Functional dependency-based diversity data restoration method
A data repair and function-dependent technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inefficiency, regardless of the cost of repair, to avoid redundancy, improve efficiency, improve efficiency and The effect of scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
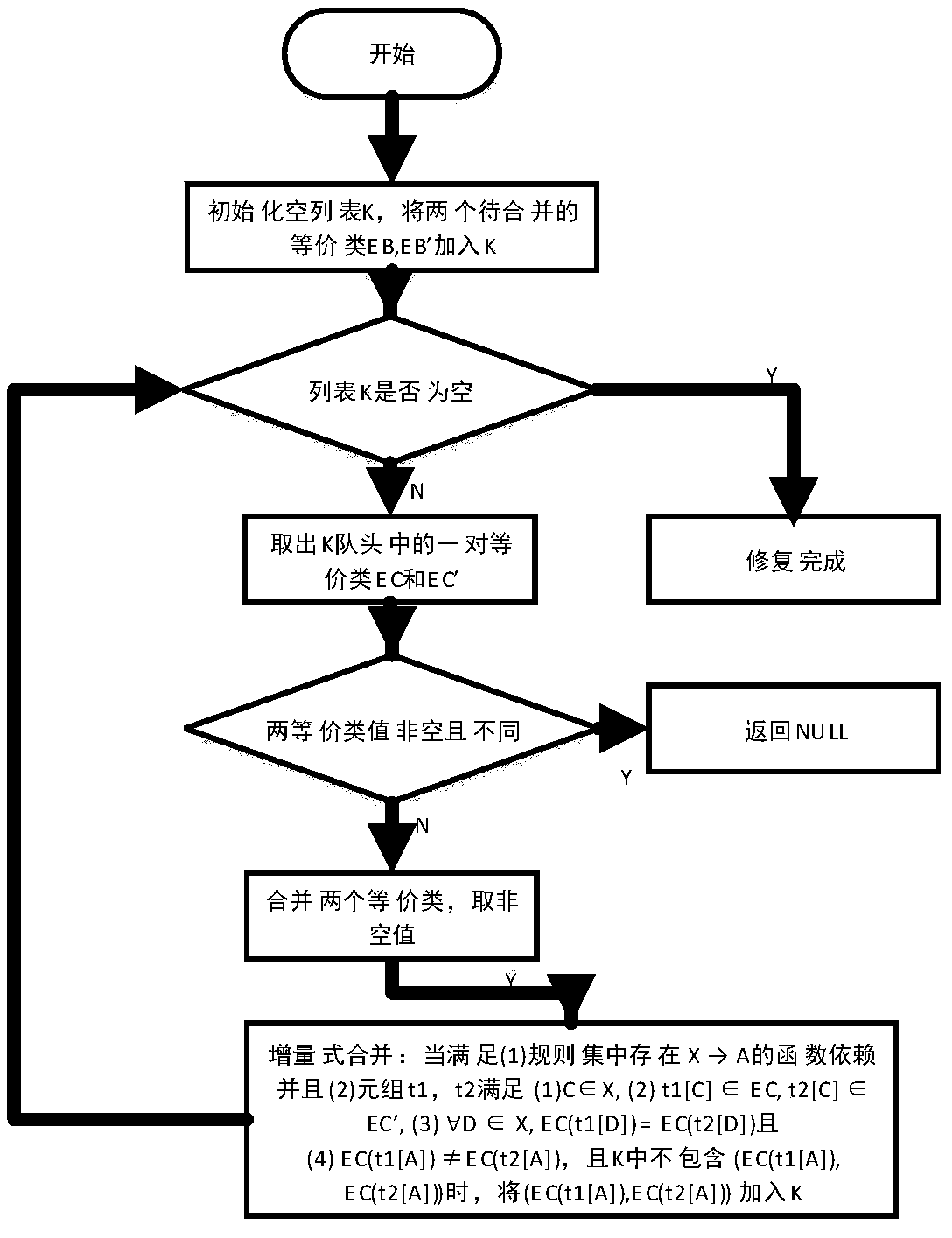
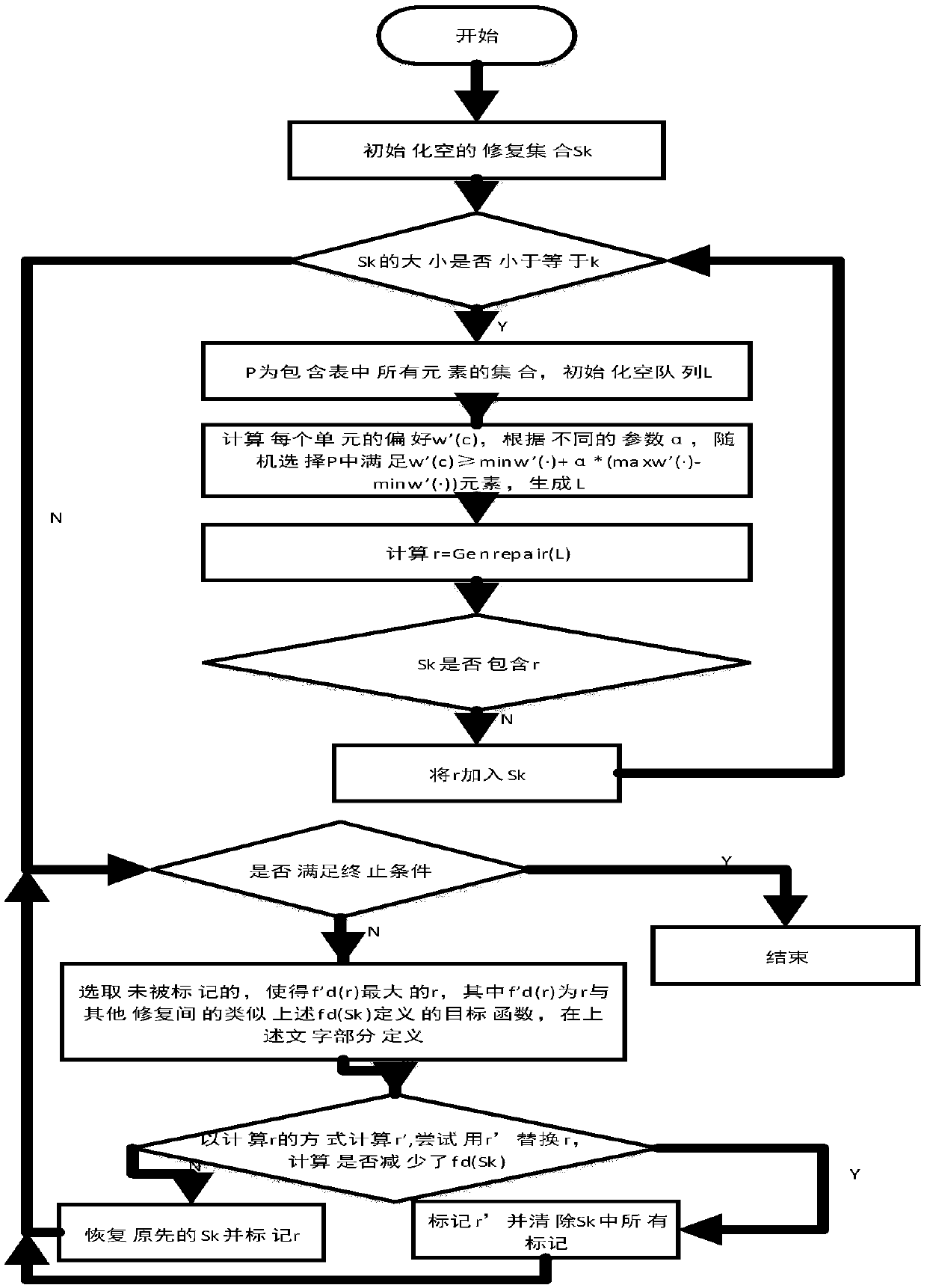
[0048] Aiming at the deficiencies of traditional methods and the needs of practical problems, this paper proposes a novel data restoration problem - diversity restoration. The goal of this problem is to find k cheap and diverse fixes. These representative inpainting results can not only be applied to interactive inpainting methods involving users to provide reliable references for users, but also can effectively summarize the entire possible inpainting space to improve the performance of methods for querying consistent results. Starting from the goal of this problem, this paper introduces a binary balance optimal problem of cost and diversity (expressed by distance), and proves that the complexity of this problem is NP-Complete.
[0049] Despite the high complexity of the diversity repair problem, this paper proposes a heuristic approach. We embed repair computation into the diversity model, and directly generate k repairs satisfying the condition through a model-guided algor...
