dc, calculates the second partial signature s based on r, tc and ds, and verifies e through the signature v...
Embodiment 3
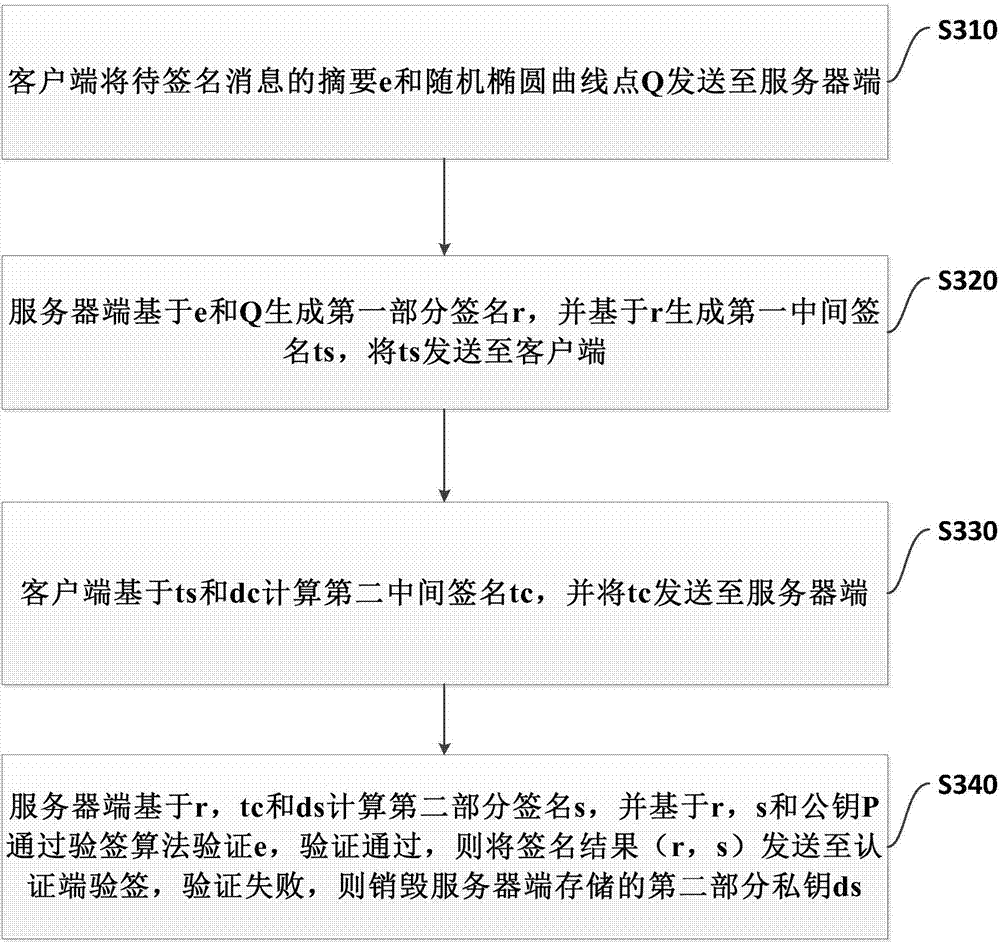
[0208] refer to Figure 4 , Figure 4 It shows a management system 300 for remotely destroying private keys provided by the present invention, wherein the client stores the first part of the private key dc, the server stores the second part of the private key ds, and the first part of the private key is coordinated with the second part of the private key An electronic signature is generated after the operation, including:
[0209] The client 31 is used to send the digest e of the message to be signed and the random elliptic curve point Q to the server; the receiving server generates a first intermediate signature ts based on the first partial signature r, and the first partial signature r is generated based on e and Q ;Calculate the second intermediate signature tc through ts and dc, and send tc to the server; so that the server can calculate the second part of the signature s based on r, tc and ds, and verify it through the signature verification algorithm based on r, s and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com