CAN bus-based multi-node automatic networking method
A CAN bus and automatic networking technology, applied in the field of CAN bus, can solve problems such as limited application occasions, increased operation difficulty, and increased host monitoring difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
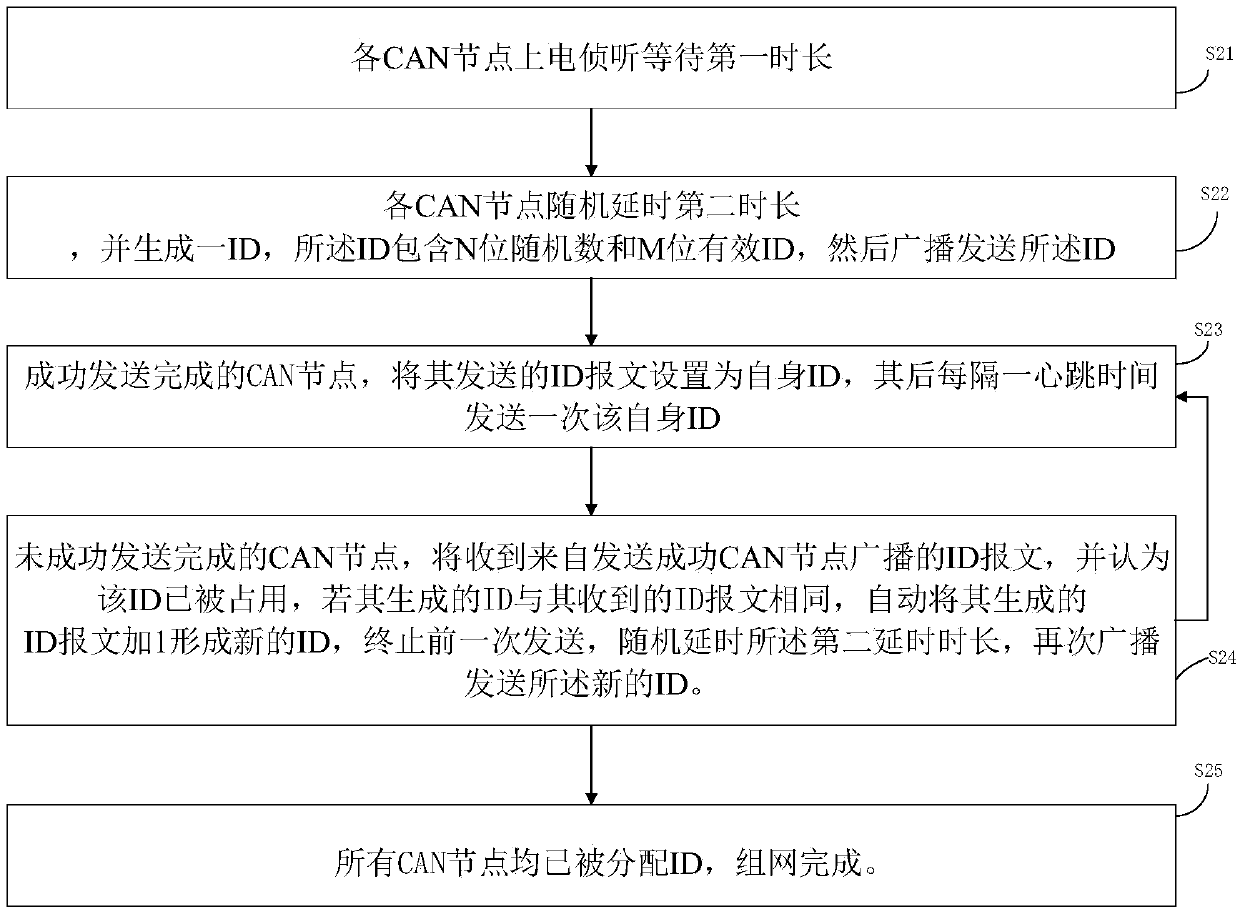
[0039] figure 2 For the first embodiment of CAN bus dynamic networking method of the present invention, comprise the steps:
[0040] Step S21 , each CAN node is powered on and waits for a first duration of listening. Used to receive ID messages on the bus. The first duration is, for example, 1S.
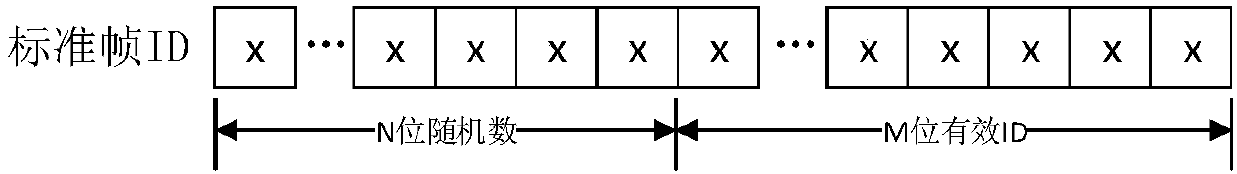
[0041] In step S22, each CAN node randomly delays for a second time length, and generates an ID, the ID includes a random number of N bits and an effective ID of M bits, and then broadcasts the ID. The ID sent by broadcast is an ID message. Such as image 3 It is composed of the standard frame of the ID described in the present invention, the number of digits of the standard frame of the ID is N+M bits, preferably, the number of digits of the standard frame of the ID is 11 digits, and wherein N is preferably N<6 , and the initial effective ID of each node is 1. In addition, the second duration is preferably less than 100ms.
[0042] Step S23 , the CAN node that has successful...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com