example 1
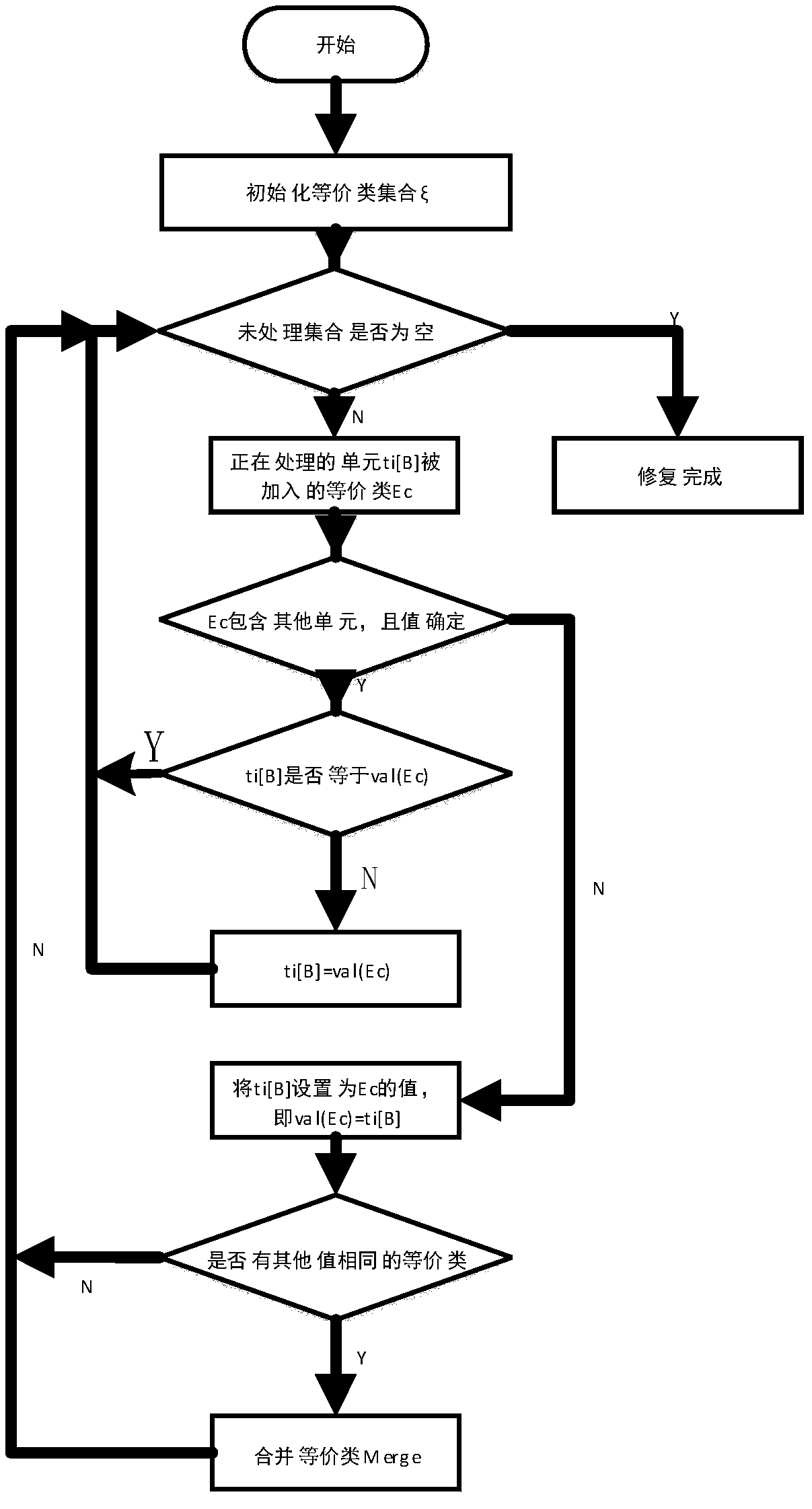
[0112]As shown in Table 1, when the internal attributes of the tuples are arranged in the order of ID, Name, Zip, and City in the order of tuples t1, t2, and t3, Genrepair generates repair 1 in Table 2, and the specific details of repair 1 The steps are shown in Table 5, Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8. At each step, we indicate the cells currently being processed by Genrepair, and indicate equivalence classes (EC) containing more than two elements by cells in the same column with dashed borders. Specifically, step 1 units t1[ID], t1[Name], t1[Zip], t1[City], t2[ID], t2[Name] in Table 5 were processed sequentially, but did not cause the transformation of attribute values. At the beginning, the value of each unit is equal to the unique value containing its own EC after being processed. For example, t2[Zip] is set to "100000", which is equal to the value of its own EC, expressed as e2Zip. Since the value of this EC is equal to the value of EC(e1City) containing t1[City], the two E...
example 2
[0115] As shown in Table 3, when the input sequence is arranged in the order of t1, t2, and t3 in the order of attribute columns ID, Name, City, and Zip, Genrepair generates repair 2. Table 9 Repair 2 Step 1 processing t1[ID], t3[ID] does not change the value of the unit, but causes the merger of equivalence classes containing t1[ID] and t3[ID], and t1[Name], t1 [Zip], t1[City] are merged with the equivalence classes of t3[Name], t3[Zip], t3[City] respectively. Table 10 Fix 2 Step 2, the value of t3[Name] was modified to "Michael", equal to the value of t1[Name], because they are in the same equivalence class, and the value of this equivalence class is in the process of t1[ Name] has been identified as "Michael". Table 11 In step 3 of repair 2, similar to the method in step 2, we modify t3[City]. Table 12 Fix 2 Step 4, when processing t2[Zip], the value of its equivalence class e2Zip is set to the same value as "100000", which will cause the equivalence class of t1[Zip] to b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com